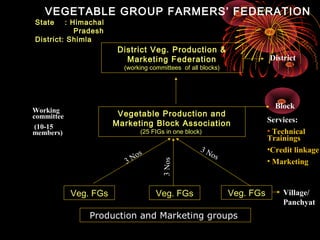
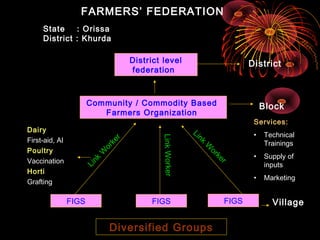
The document discusses the importance of farmer organizations for empowering farmers, accessing services, and influencing policies. It provides examples of different types of farmer organizations in various Indian states and the roles they play in providing services to members like access to inputs, credit, marketing, and training. Farmer organizations are seen as important for strengthening farmer participation in extension activities and development programs.