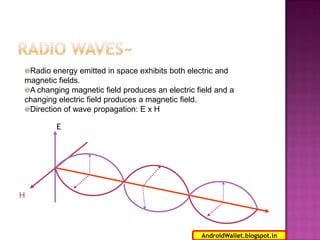
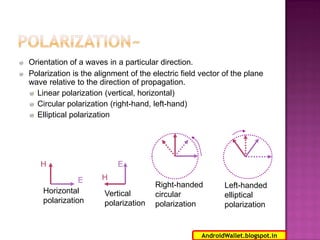
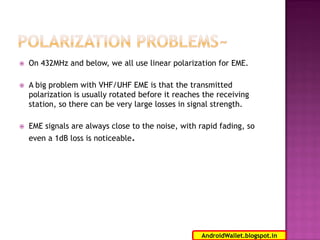
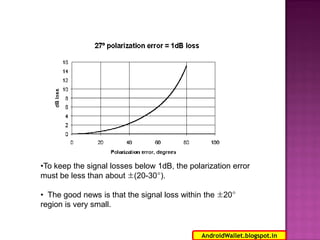
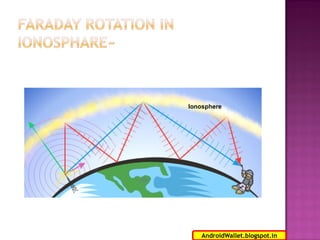
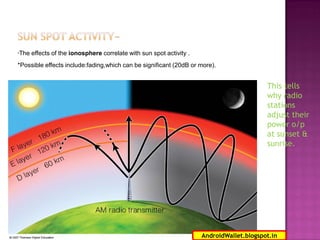
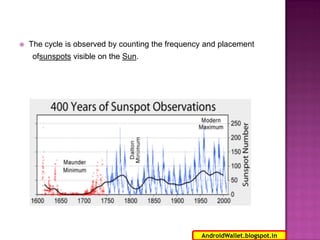
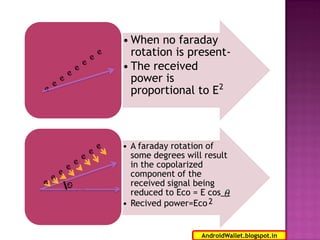
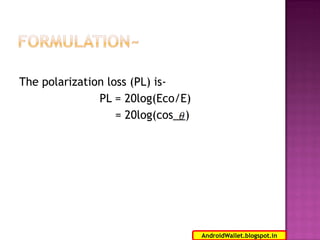
Radio waves propagating through space exhibit electric and magnetic fields that are oriented perpendicular to each other and the direction of propagation. Polarization describes the orientation of these oscillating fields and can be linear, circular, or elliptical. For Earth-Moon-Earth (EME) communications, linear polarization is typically used below 432MHz to minimize signal losses from polarization rotation caused by propagation through the ionosphere, which can exceed 1dB for rotations greater than 20-30 degrees. Faraday rotation, proportional to electron density and wavelength squared, further contributes to polarization rotation as radio waves pass through the ionosphere.