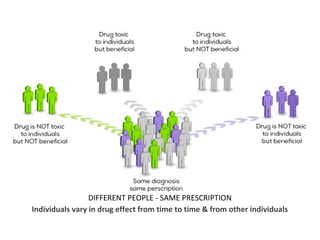
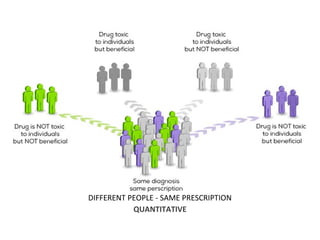
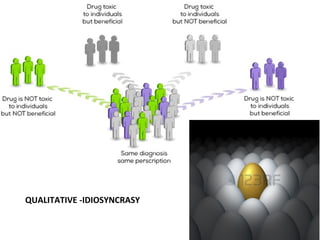
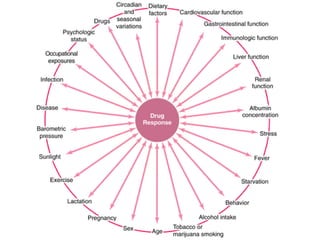
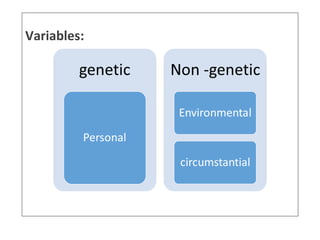
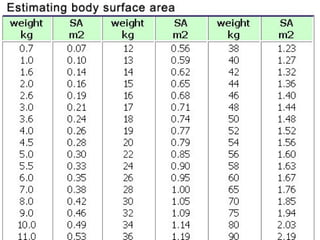
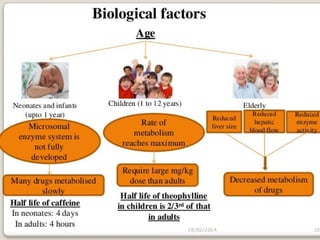
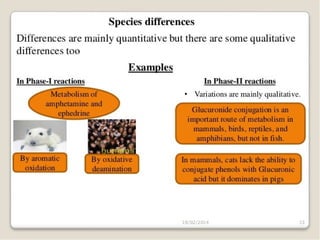
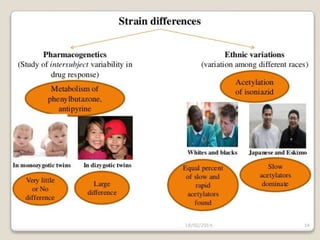
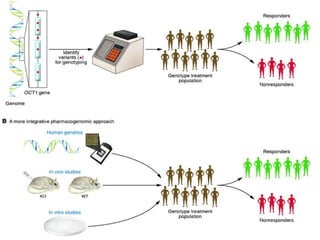
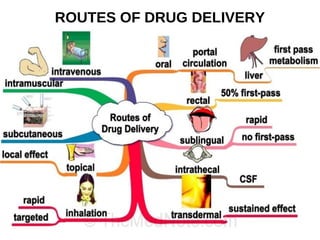
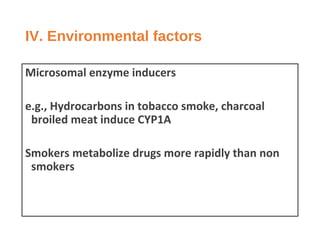
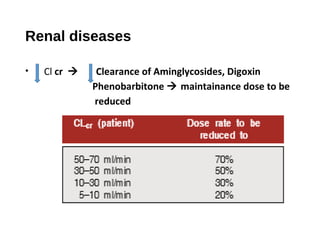
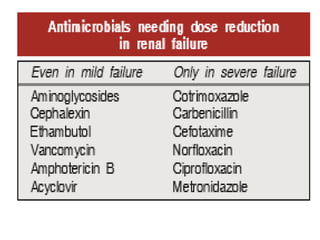
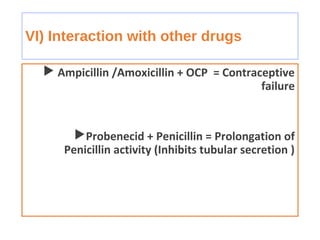
This document discusses factors that can modify drug actions in different individuals. It notes that individuals can vary in how they metabolize and respond to drugs due to differences in physiology, pathology, environmental exposures, and psychological state. Some key modifying factors mentioned are body size, age, pregnancy, liver and kidney function, smoking, and interactions with other medications. Understanding these sources of variability helps explain why the same prescription may have different effects between people.