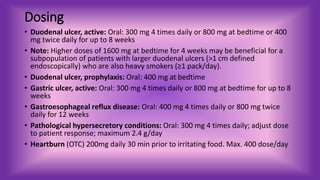
Cimetidine is an H2 antagonist used to reduce gastric acid secretion and treat conditions like ulcers and GERD. It undergoes hepatic metabolism and renal excretion. Standard doses are 300-800mg but may be increased to 1600mg for heavy smokers with large duodenal ulcers. Dosing needs to be adjusted for renal impairment and geriatric patients. Cimetidine can cause confusion in the elderly or impaired and B12 deficiency with prolonged use. Patients should be monitored for signs of liver problems, pancreatitis, cardiac issues, or confusion and report them immediately.