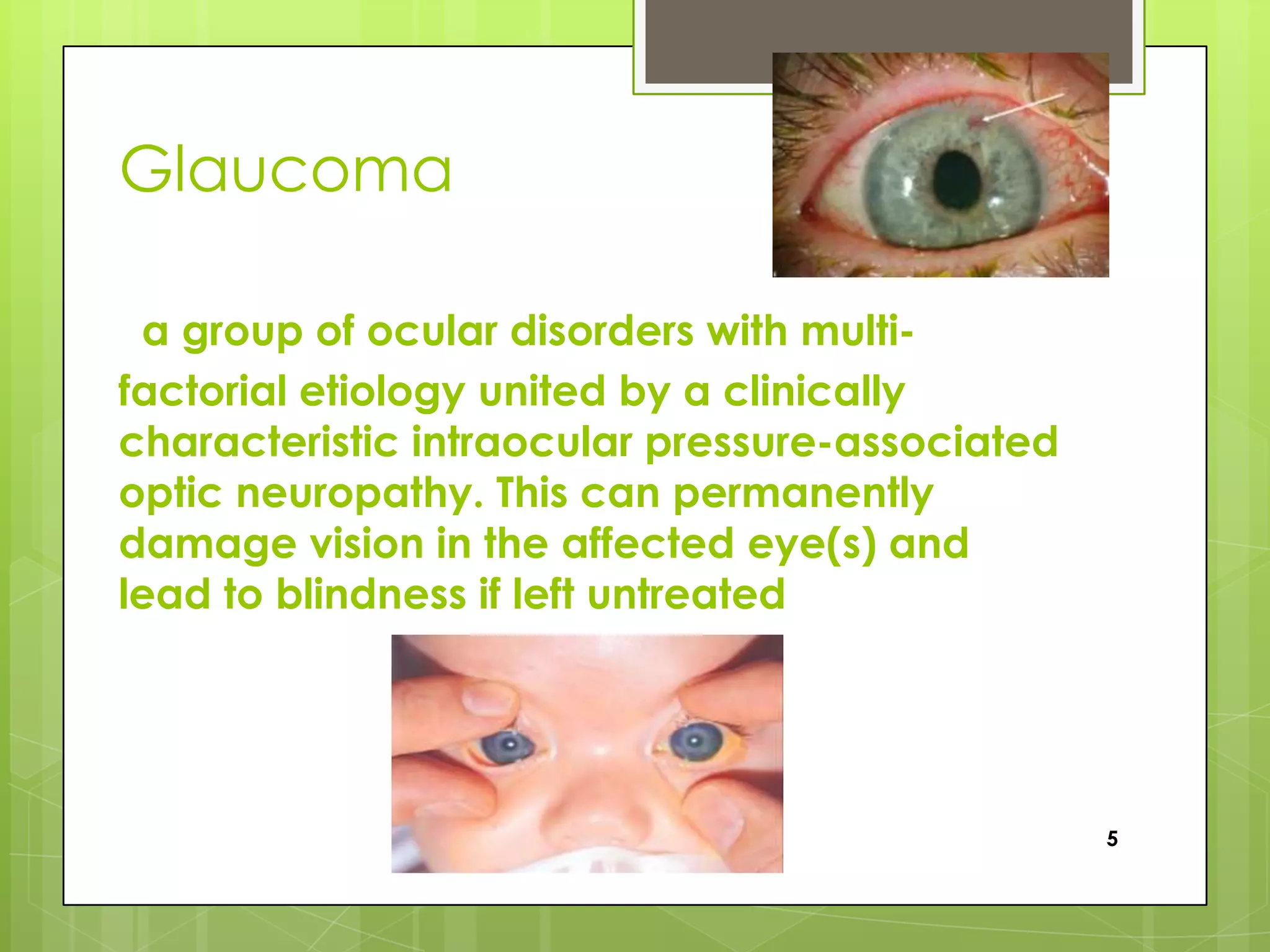
Eye disease is an impairment or abnormal functioning of the eye that affects vision and can cause blindness. Some common eye diseases include cataracts, glaucoma, trachoma, and retinal disorders. Cataracts cause cloudiness of the lens that impairs vision. Glaucoma permanently damages vision through increased intraocular pressure. Trachoma is an infectious disease caused by bacteria that roughens the inner eyelids. Retinal disorders affect the retina and can damage central vision. Treatments depend on the disease but may include surgery, eye drops, laser treatment, or antibiotics to prevent further vision loss or blindness.