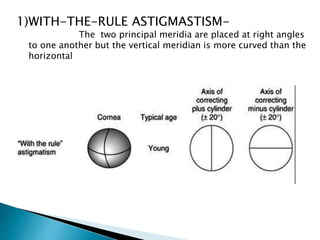
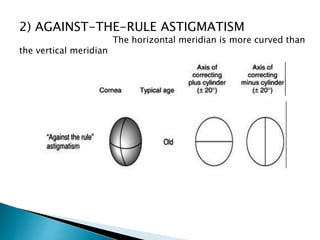
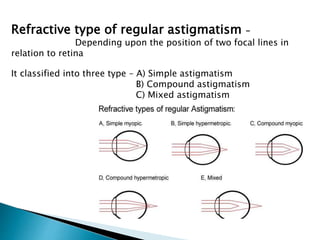
Astigmatism is a refractive error where the refraction varies in different meridians. There are two types: regular and irregular. Regular astigmatism has two principal meridians and can be with-the-rule, against-the-rule, oblique, or bi-oblique depending on the axis. Irregular astigmatism has an irregular change in refractive power. Both cause blurred vision and symptoms. Regular astigmatism is treated with cylindrical lenses, contact lenses, or LASIK while irregular astigmatism may require contact lenses, phototherapeutic keratectomy, or surgery.