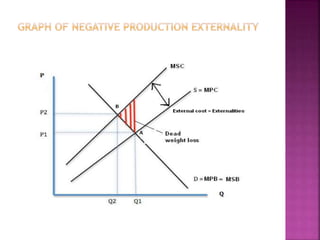
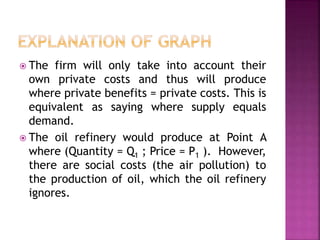
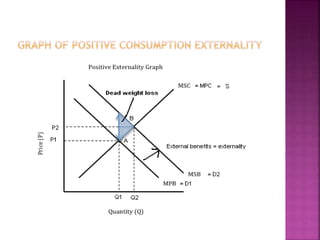
This document discusses public goods and economics concepts. It begins by defining public goods as non-excludable and non-rivalrous goods. The government provides various public goods like roads, parks, and utilities.
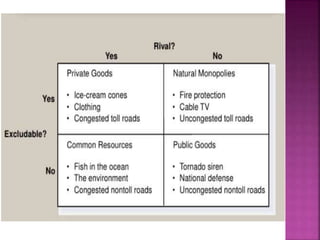
Public goods have three key characteristics - non-divisibility meaning they benefit all, non-rivalry meaning one's consumption does not reduce availability to others, and non-exclusivity meaning it is difficult to exclude non-payers. There are also subclasses of public goods discussed like congestible public goods and club goods.
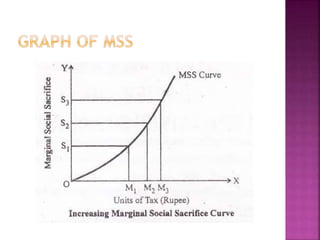
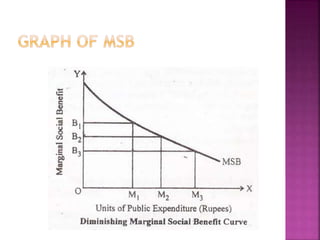
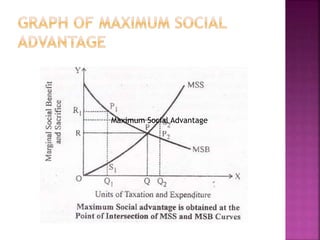
The free rider problem is explained, where individuals may not pay for a public good hoping others will pay instead. Cost-benefit analysis and the principle of maximum social advantage are also









![Public goods Private good
Property rights Non excludable Excludable
Consumption Non-rival Rival
Aggregate demand curve Vertical additional of
individual demand curve
Horizontal additional of
individual demand curves
Partial equilibrium
condition for optimum
provision
The sum of marginal
utilities equals marginal
costs
Marginal utility for each
consumer equals
marginal cost
[MUi=MU with i the
individual consumer].
Efficient pricing rule The sum of individual
prices equals marginal
cost
Price equals marginal
cost
[P=MC]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/publicgoodsandexternalities-190712101014/85/Public-goods-and-externalities-10-320.jpg)