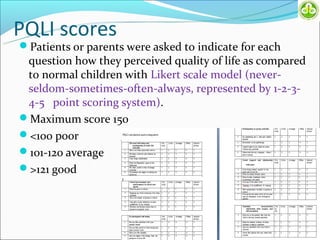
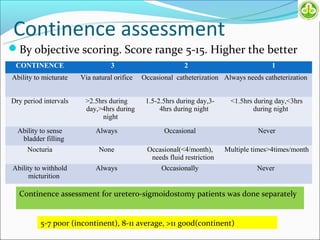
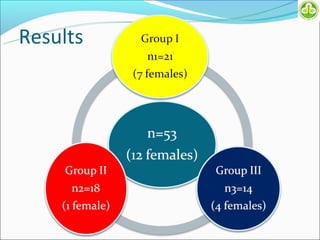
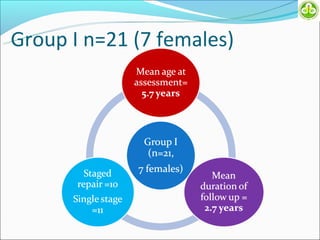
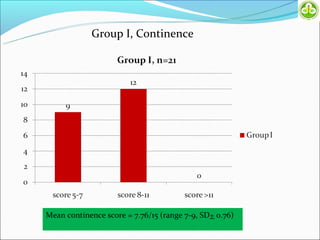
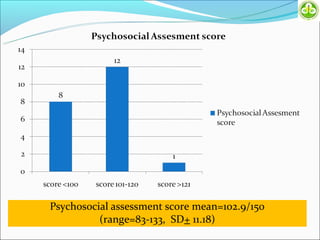
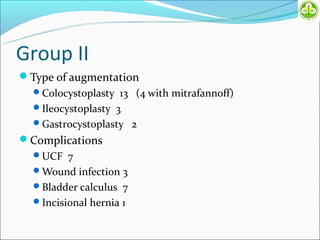
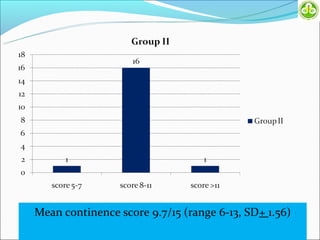
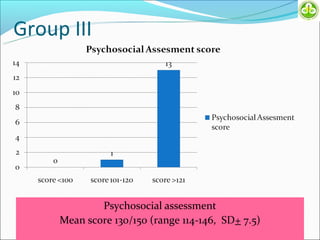
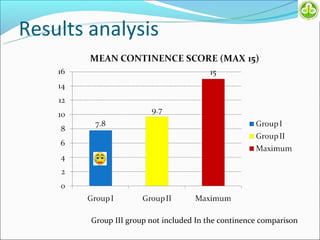
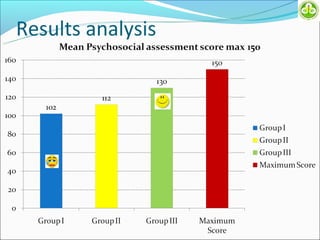
This study evaluated outcomes for patients with bladder exstrophy managed with primary repair, augmentation, or uretero-sigmoidostomy. The study included 21 primary repair patients, 18 augmentation patients, and 14 uretero-sigmoidostomy patients. Primary repair patients had poor continence and quality of life, with a 42% incontinence rate. Augmentation patients had improved outcomes, with 88% achieving average or better continence. Uretero-sigmoidostomy patients all had good quality of life and were largely continent, with 76.9% passing urine voluntarily. The study concluded that augmentation and uretero-sigmoidostomy resulted in better continence and quality of life outcomes compared to primary repair alone.