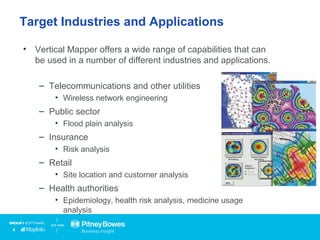
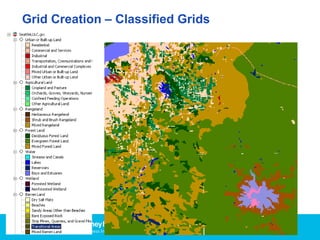
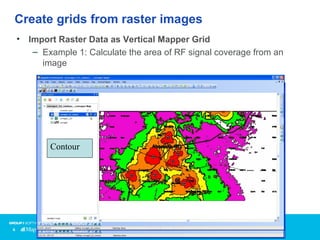
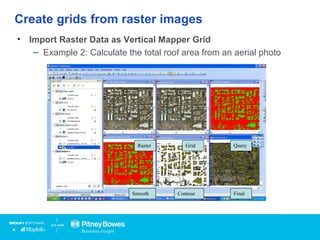
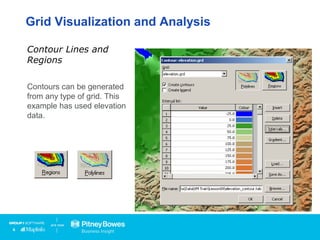
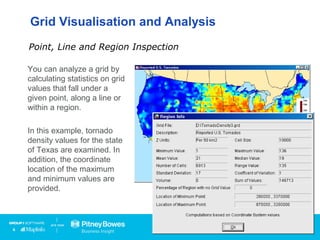
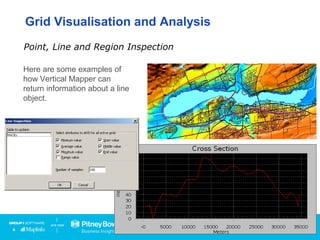
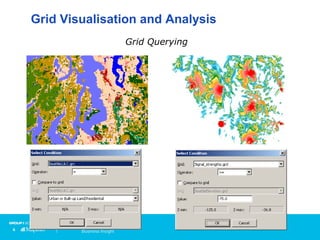
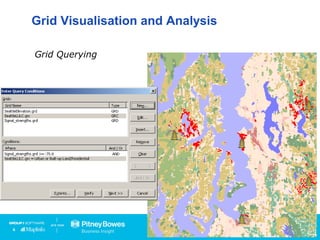
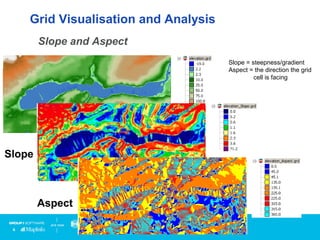
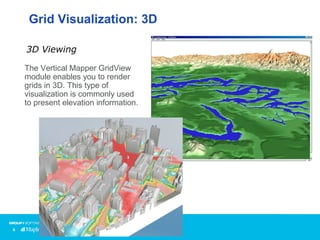
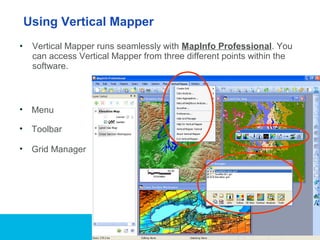
Vertical Mapper is software that transforms point data into continuous grid surfaces that can be analyzed and visualized. It allows users to generate grid surfaces through interpolation of point data, modify grid colors and legends, generate contours, render grids in 3D, query multiple grid layers, and edit grids. Key industries that benefit include telecommunications for wireless network planning, public sector for flood risk analysis, insurance for risk analysis, and retail for customer analysis. The presentation provides examples of how Vertical Mapper has been used in these industries and highlights its capabilities for grid creation, visualization, analysis, and custom application development.