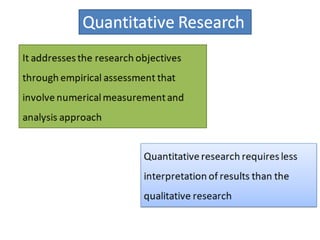
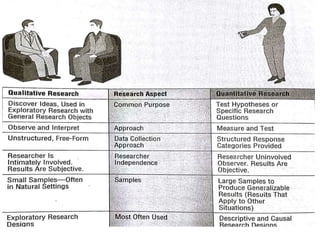
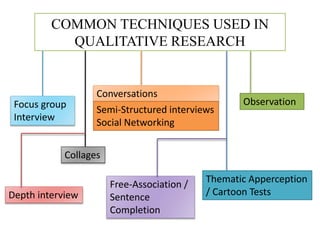
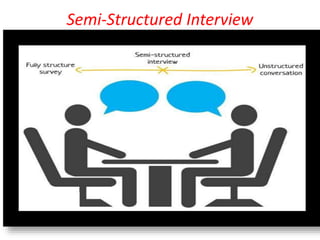
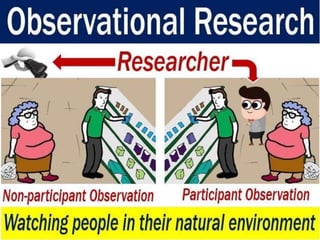
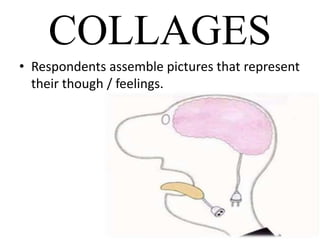
This document discusses qualitative research methods. It explains that qualitative research focuses more on qualities than quantities and aims to elaborate on market phenomena without relying on numerical data. Some common qualitative research techniques discussed include focus groups, interviews, observation, collages, word association tests, and thematic apperception tests. Specific methods like phenomenology, ethnography, grounded theory, and case studies are also outlined.