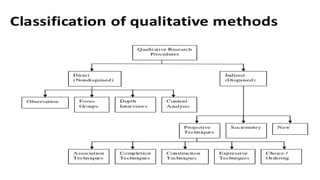
Qualitative data collection methods are techniques used to gather non-numerical information, focusing on understanding experiences, behaviors, and social phenomena in depth. Common methods include interviews, where researchers conduct one-on-one or group discussions to explore personal perspectives; focus groups, which involve guided discussions with multiple participants to generate diverse viewpoints; observations, where researchers study participants in their natural environment to capture real-life interactions; and document analysis, which involves reviewing written materials, such as reports, letters, or social media content, to understand underlying themes. These methods allow researchers to gain rich, detailed insights into human experiences, making them essential for fields like social sciences, healthcare, and education.Interviews are one of the most commonly used qualitative data collection methods. They involve direct, face-to-face, telephone, or online interactions between a researcher and a participant. Interviews can be structured, semi-structured, or unstructured, depending on the degree of flexibility in the questioning process.Focus groups involve group discussions guided by a moderator to explore shared experiences, opinions, or attitudes. Typically consisting of 6 to 10 participants, focus groups allow researchers to observe interactions, disagreements, and consensus-building among participants. This method is commonly used in marketing, psychology, and public health research.Observation is a qualitative data collection method where researchers systematically watch and record behaviors, interactions, and environmental factors. This method allows for a real-time, naturalistic understanding of a phenomenon without relying solely on participants' self-reports.Case studies involve an in-depth examination of a single case, event, or individual to explore complex issues. They are commonly used in psychology, business, and healthcare research. A case study may focus on a specific patient, organization, or community, providing rich insights into unique circumstances.
This method is valuable for studying rare or complex phenomena that cannot be easily quantified. For example, in medicine, case studies of rare diseases provide insights into symptoms, treatments, and patient experiences. In business research, a case study of a successful company can highlight effective management strategies.