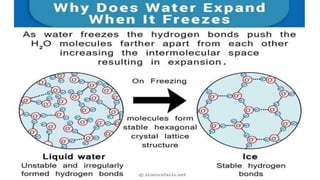
The document discusses various exogenic (surface) processes including weathering, mass wasting, and soil erosion. It describes three main types of weathering - physical, chemical, and biotic weathering. Physical weathering breaks rocks into smaller pieces through mechanical processes like heating/cooling or frost action without changing the chemical composition. Chemical weathering alters the chemical makeup of rocks through oxidation, carbonation, hydration, or solution. Biotic weathering is caused by living organisms through root growth, burrowing, or human activities. Mass wasting and soil erosion are also exogenic processes that transport weathered material downslope or remove soil faster than replacement through water, wind, ice, or gravity.