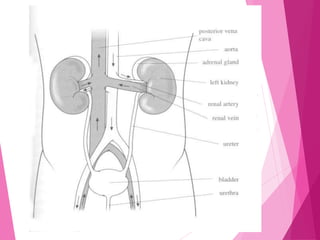
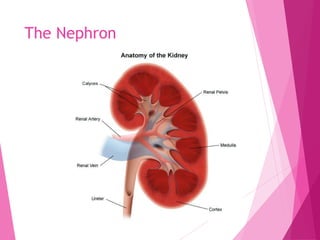
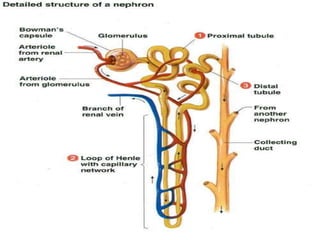
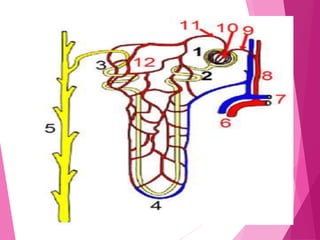
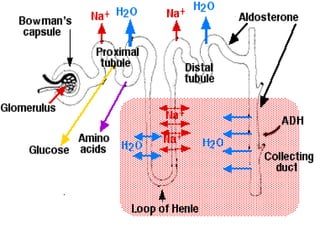
The document summarizes the human excretory system. The skin and kidneys are the main excretory organs, with the kidneys filtering blood and removing waste from the body. The kidneys regulate water and salt concentrations in the body through a process called osmoregulation. The basic unit of the kidney is the nephron, which filters blood and selectively reabsorbs nutrients while excreting waste as urine. Urine is stored in the bladder and released through the urethra.