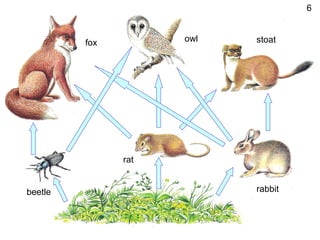
1) Organisms are interdependent as the bee depends on flowers for nectar and flowers depend on bees for pollination. Food chains also demonstrate interdependence as organisms rely on others for food.
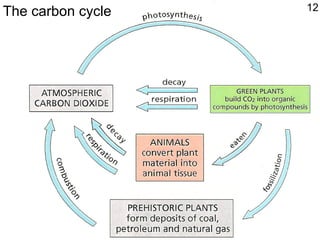
2) Photosynthesis by plants provides food for animals, while respiration and decay recycle carbon dioxide and nutrients in a carbon cycle.
3) Bacteria and fungi are decomposers that break down dead organisms, recycling nutrients and preventing a build up of waste. All organisms depend on this recycling.