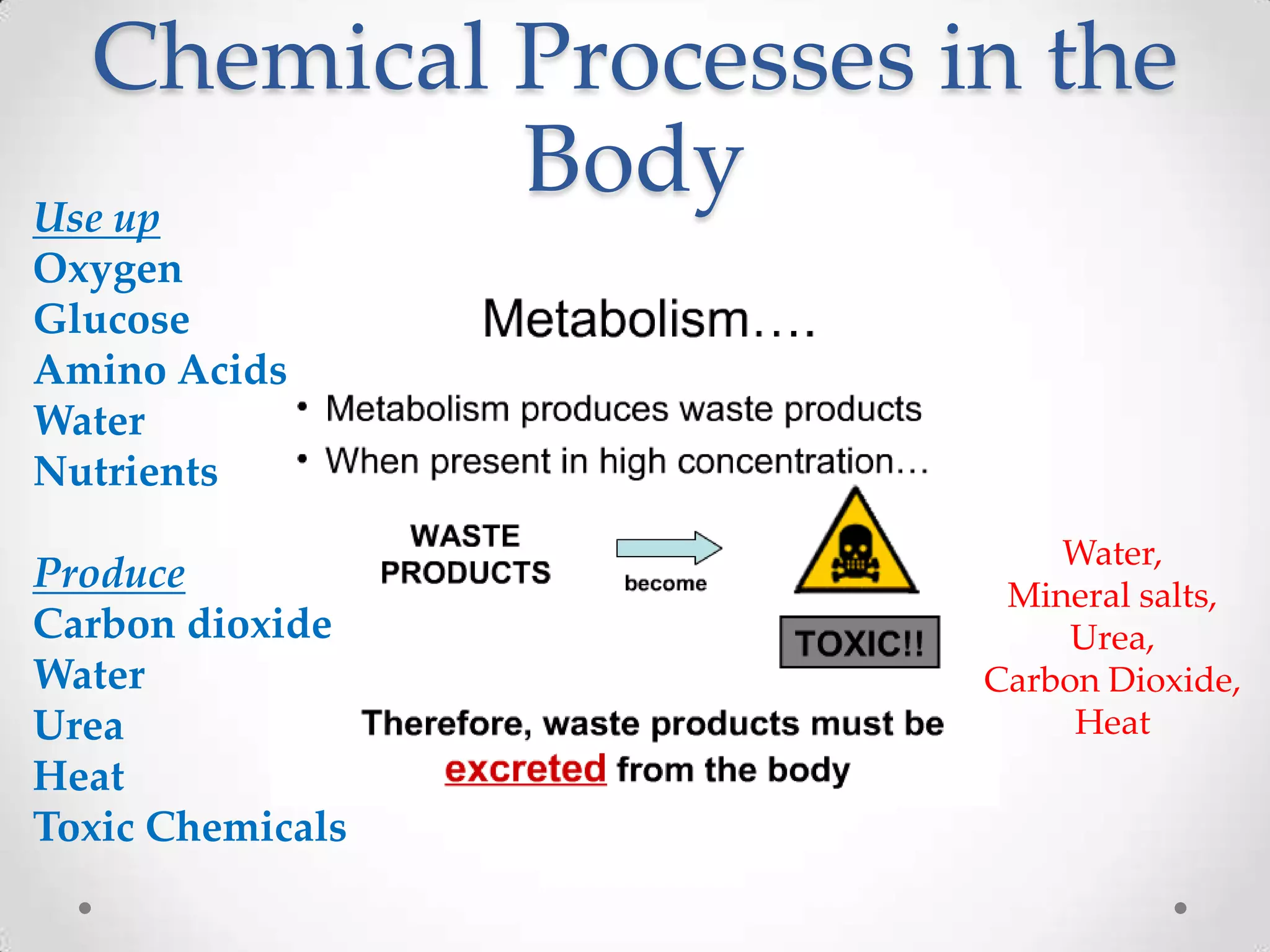
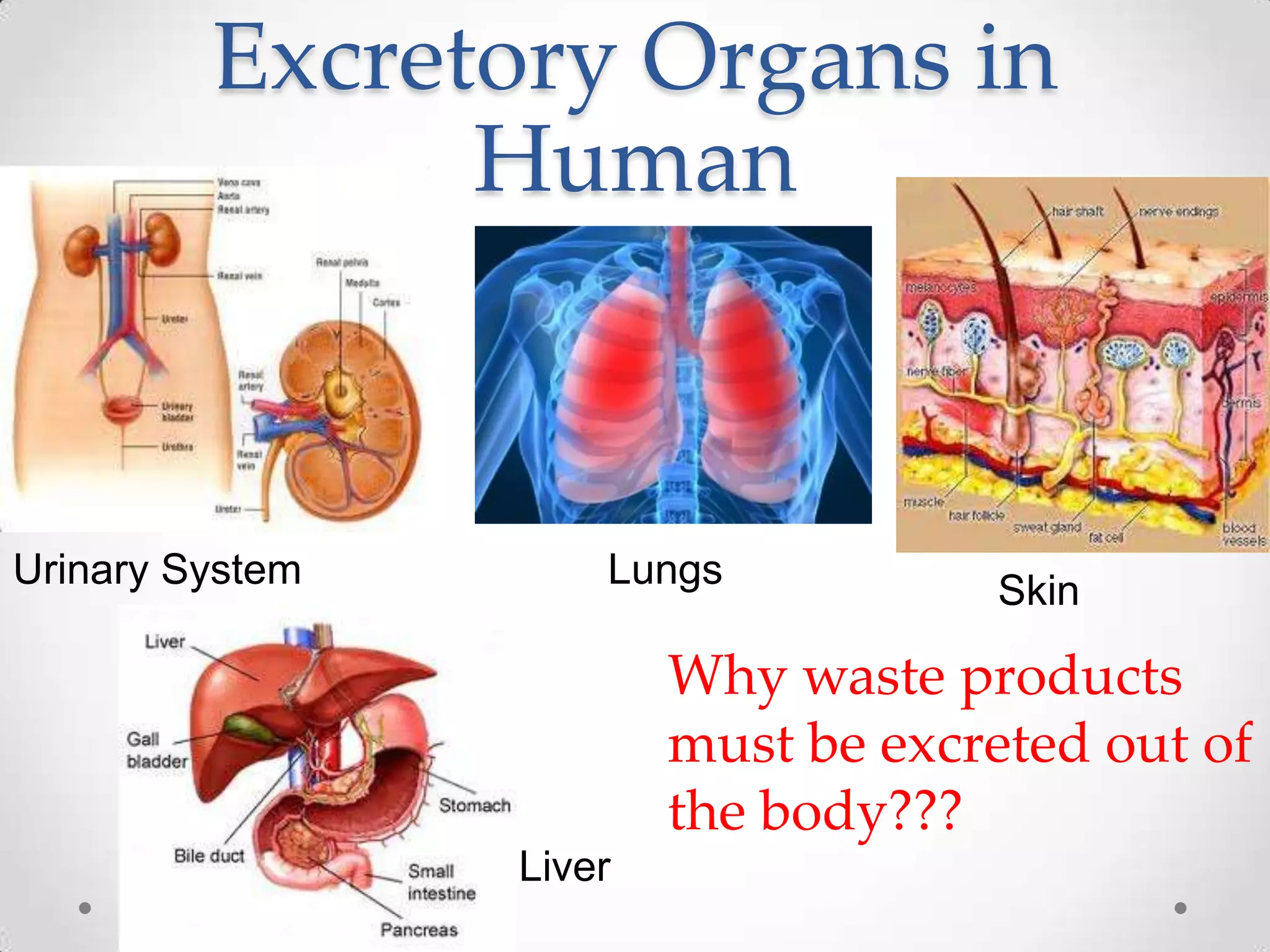
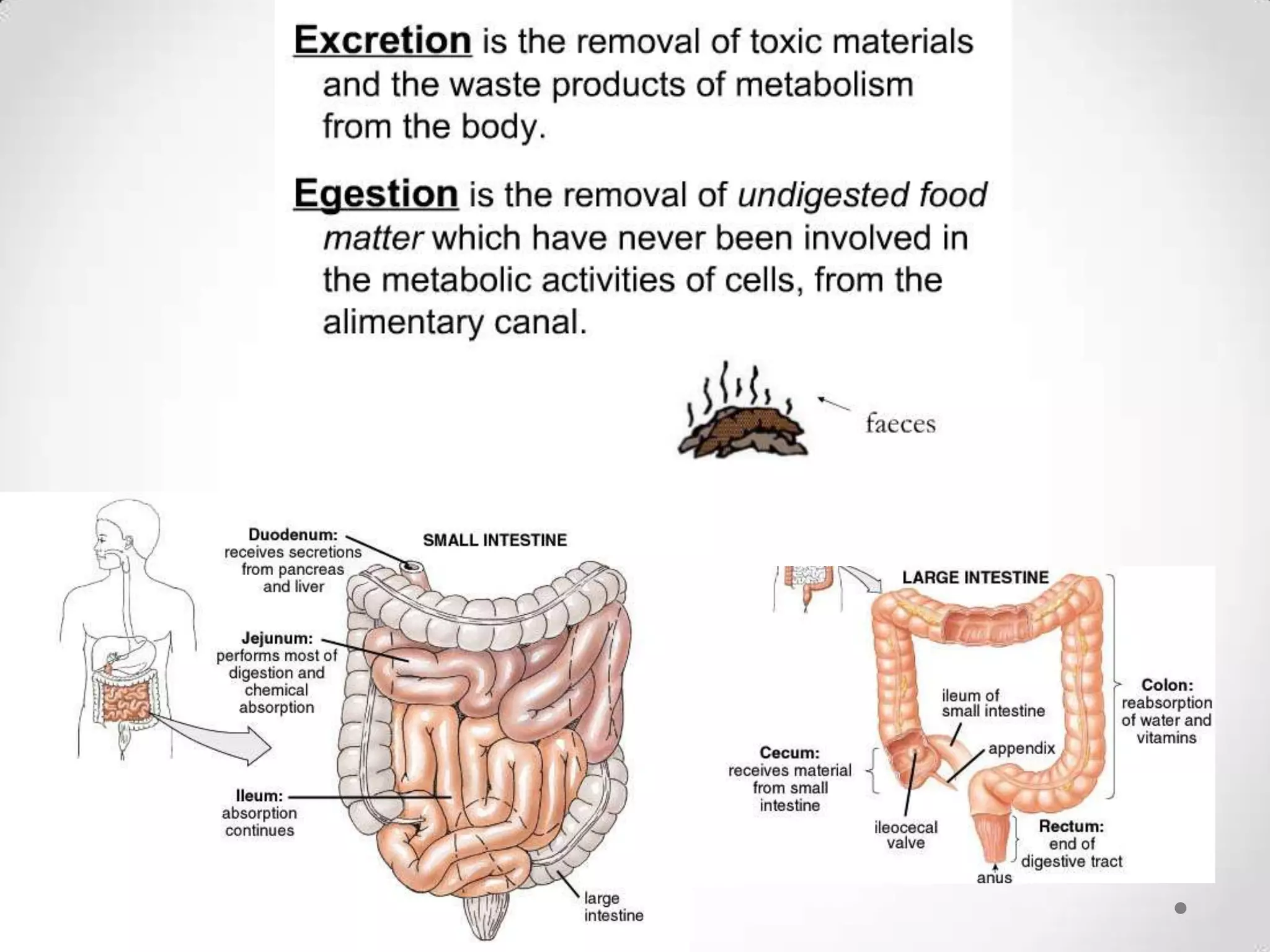
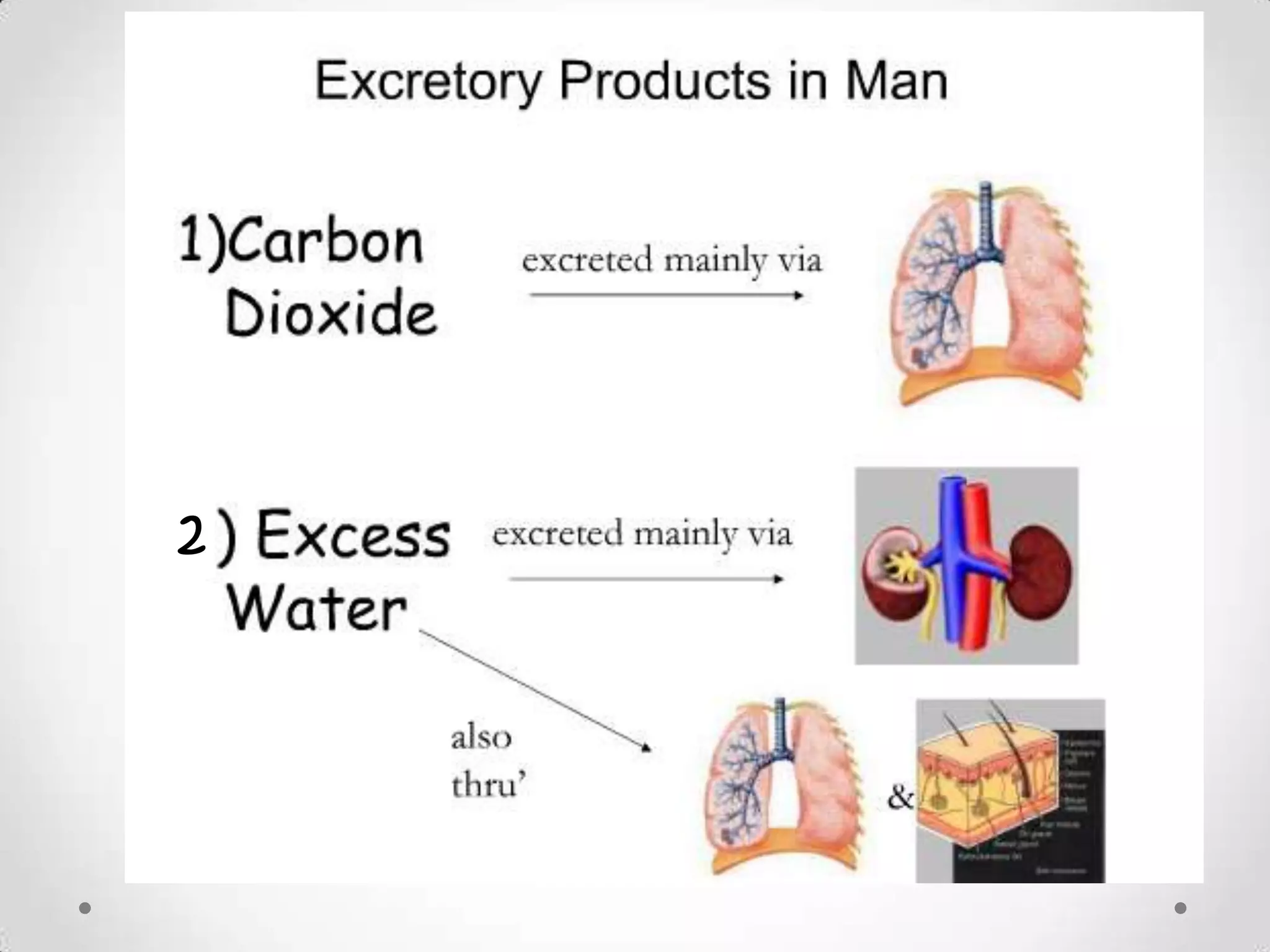
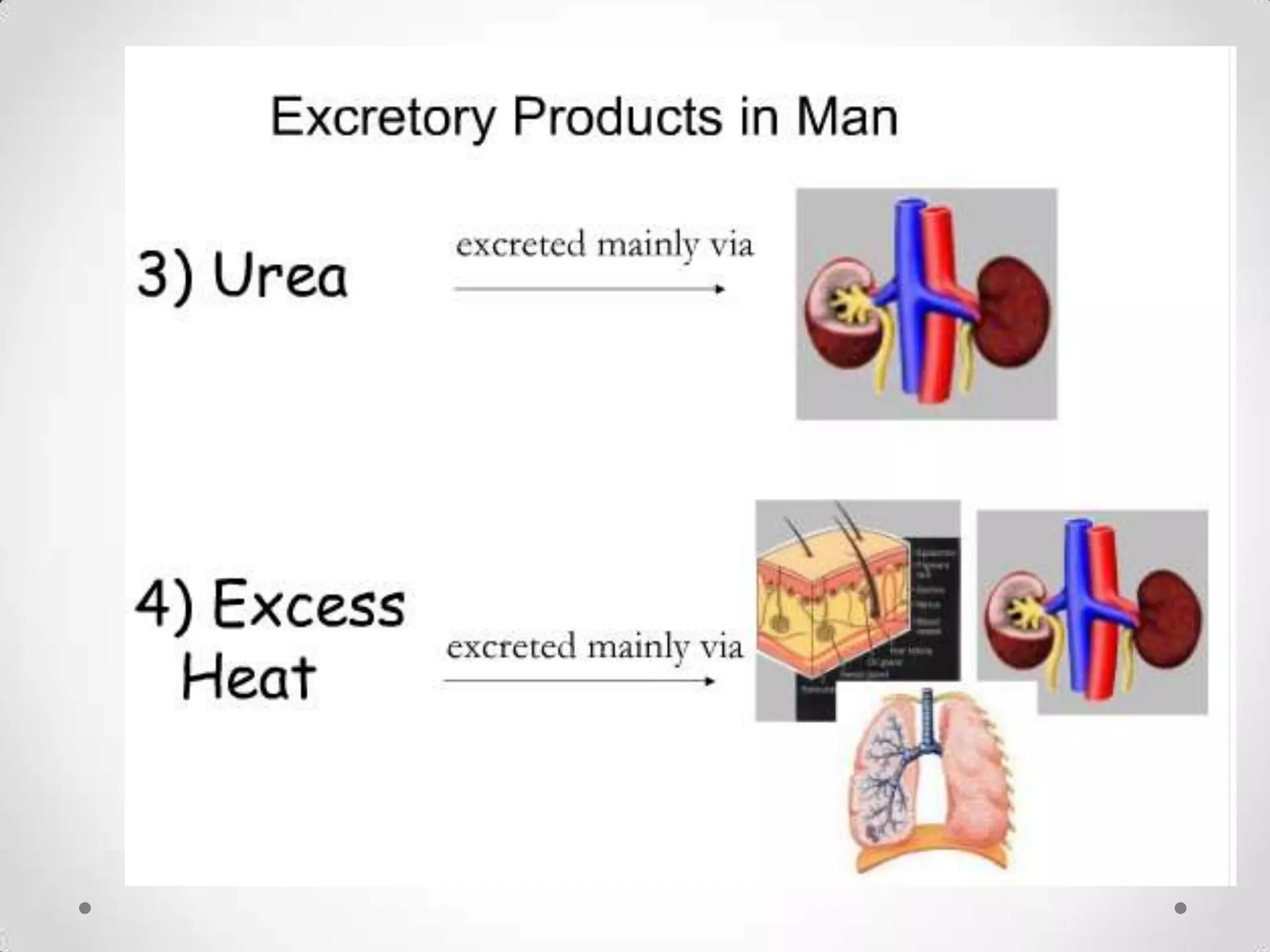
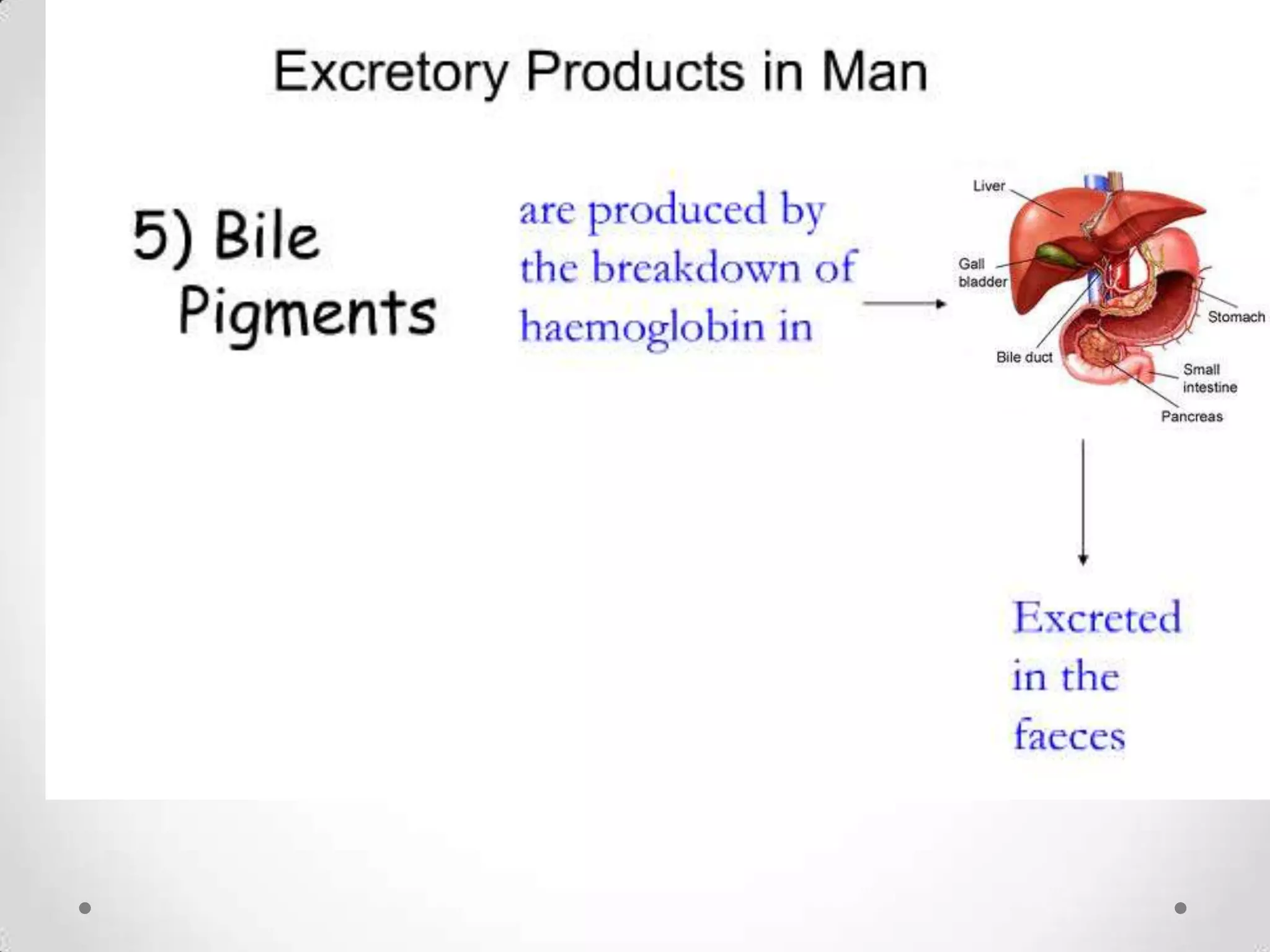
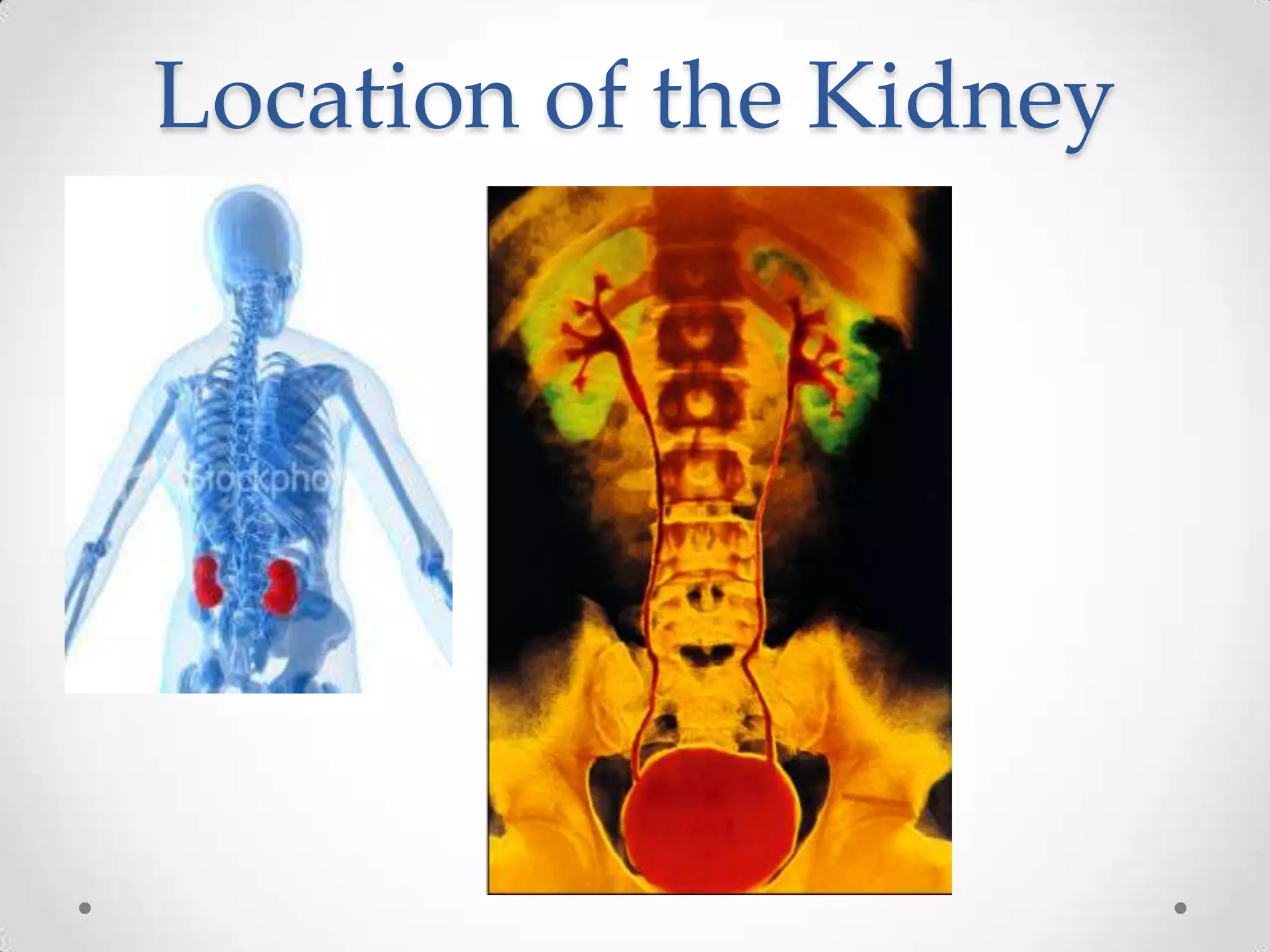
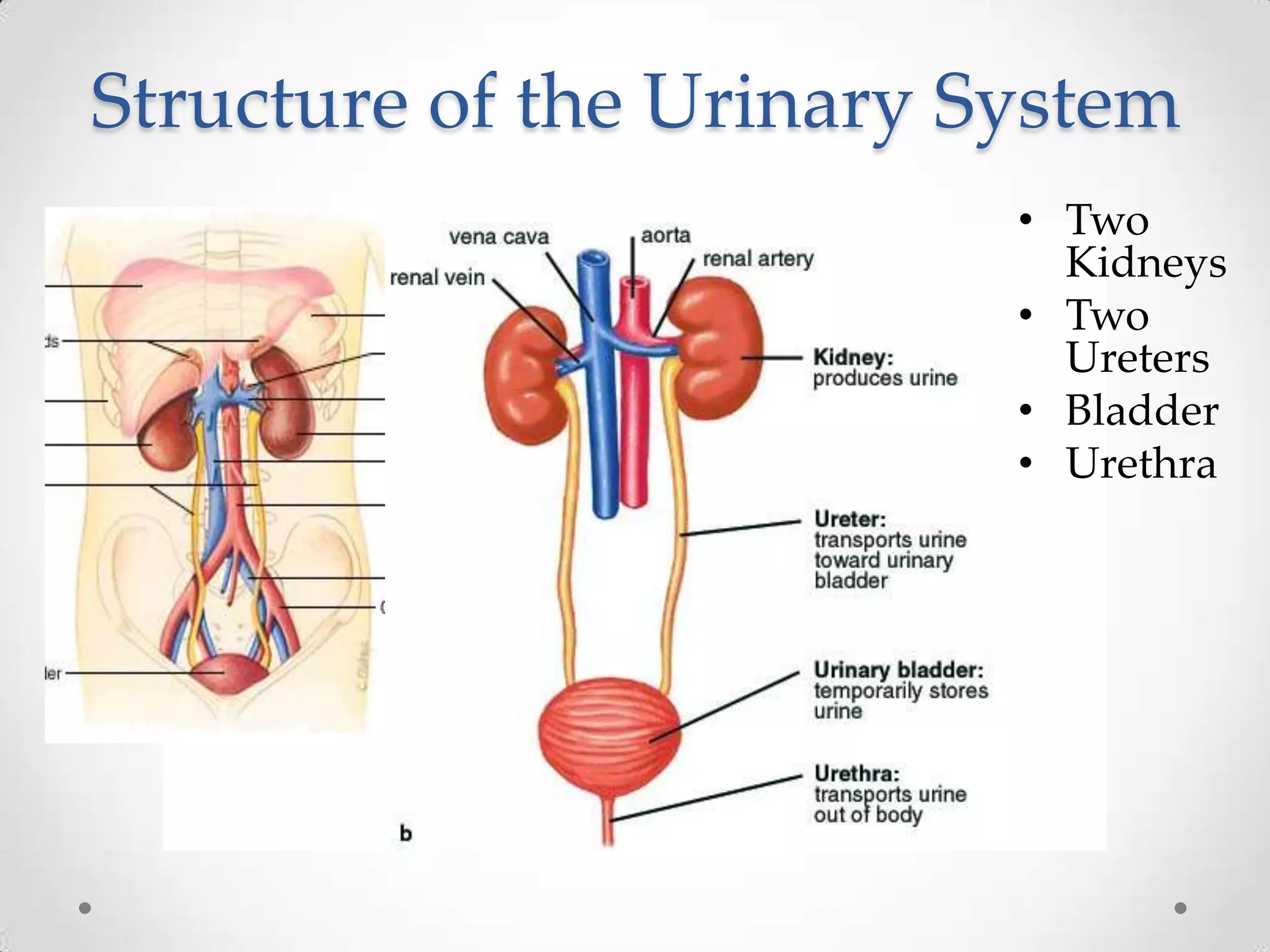
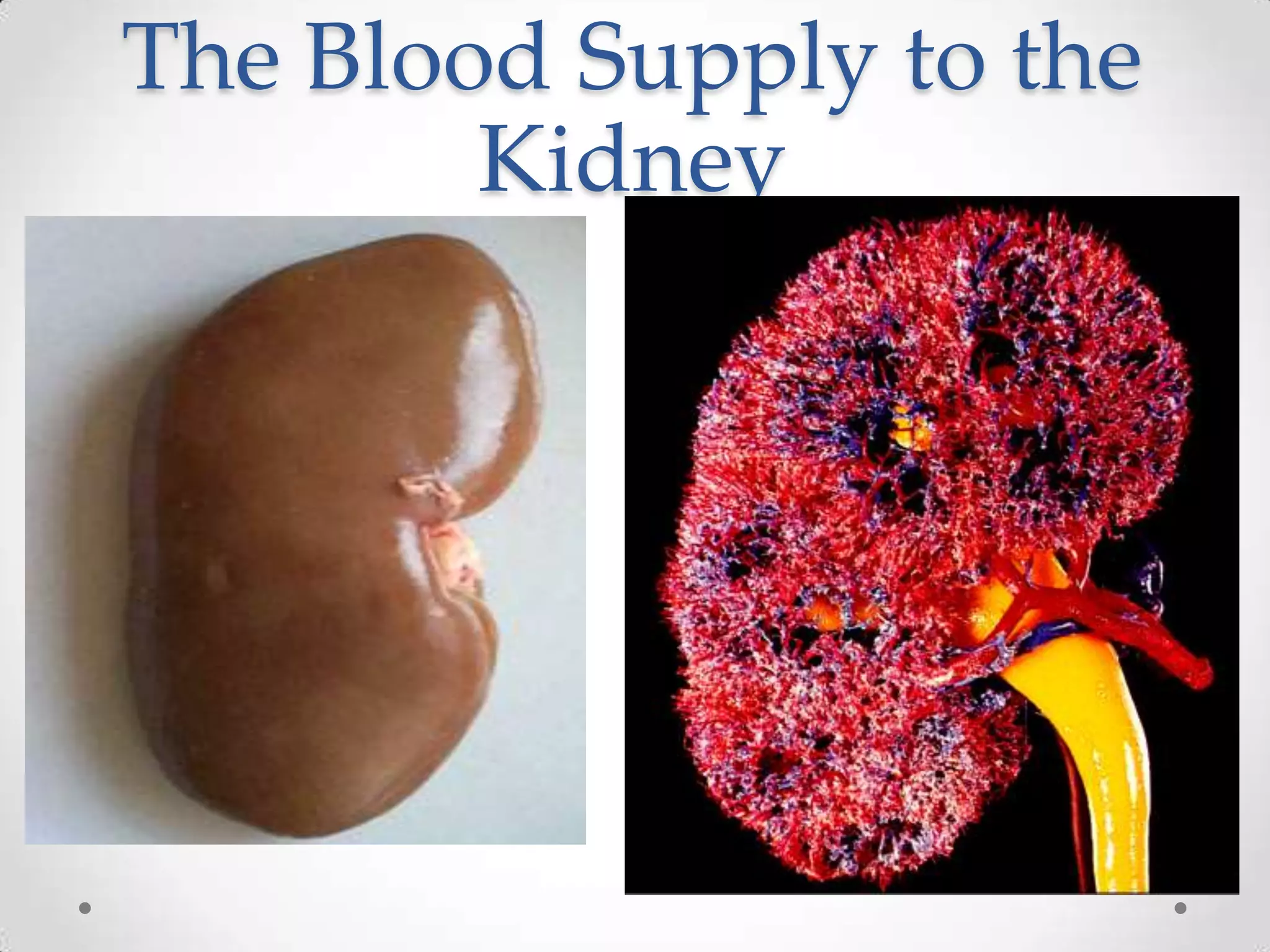
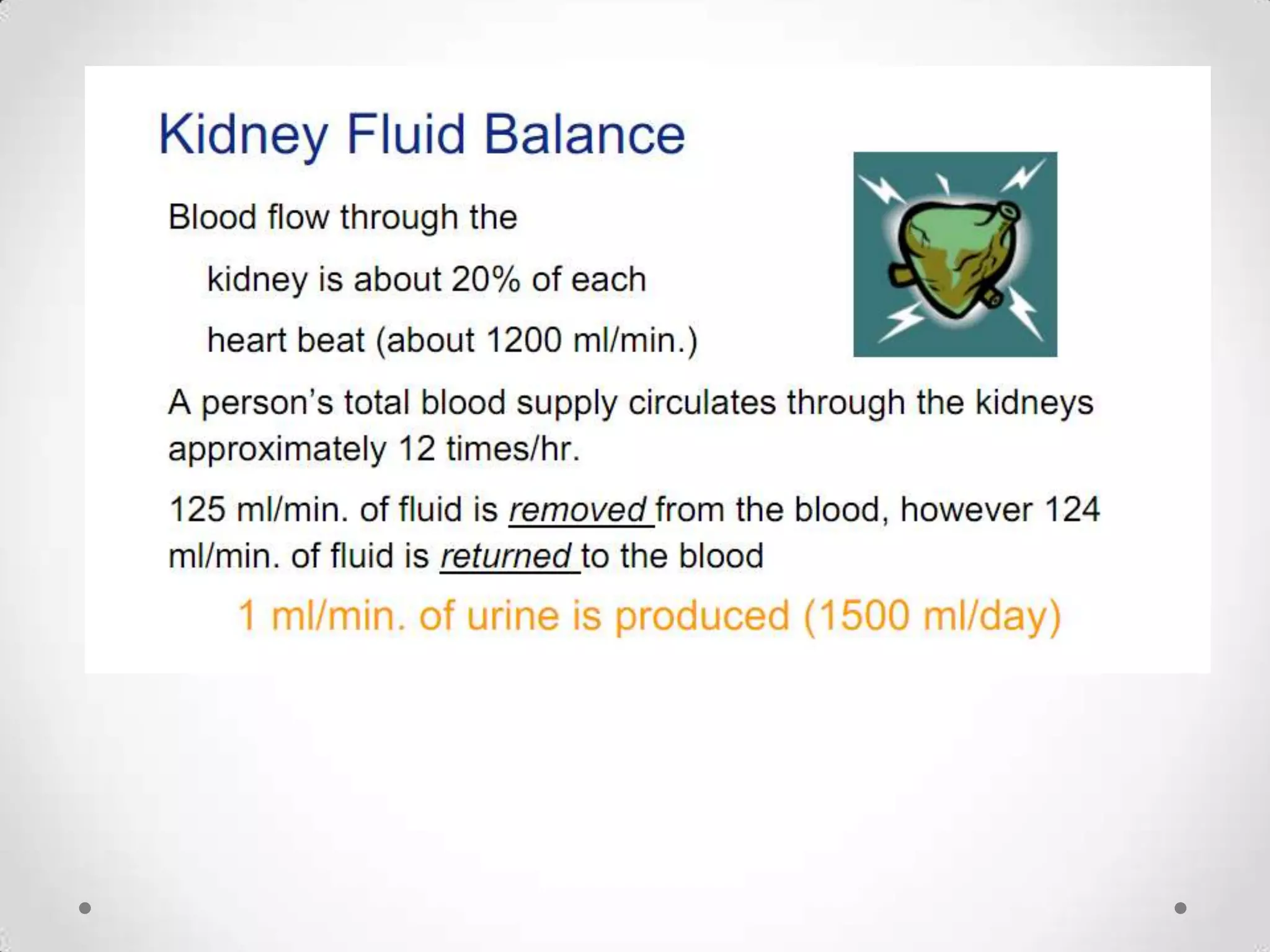
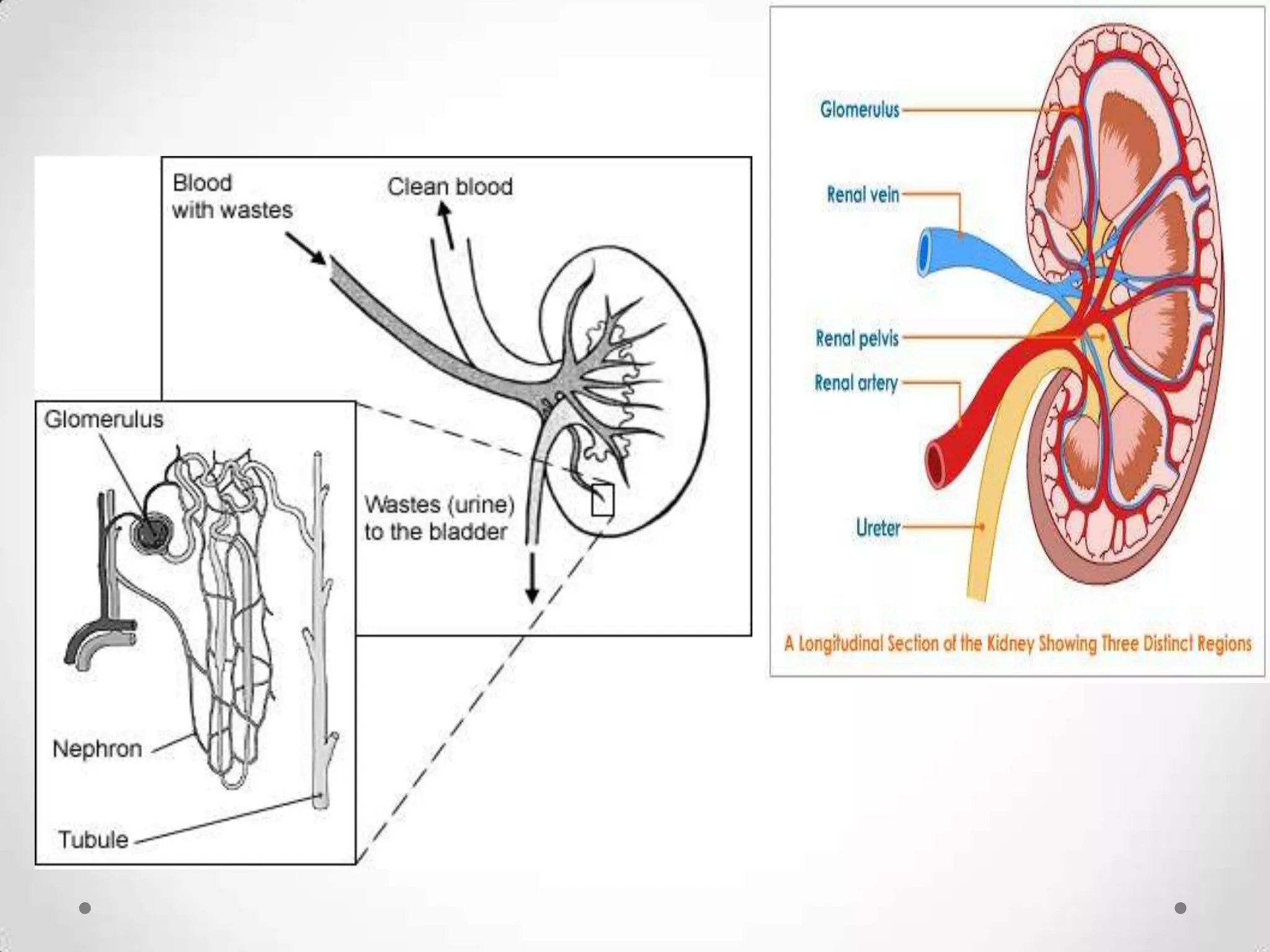
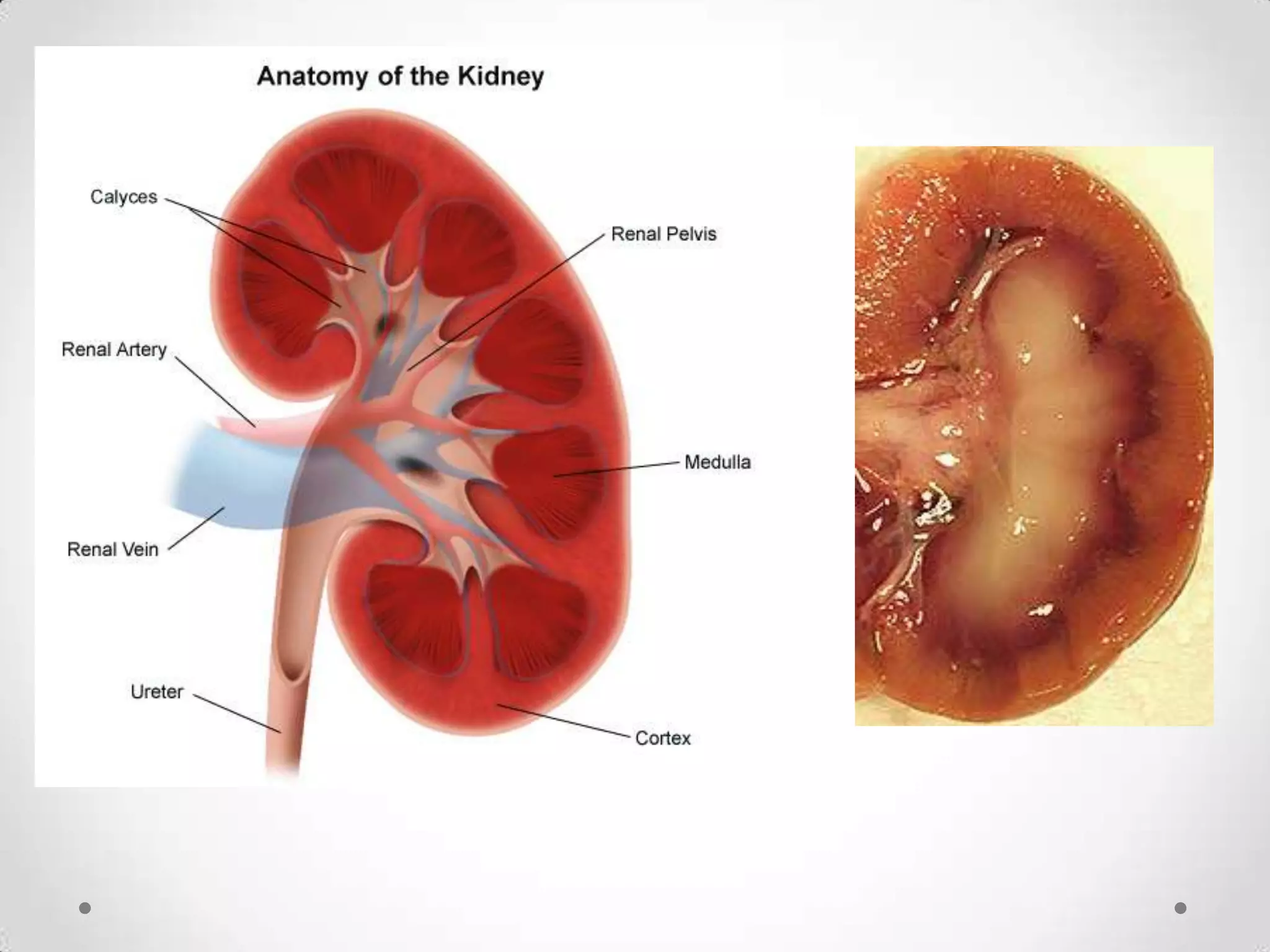
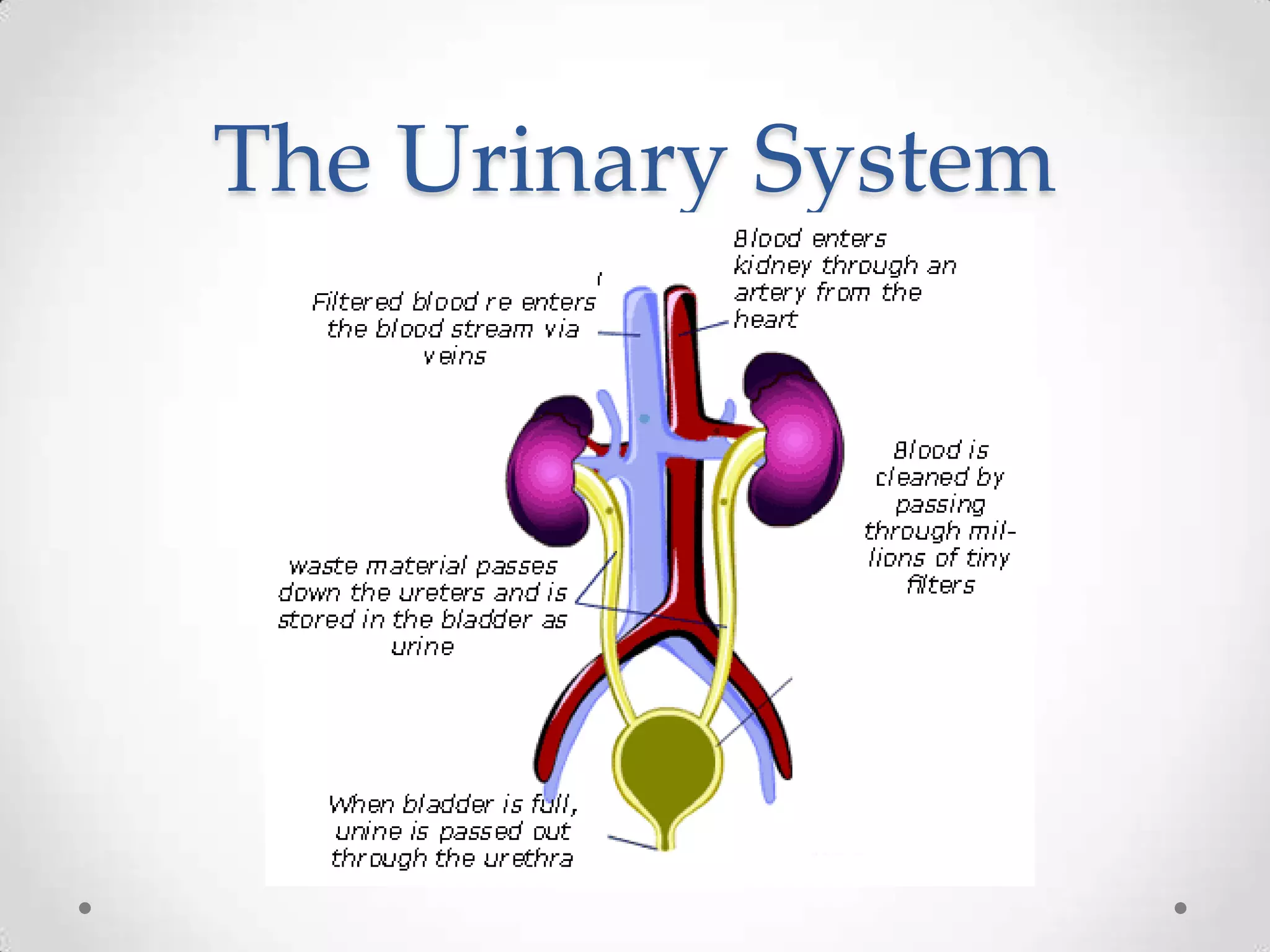
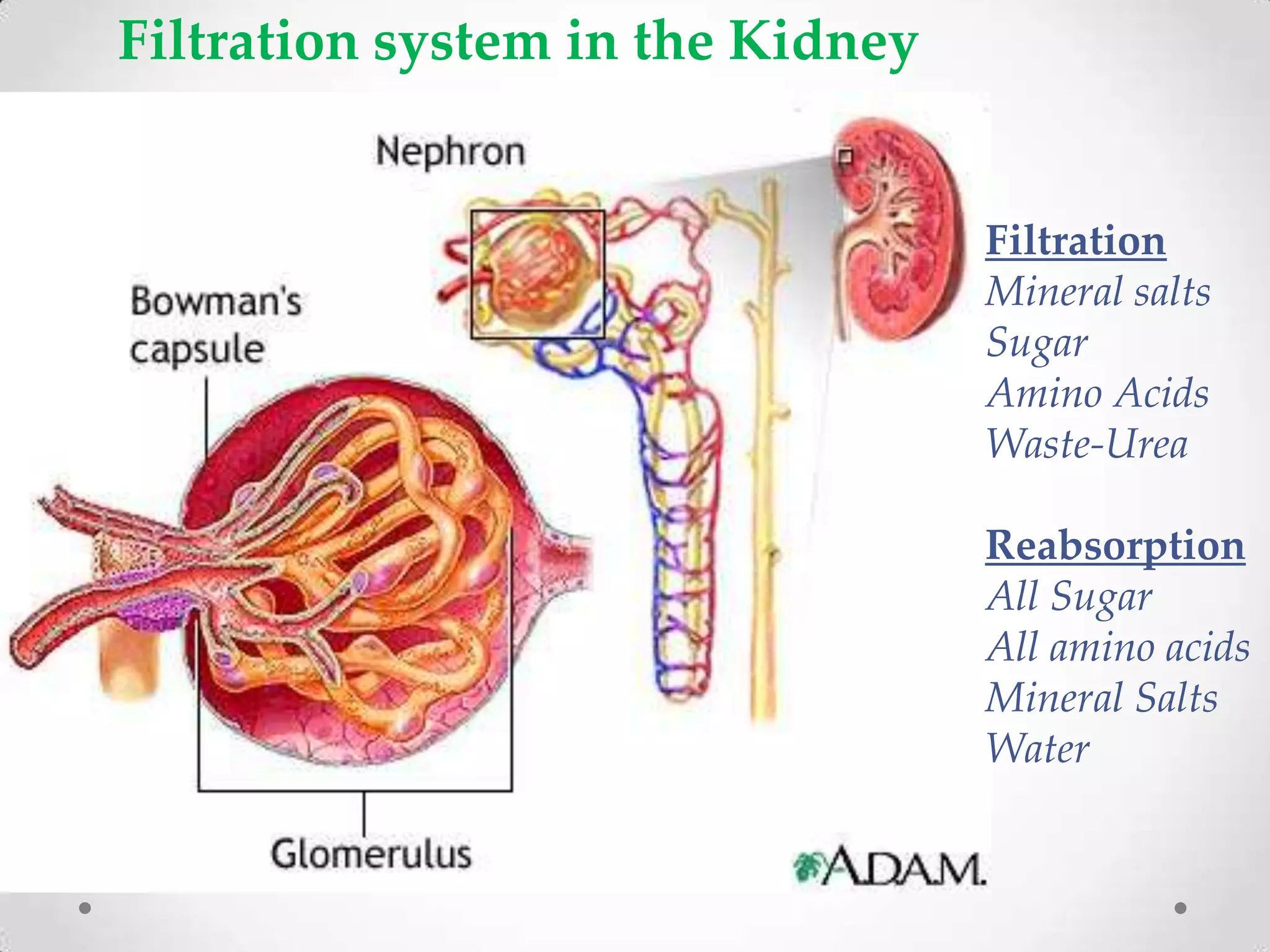
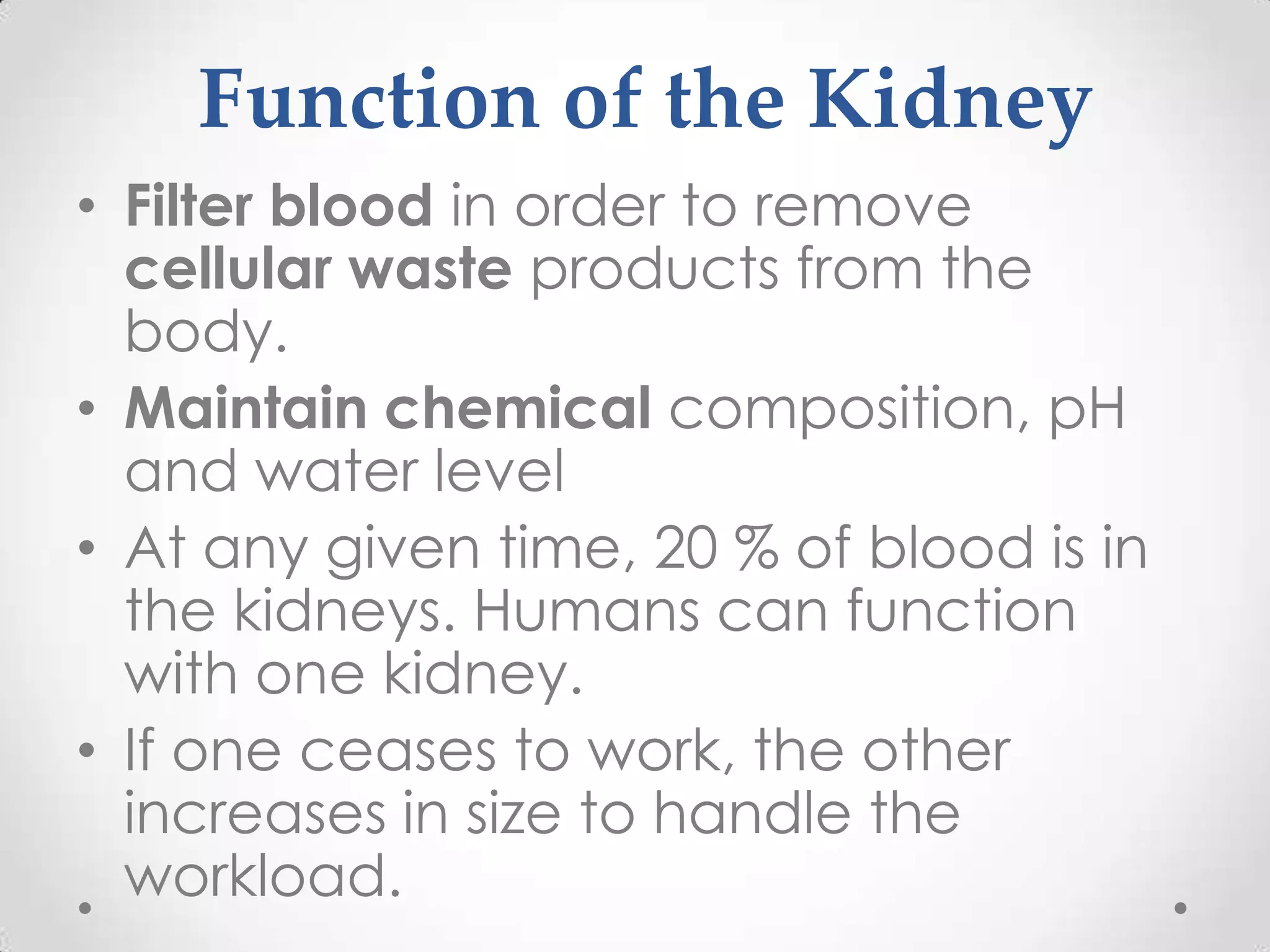
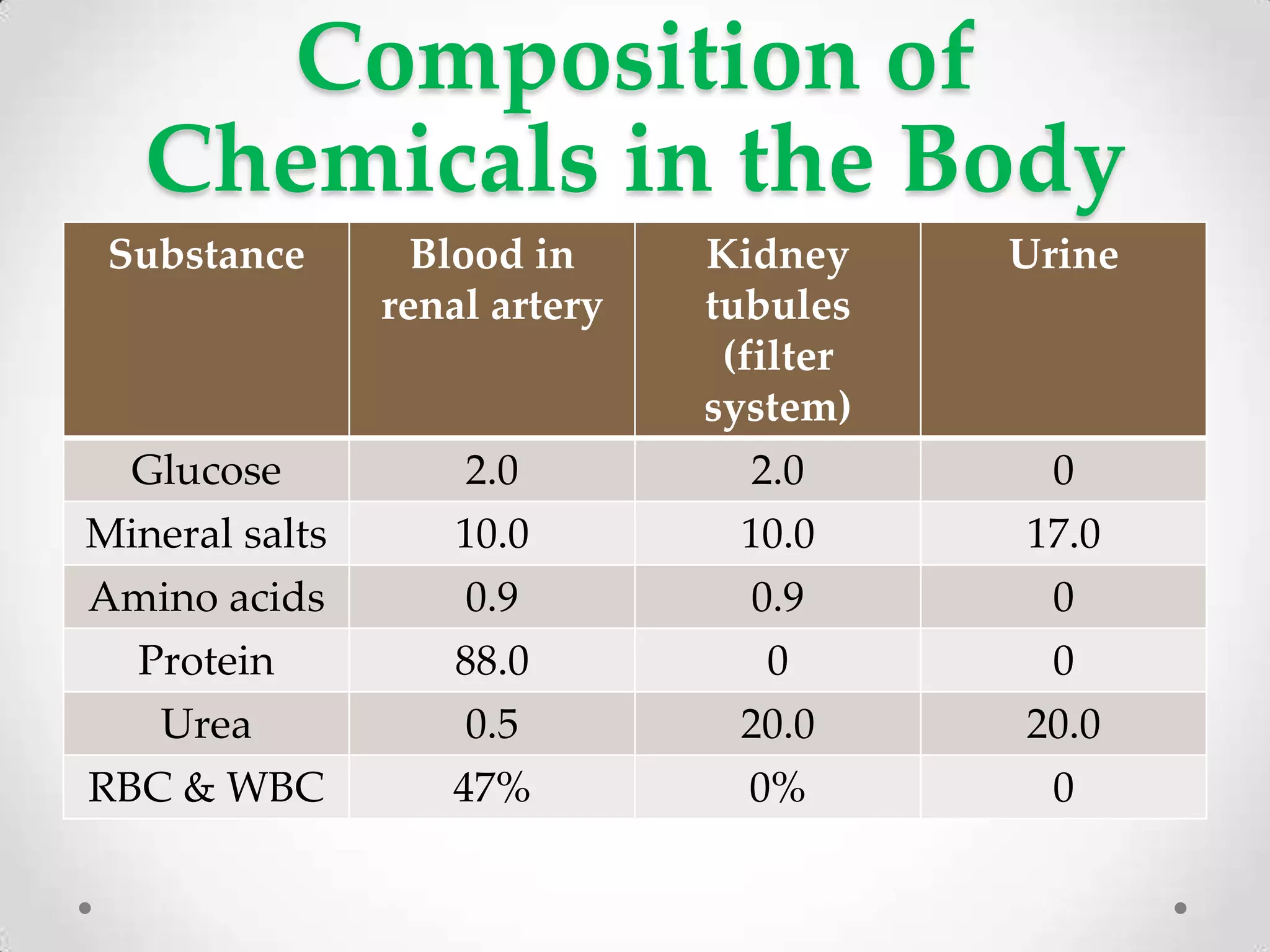
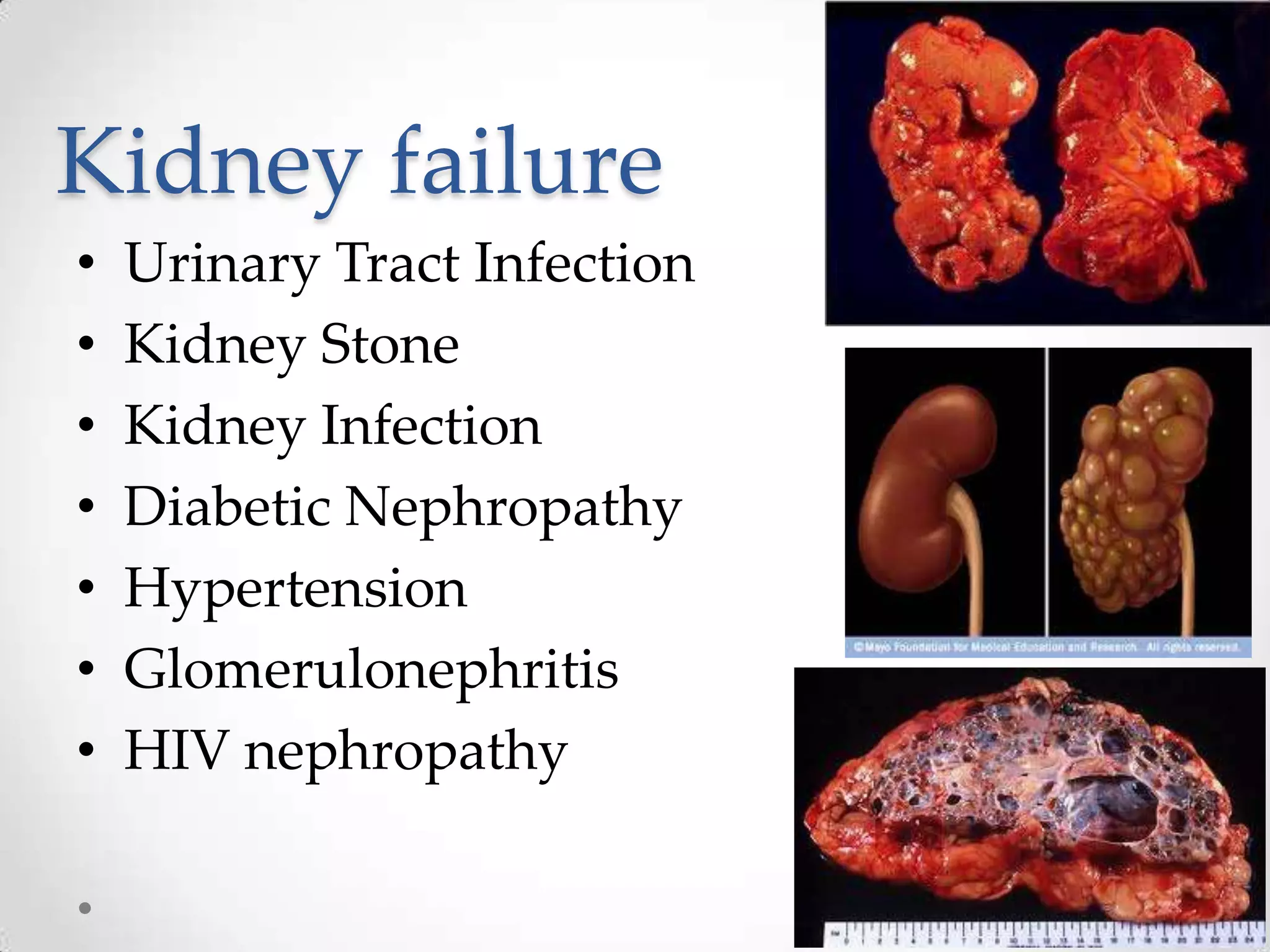
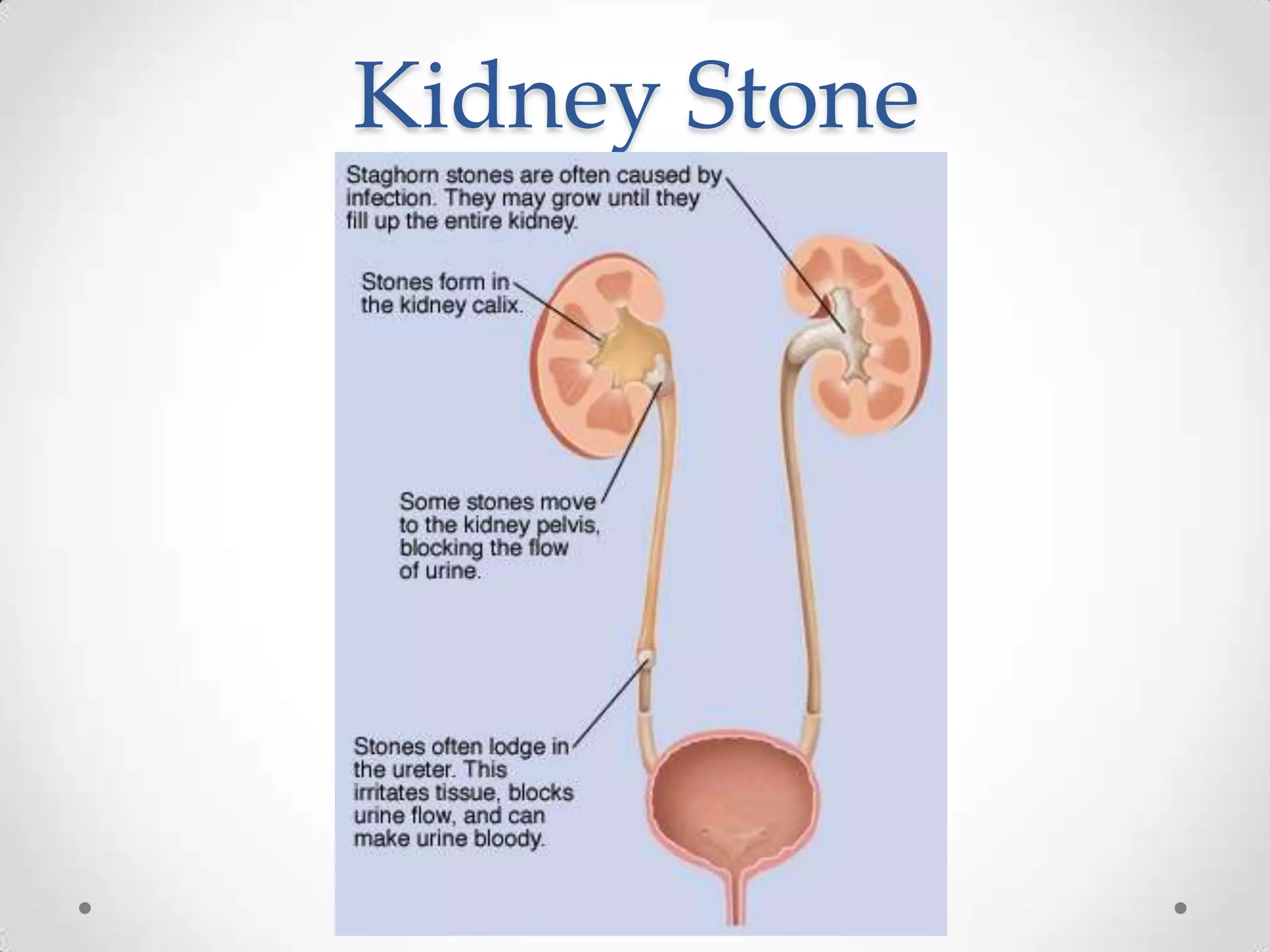
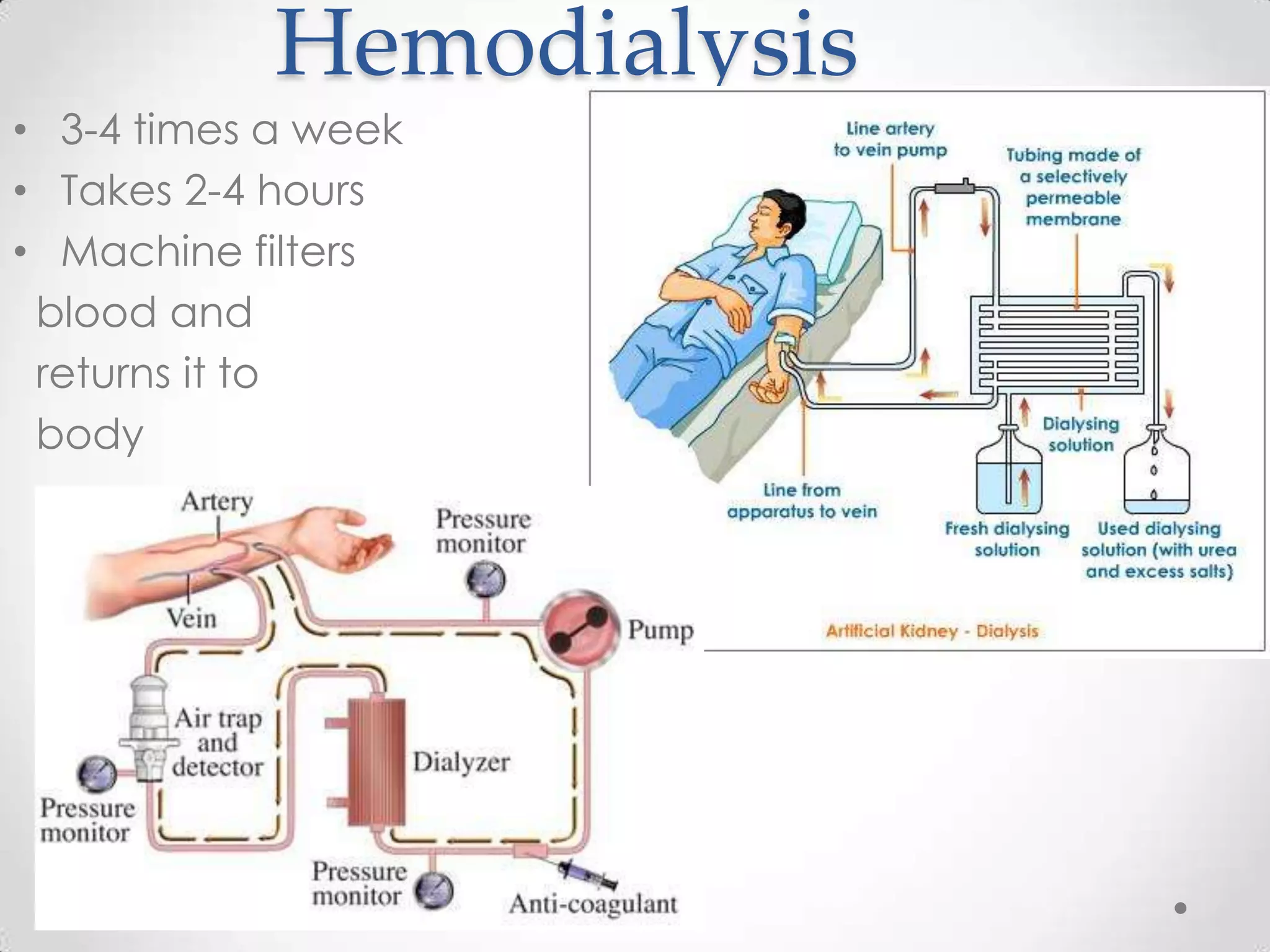
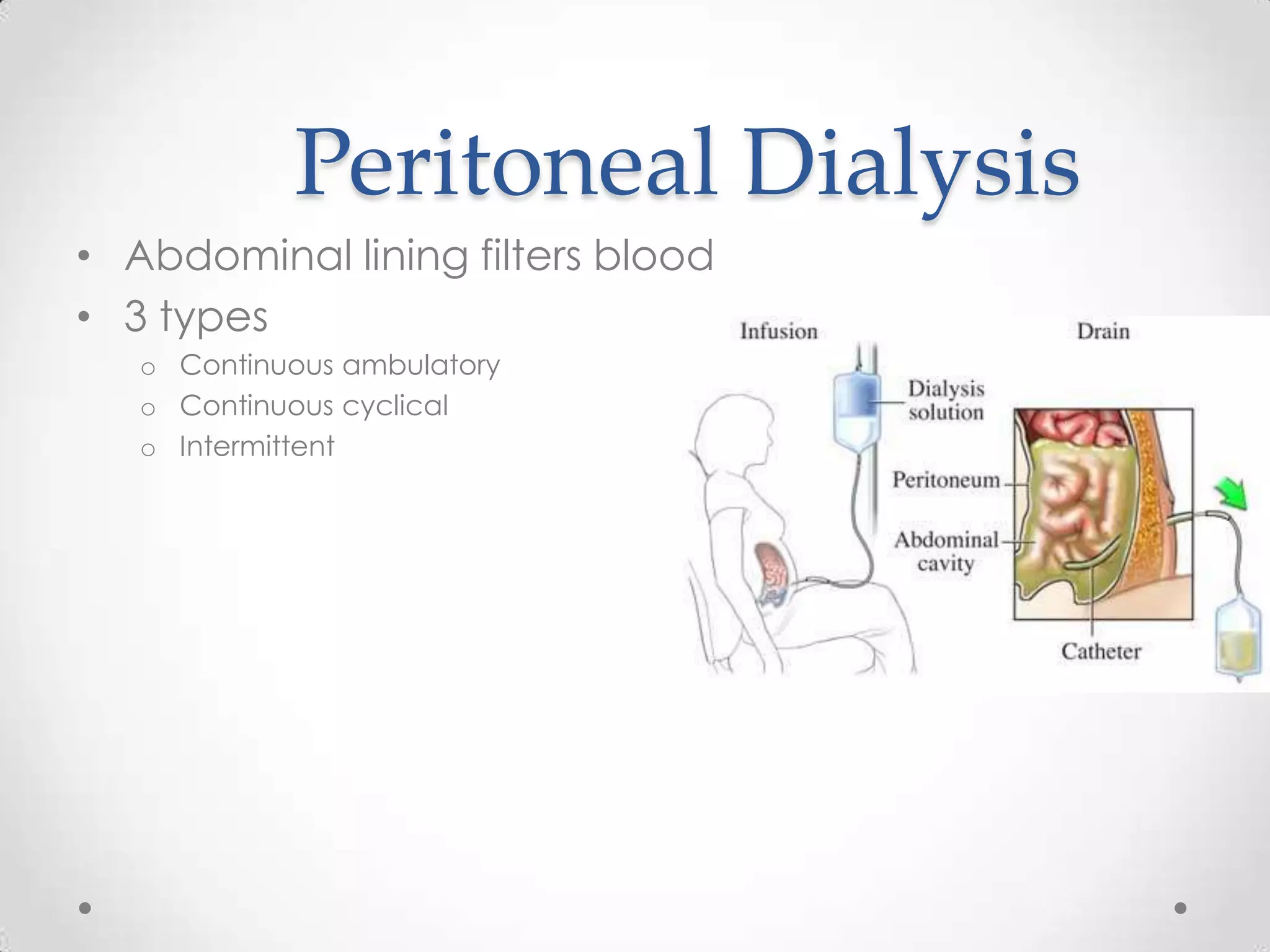
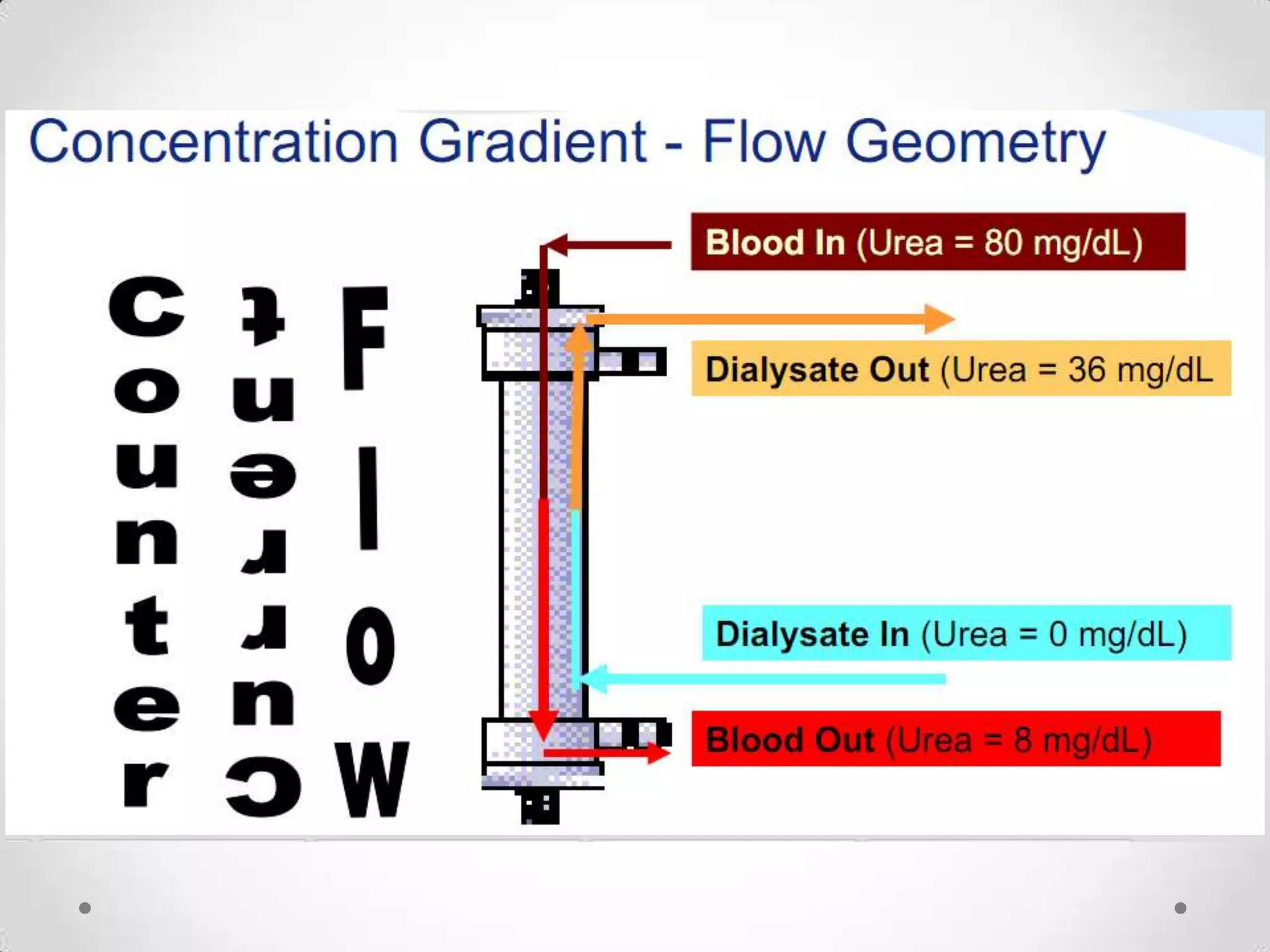
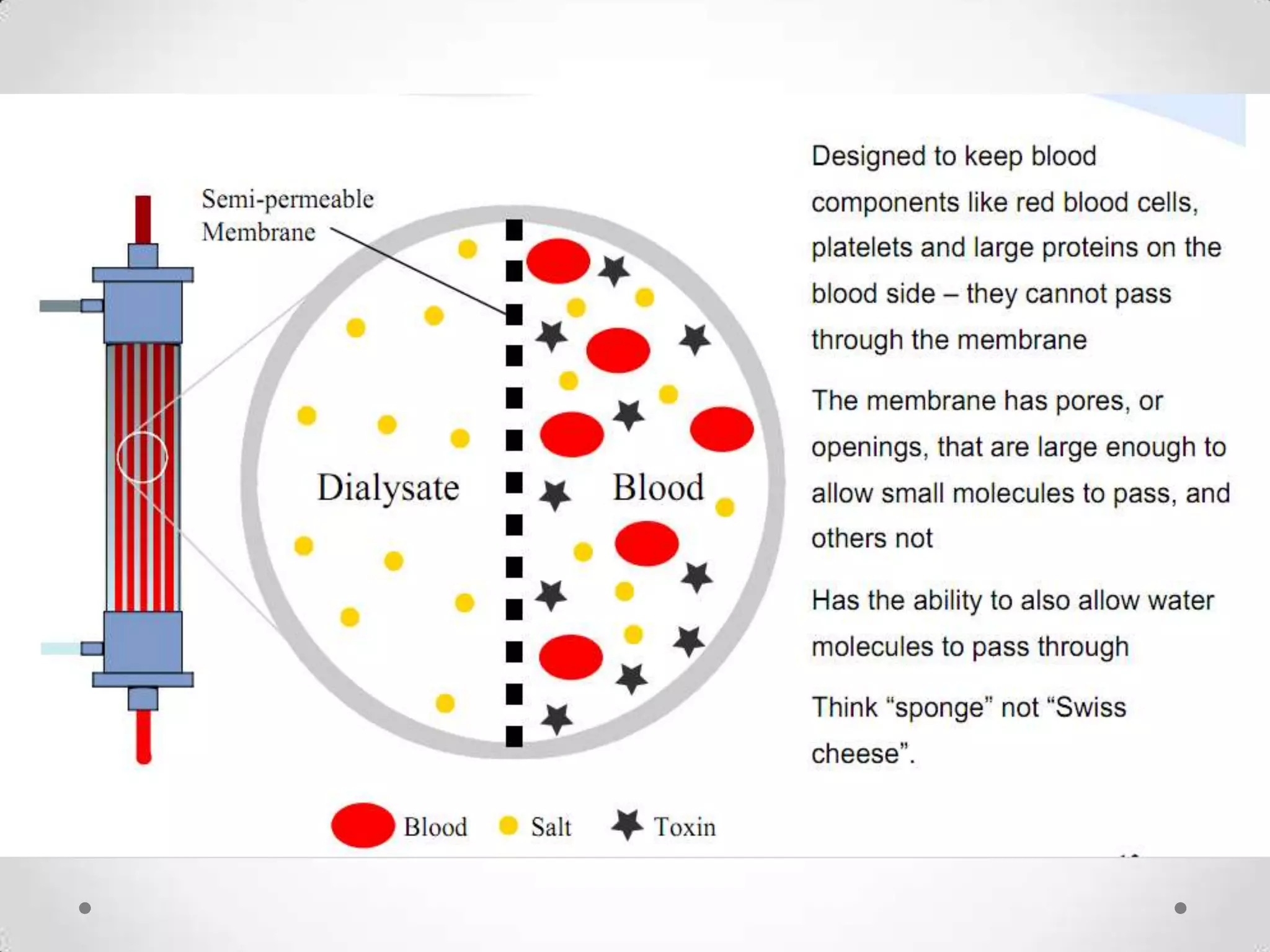
The kidneys filter waste from the blood and regulate water and electrolyte balance. They remove urea, uric acid, and creatinine. The kidneys are supplied by blood from the renal arteries and drain into the ureters. They filter minerals, sugars, amino acids and waste from the blood and reabsorb useful substances while excreting waste like urea in the urine. Kidney failure requires dialysis or transplant to filter the blood.