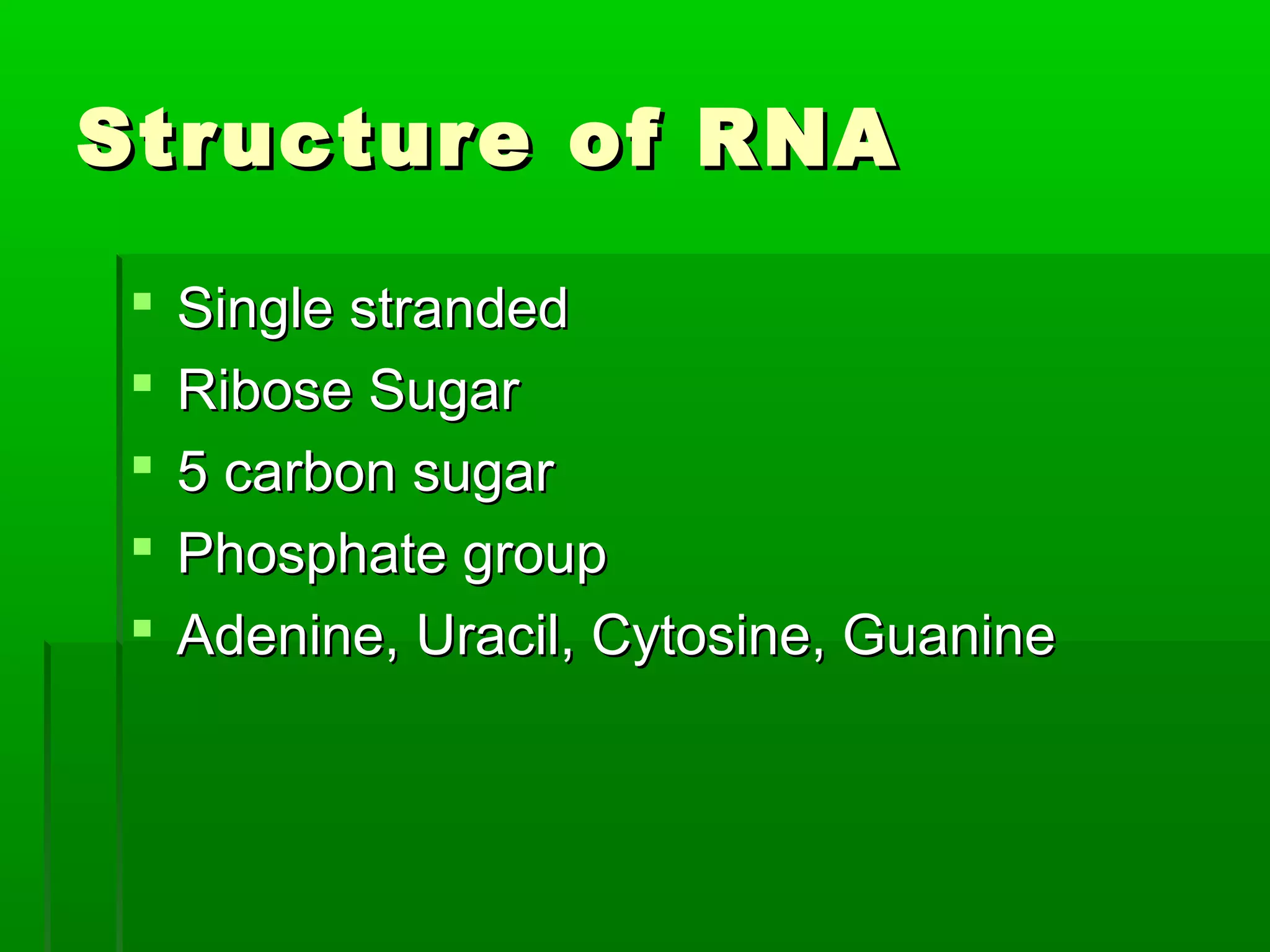
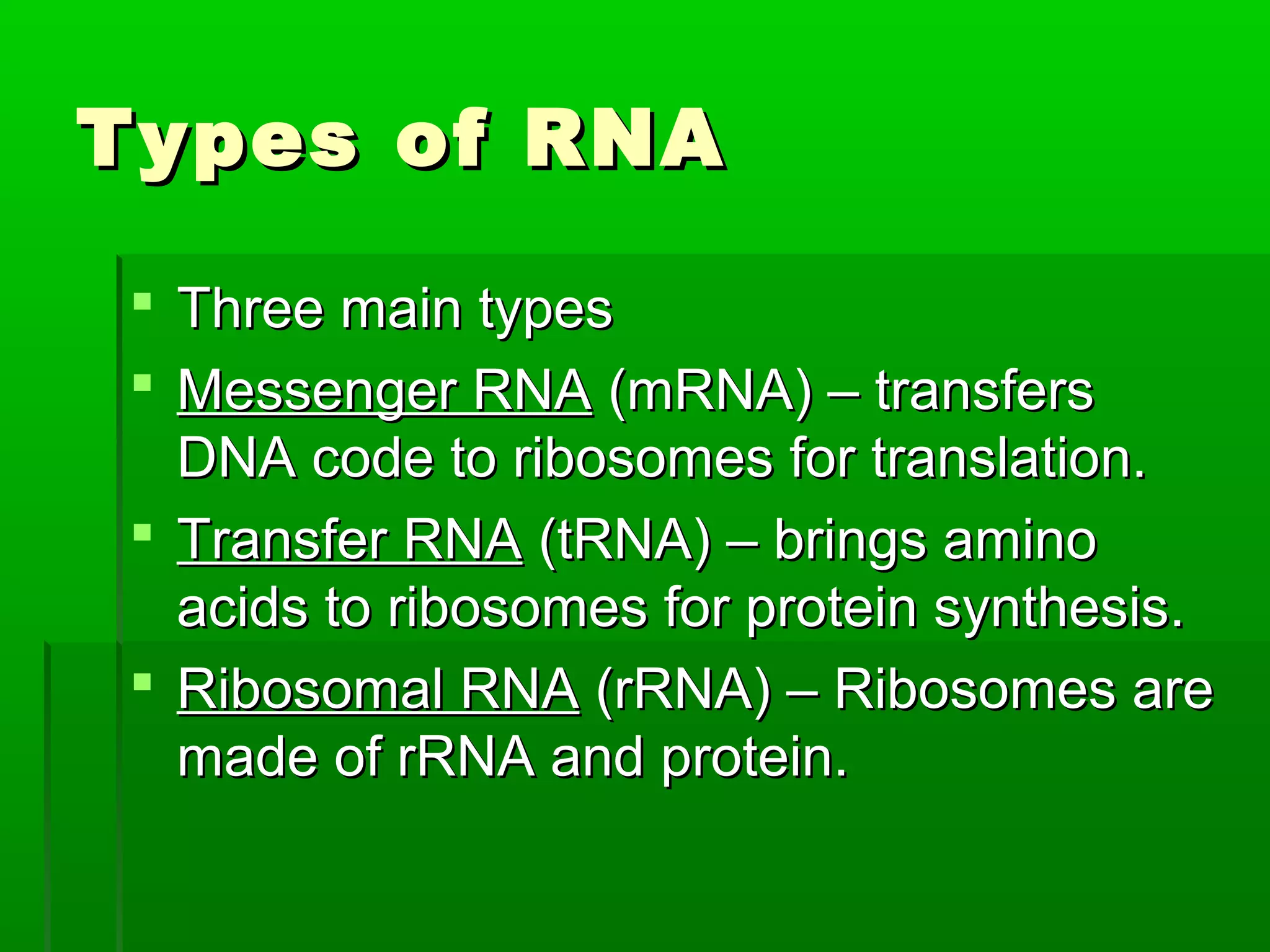
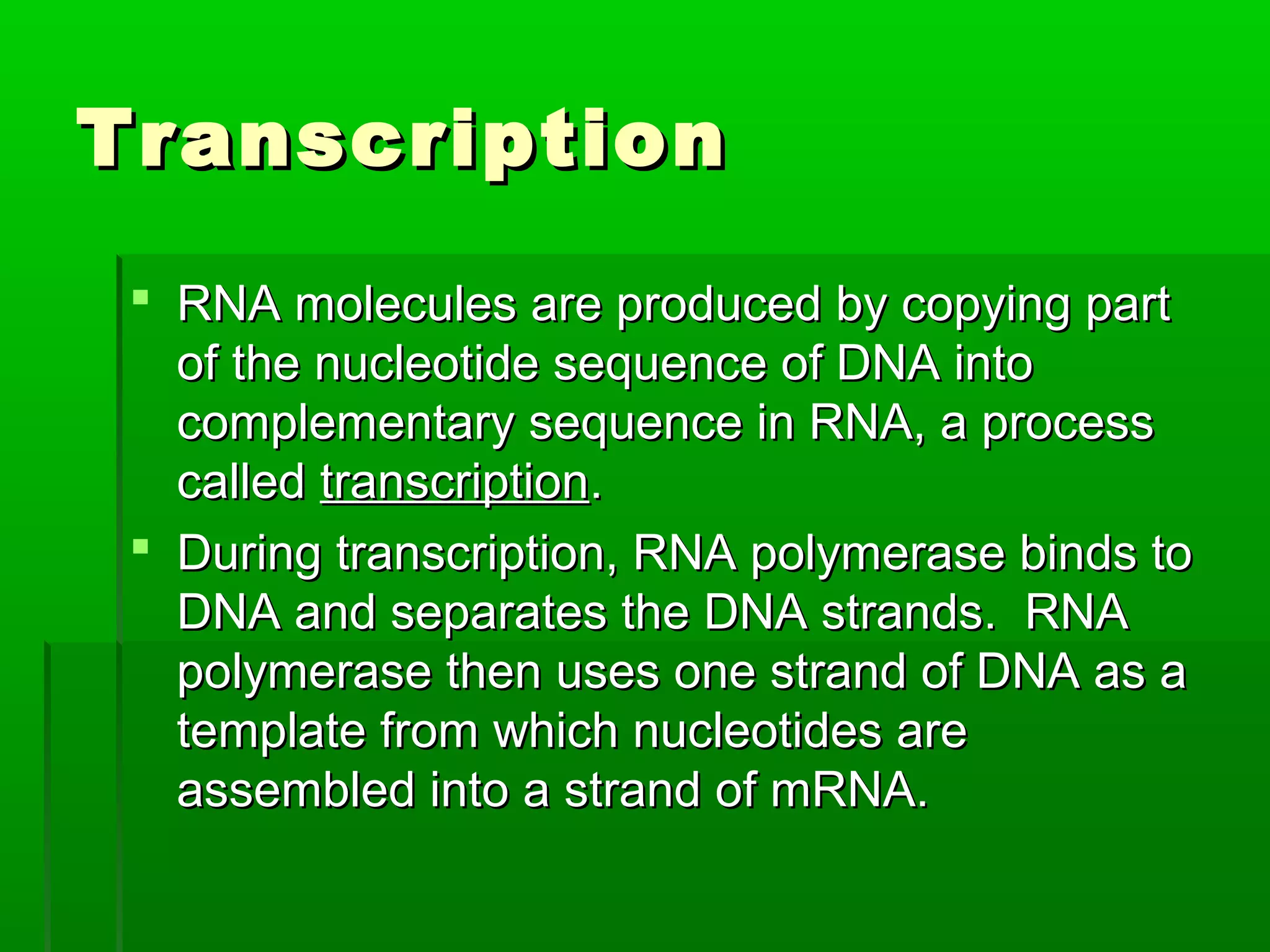
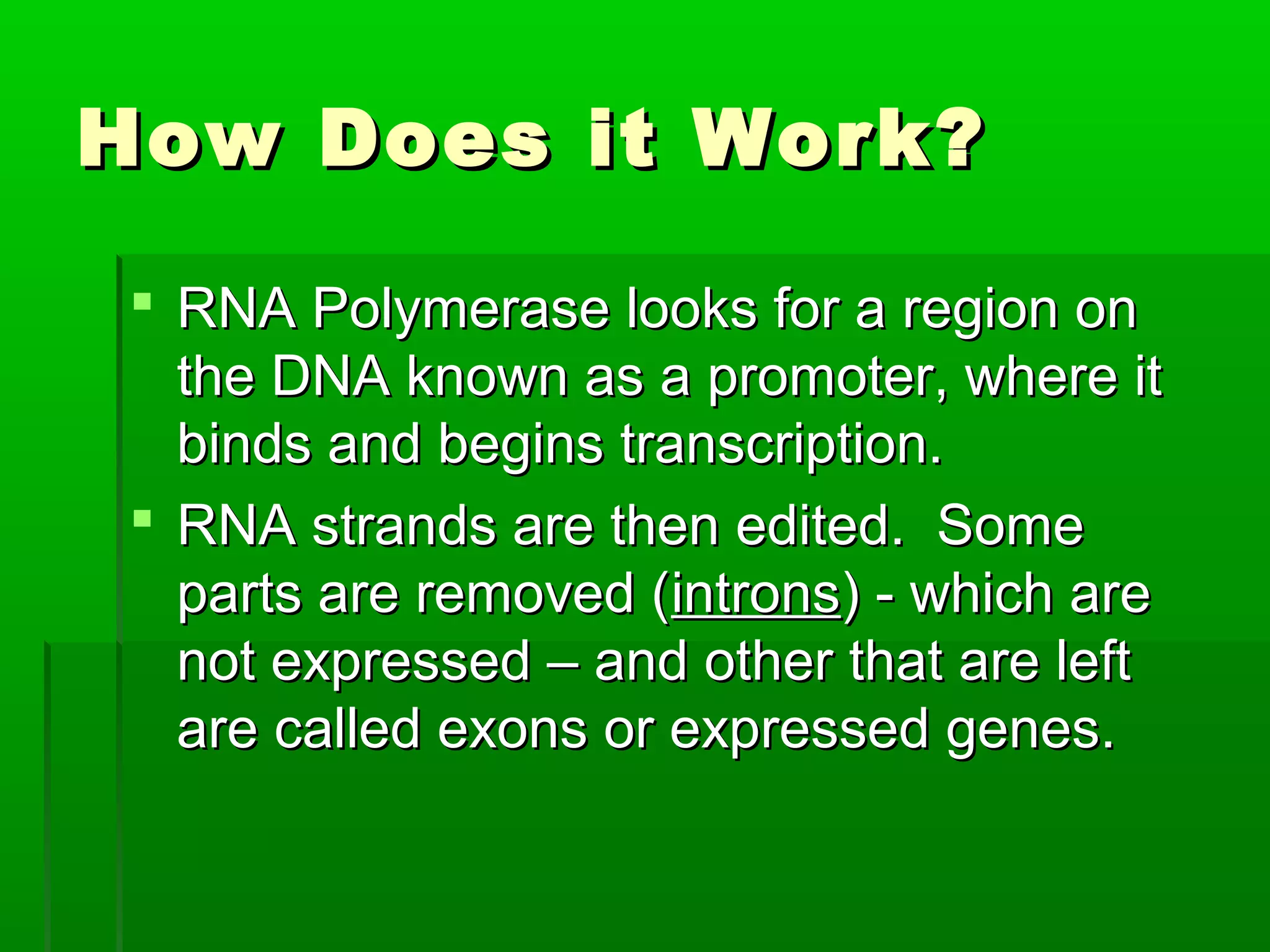
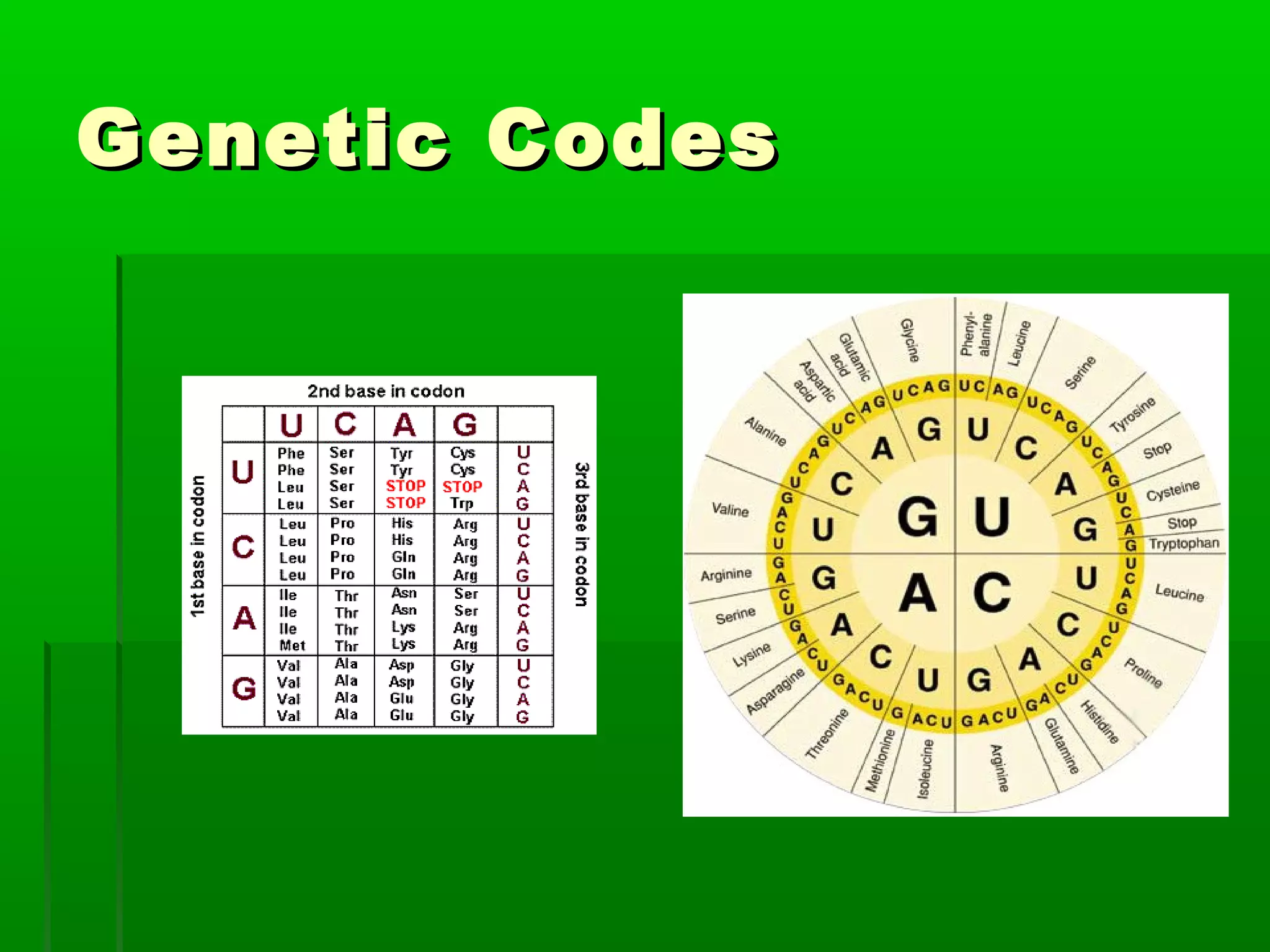
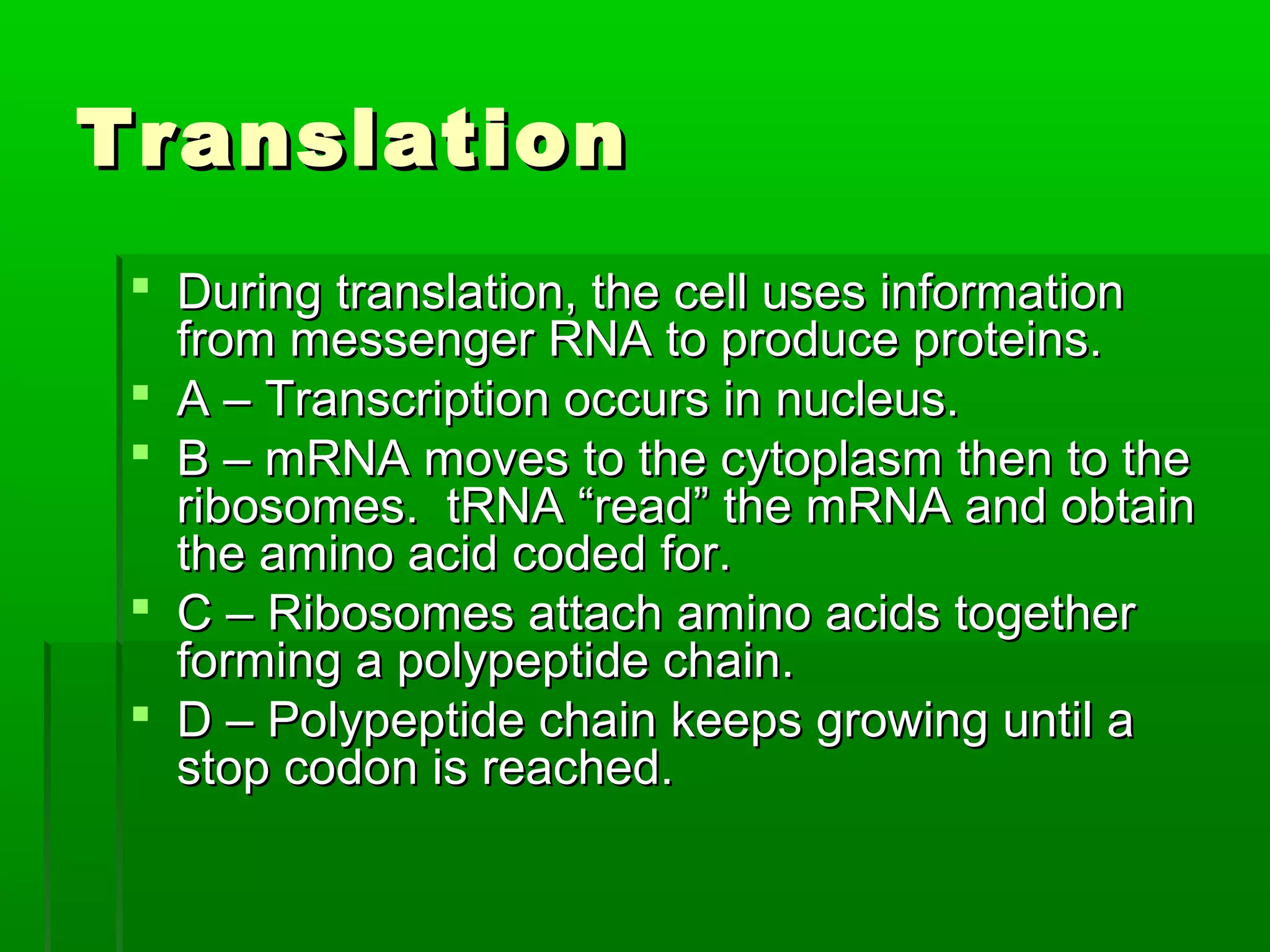
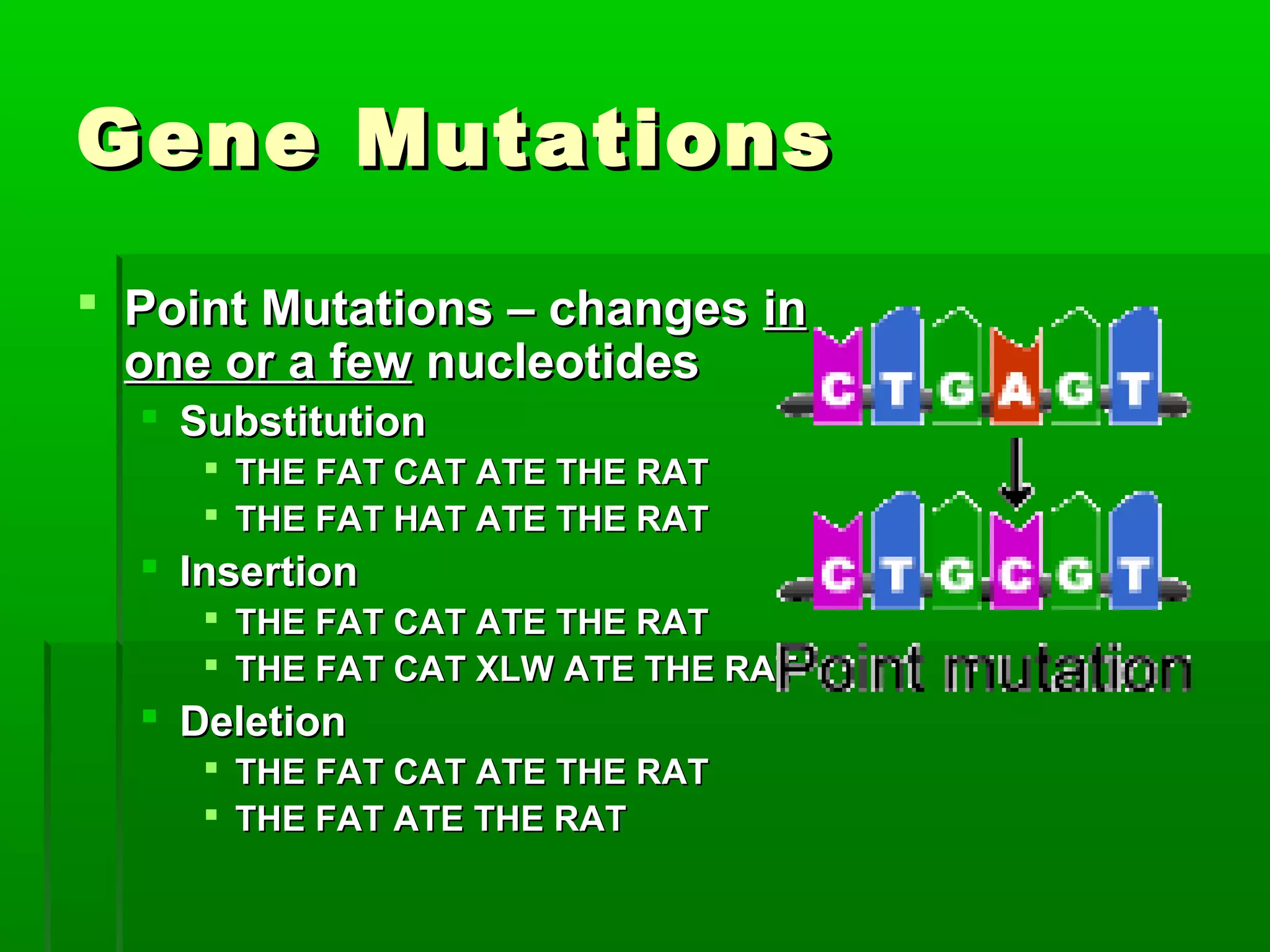
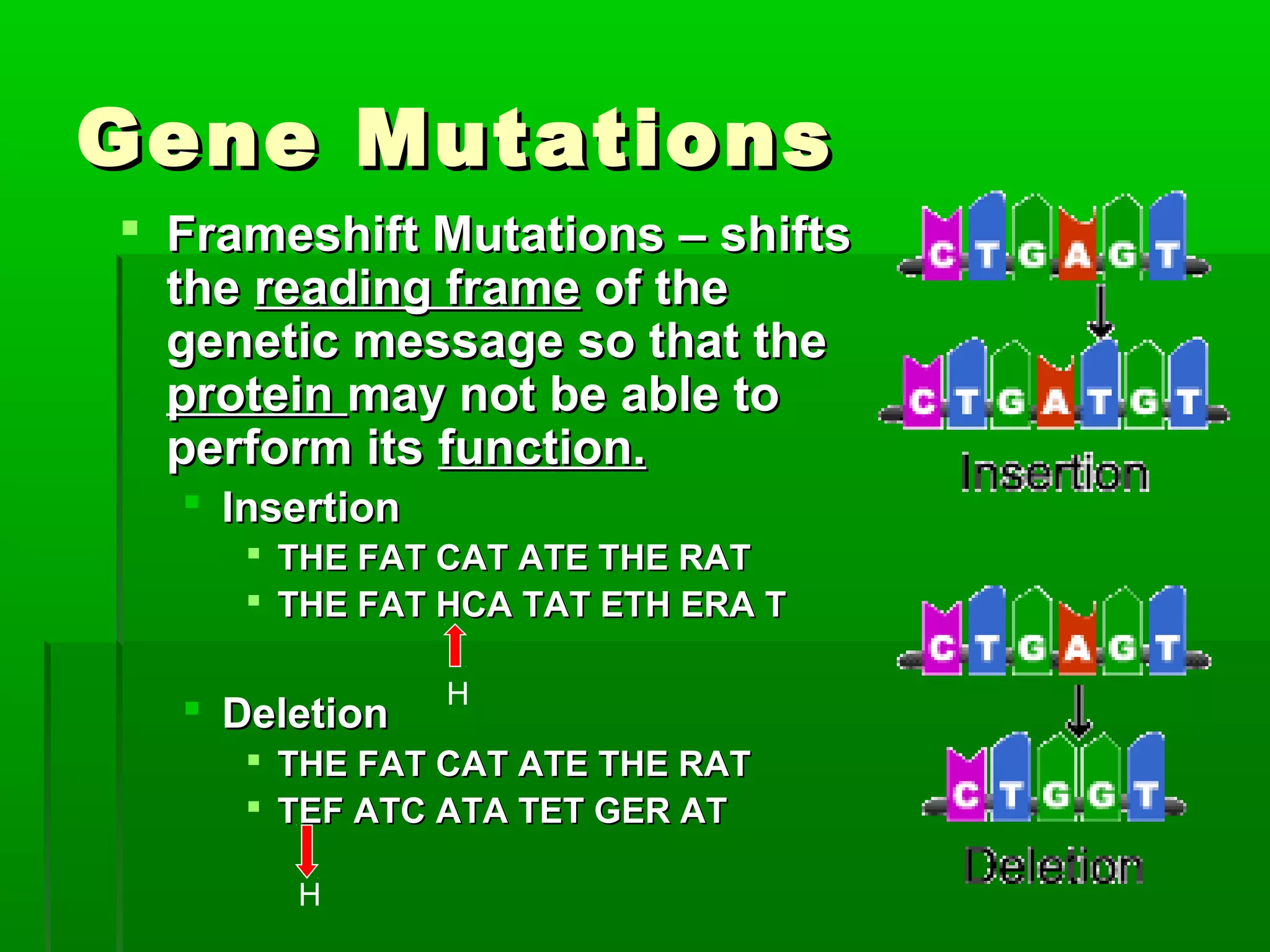
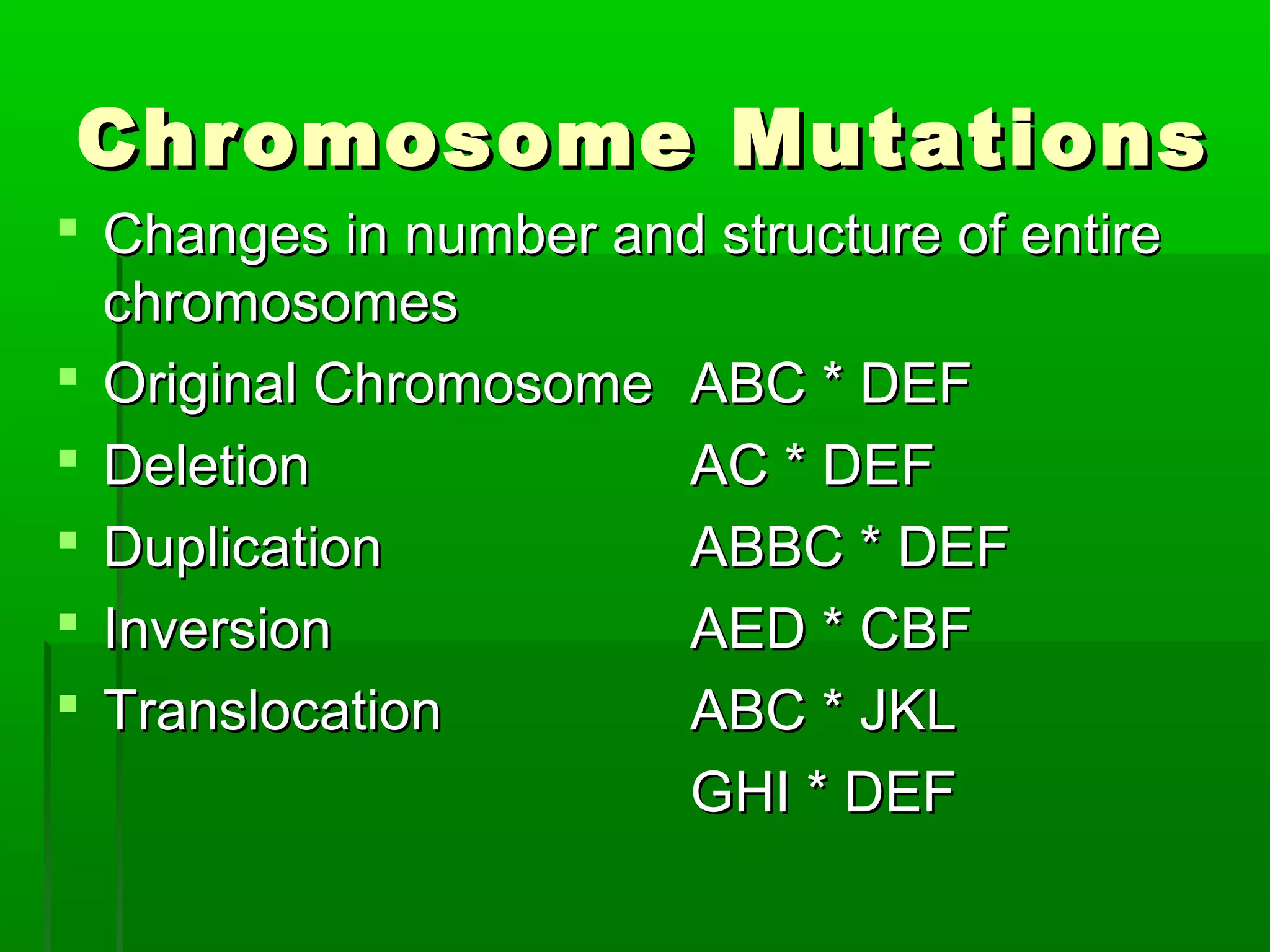
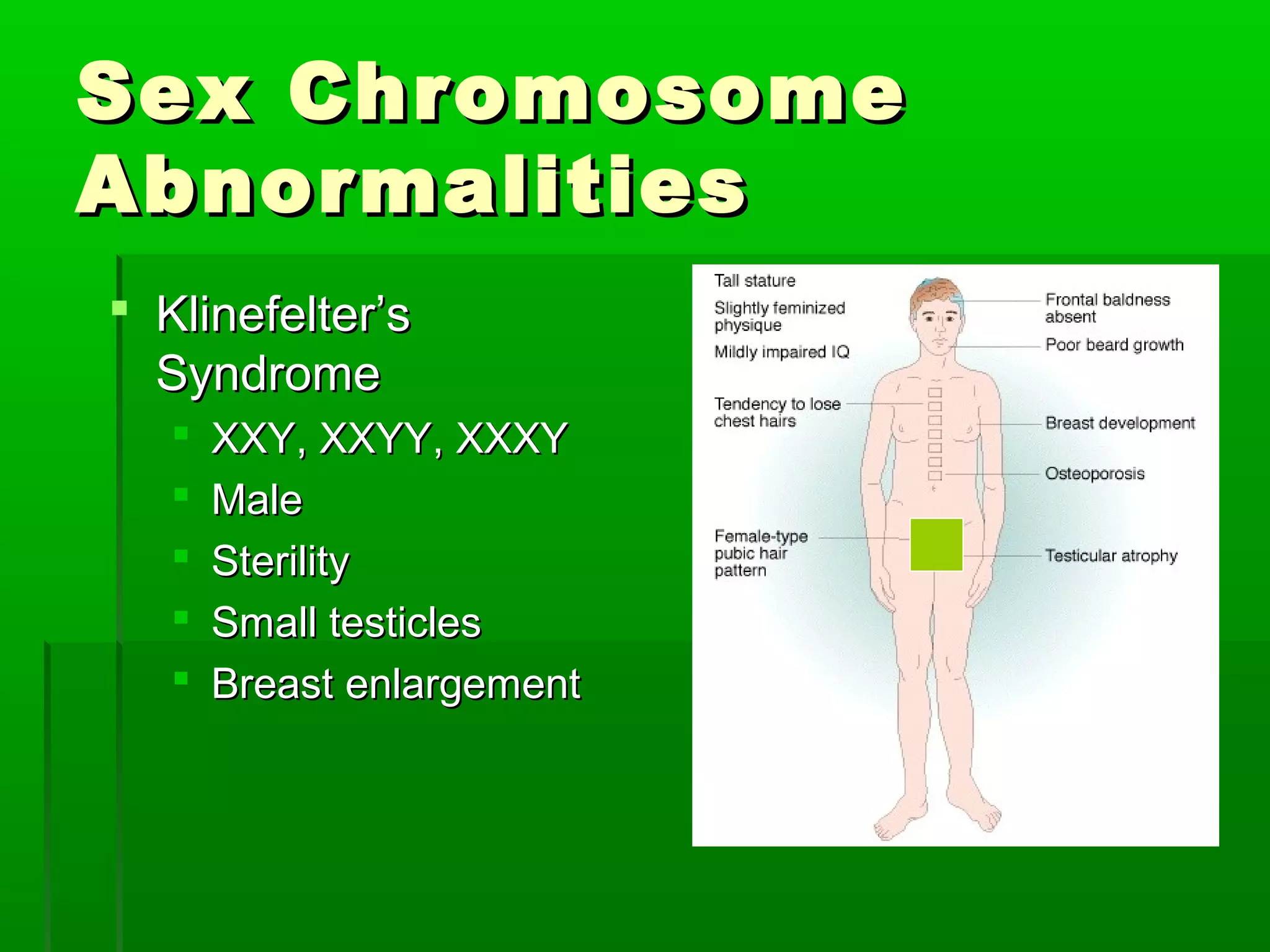
RNA is a single-stranded molecule that plays several roles in protein synthesis. There are three main types of RNA: messenger RNA (mRNA) which carries DNA's protein instructions to the ribosome, transfer RNA (tRNA) which brings amino acids to the ribosome during protein assembly, and ribosomal RNA (rRNA) which makes up the ribosome. RNA is produced through transcription, where RNA polymerase copies a DNA sequence into a complementary RNA strand. The RNA is then edited and moves to the ribosome for translation into a polypeptide chain. Mutations can occur through changes in single genes or whole chromosomes and can be inherited or acquired through environmental damage. While most mutations are neutral, some can cause genetic disorders