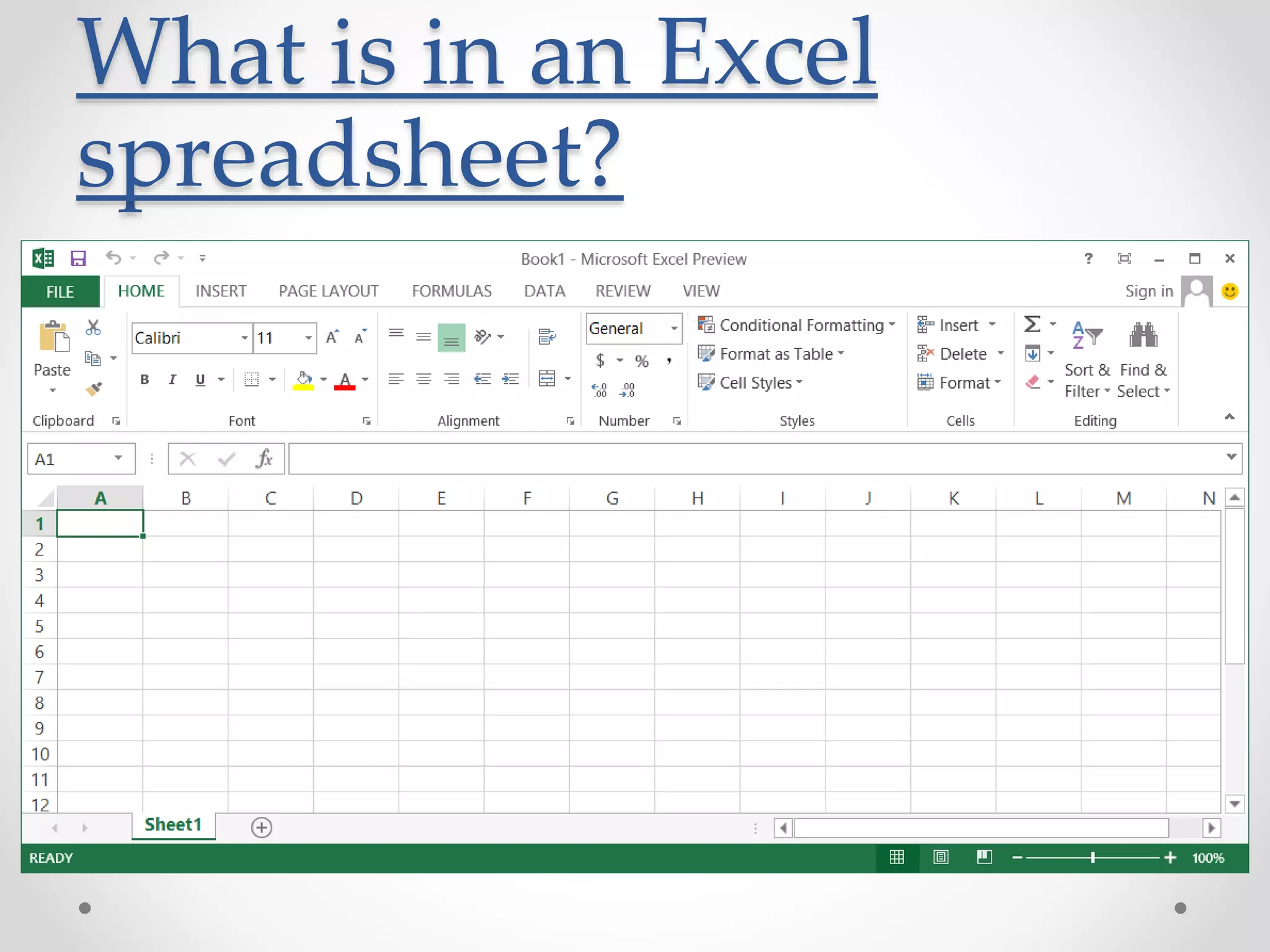
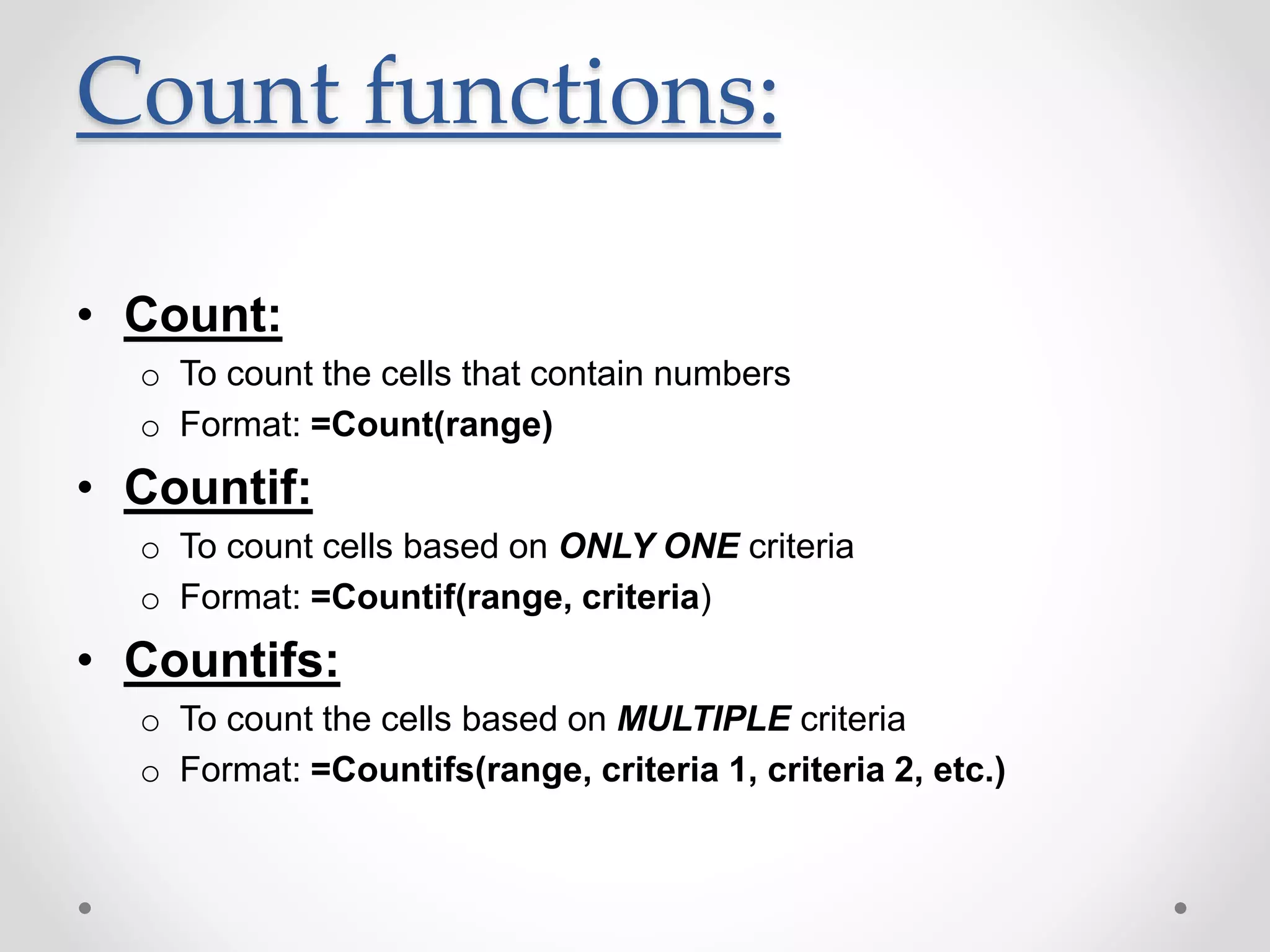
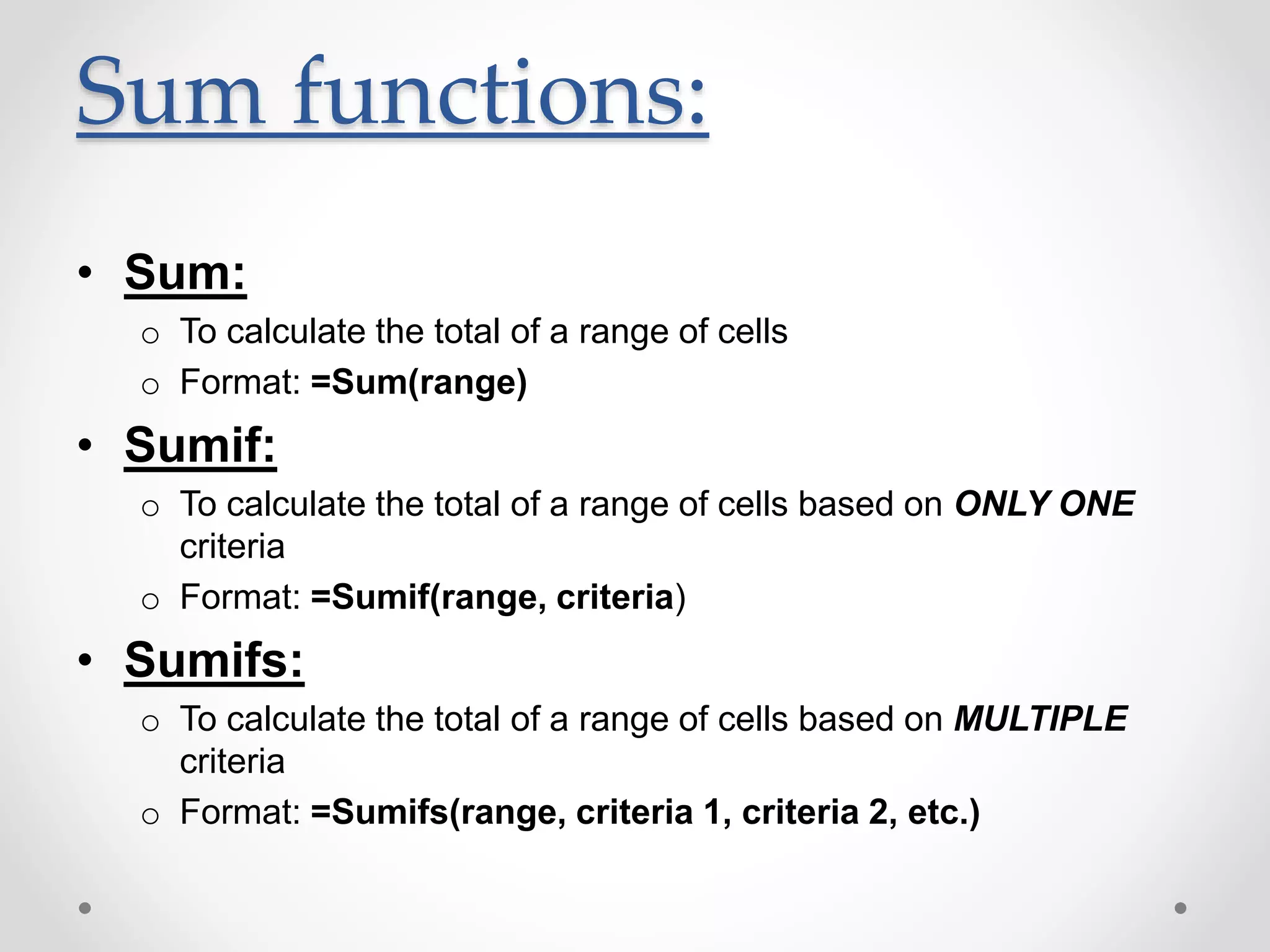
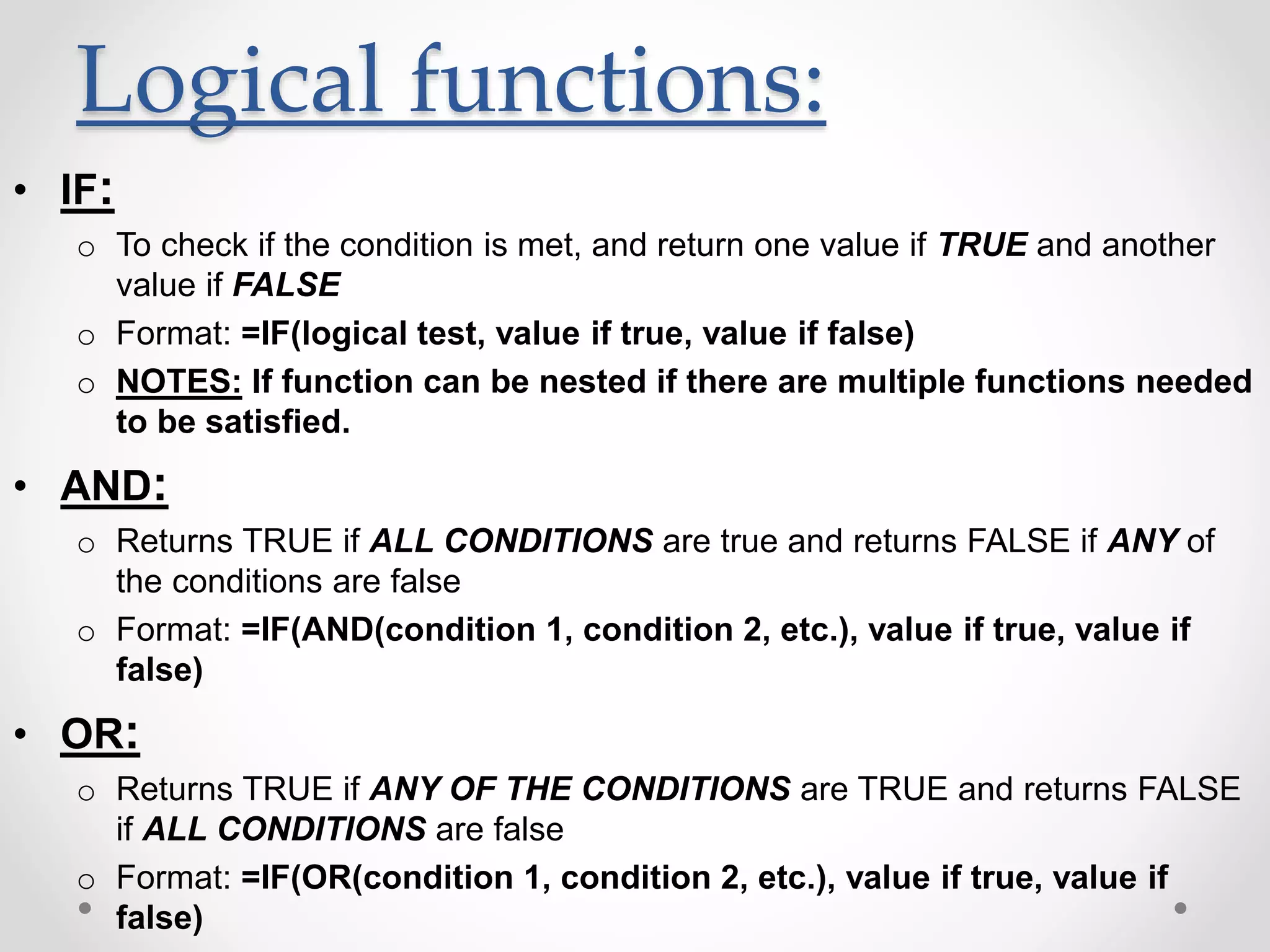
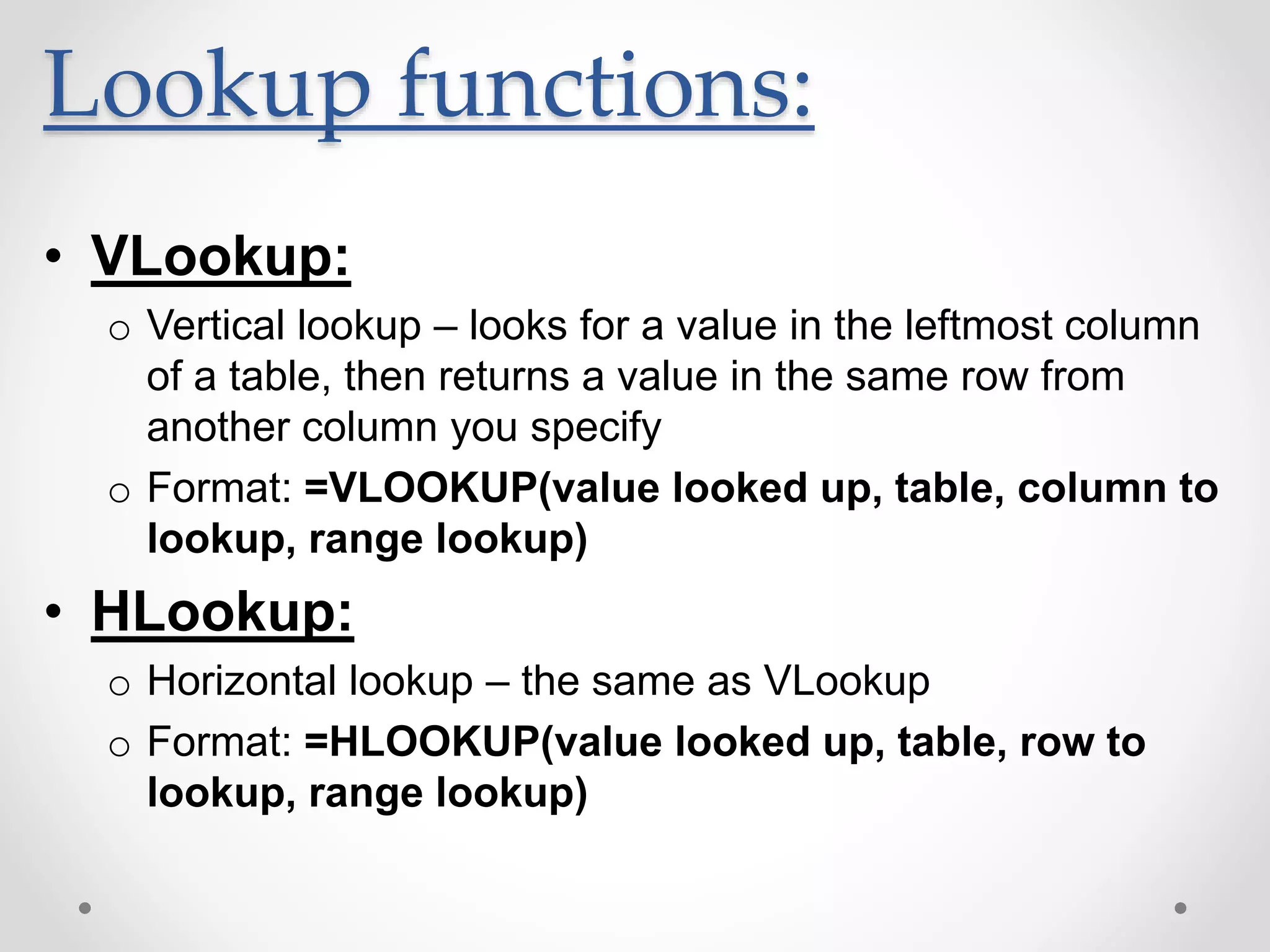
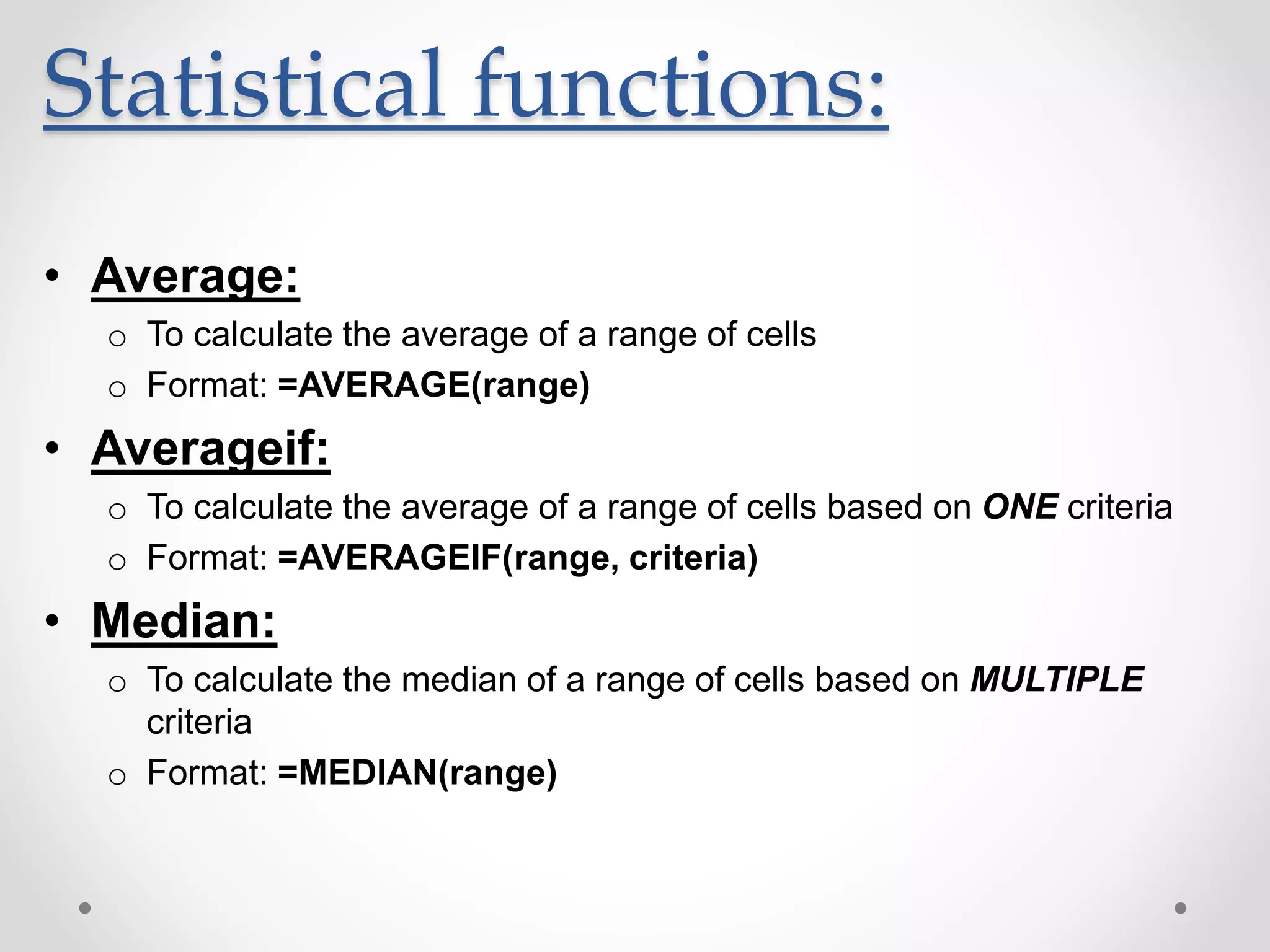
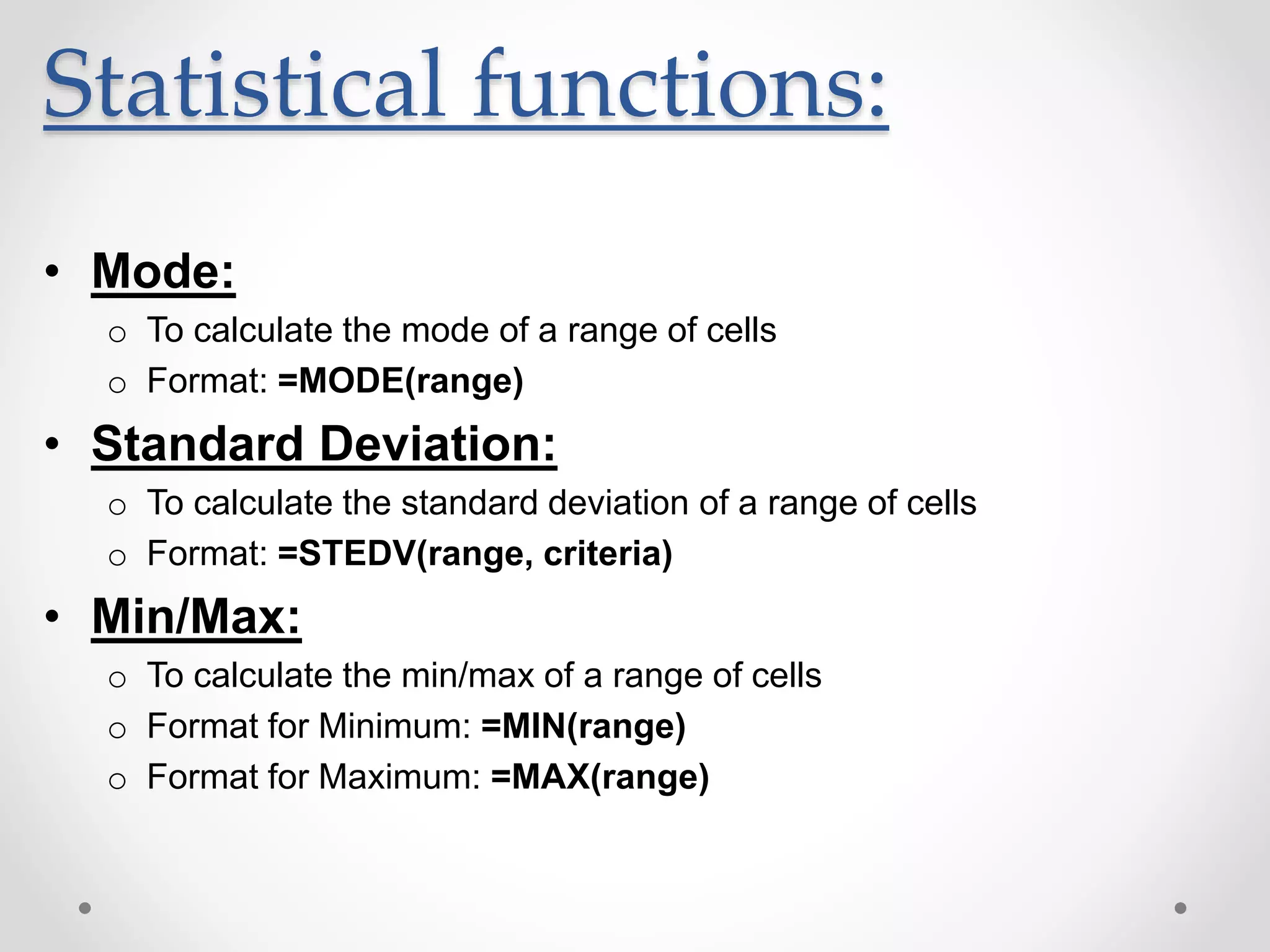
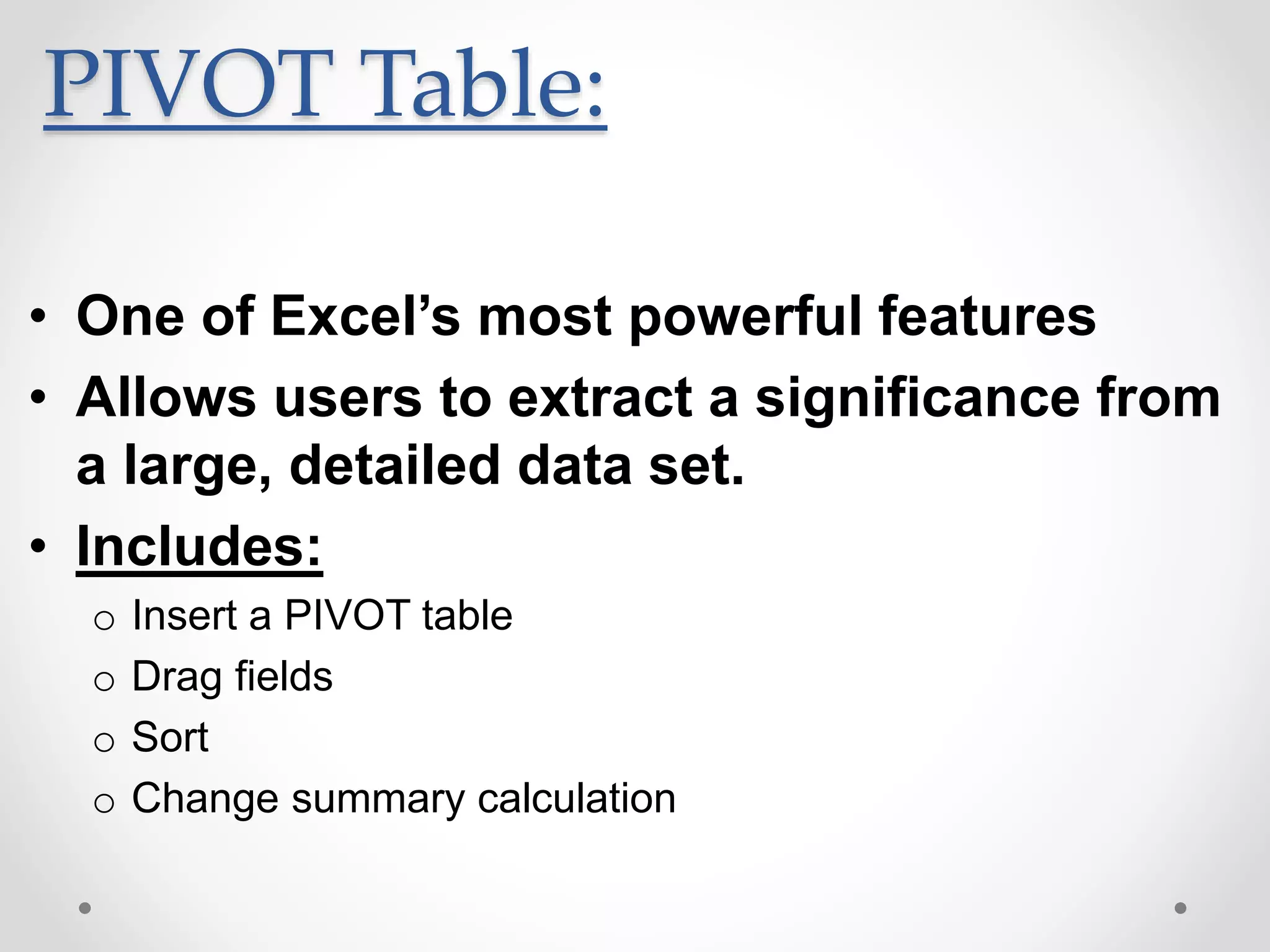
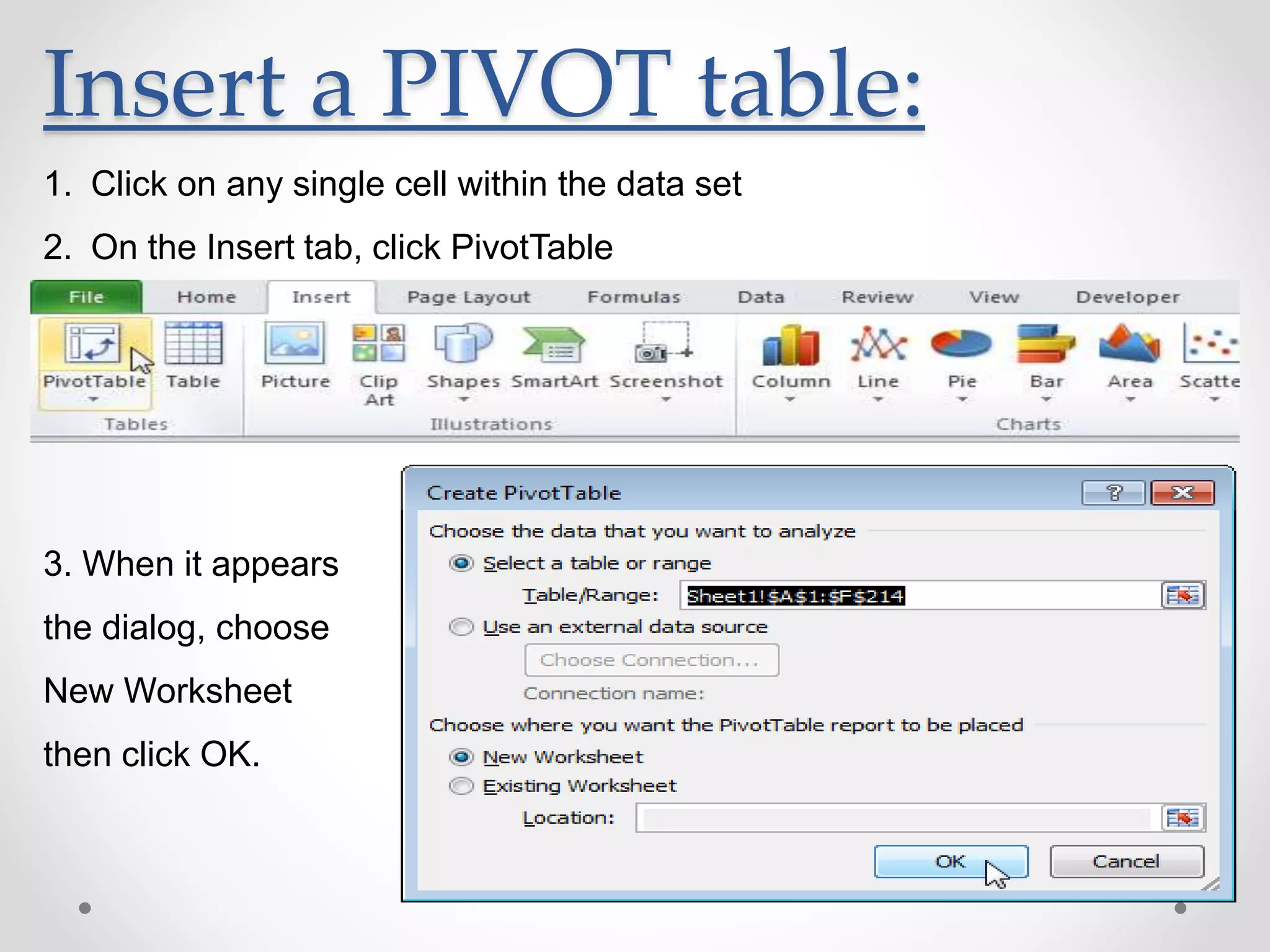
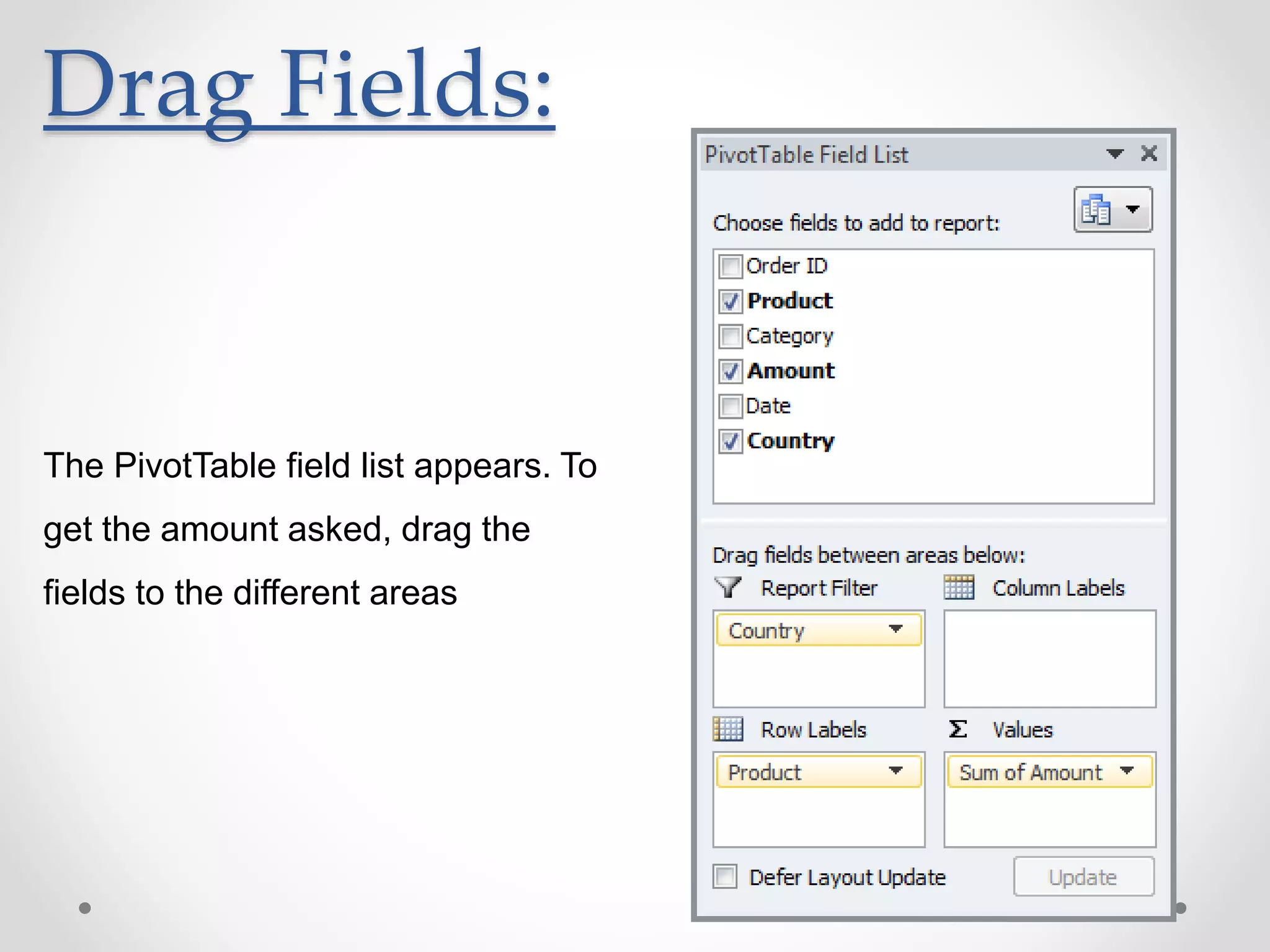
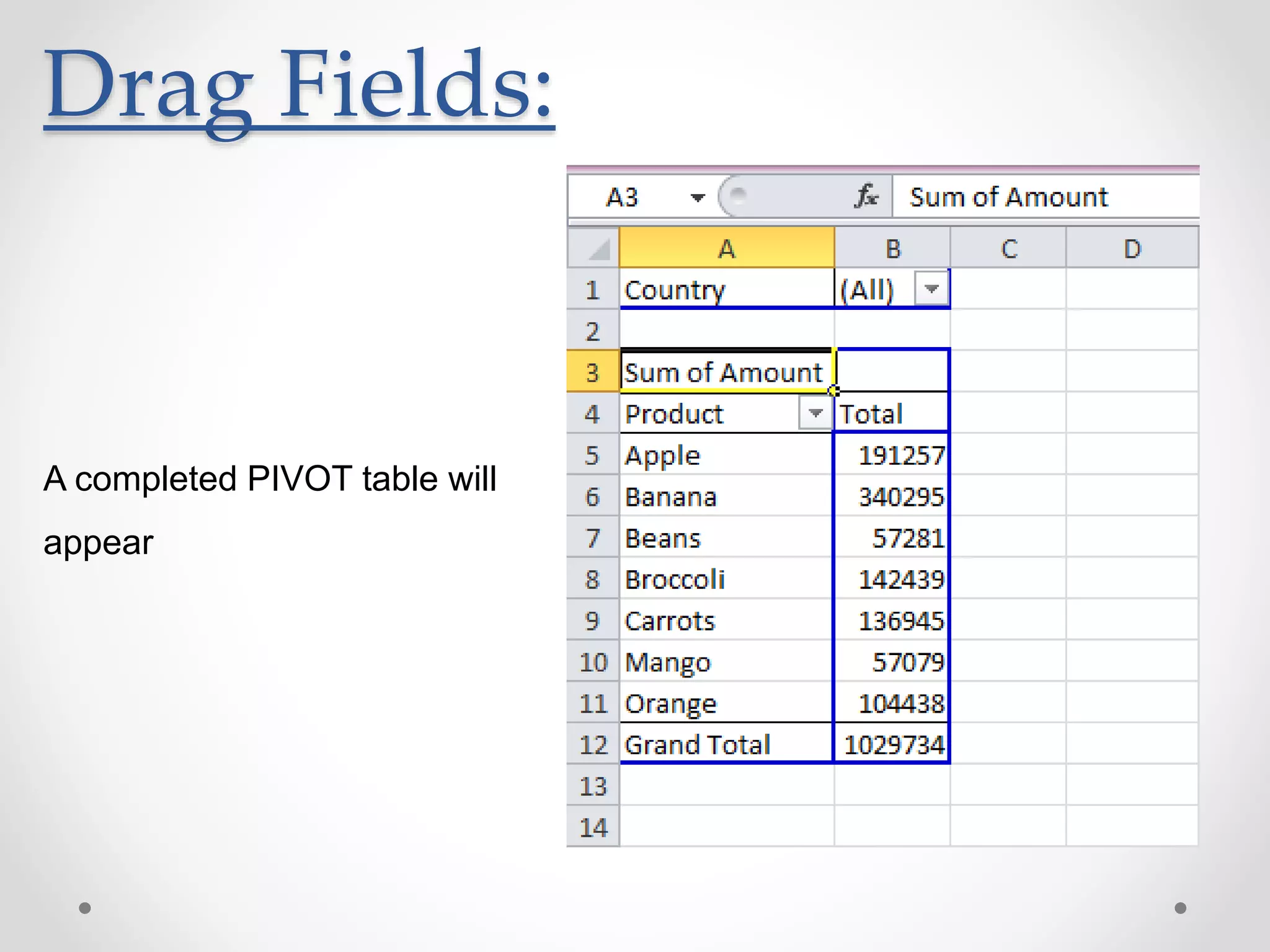
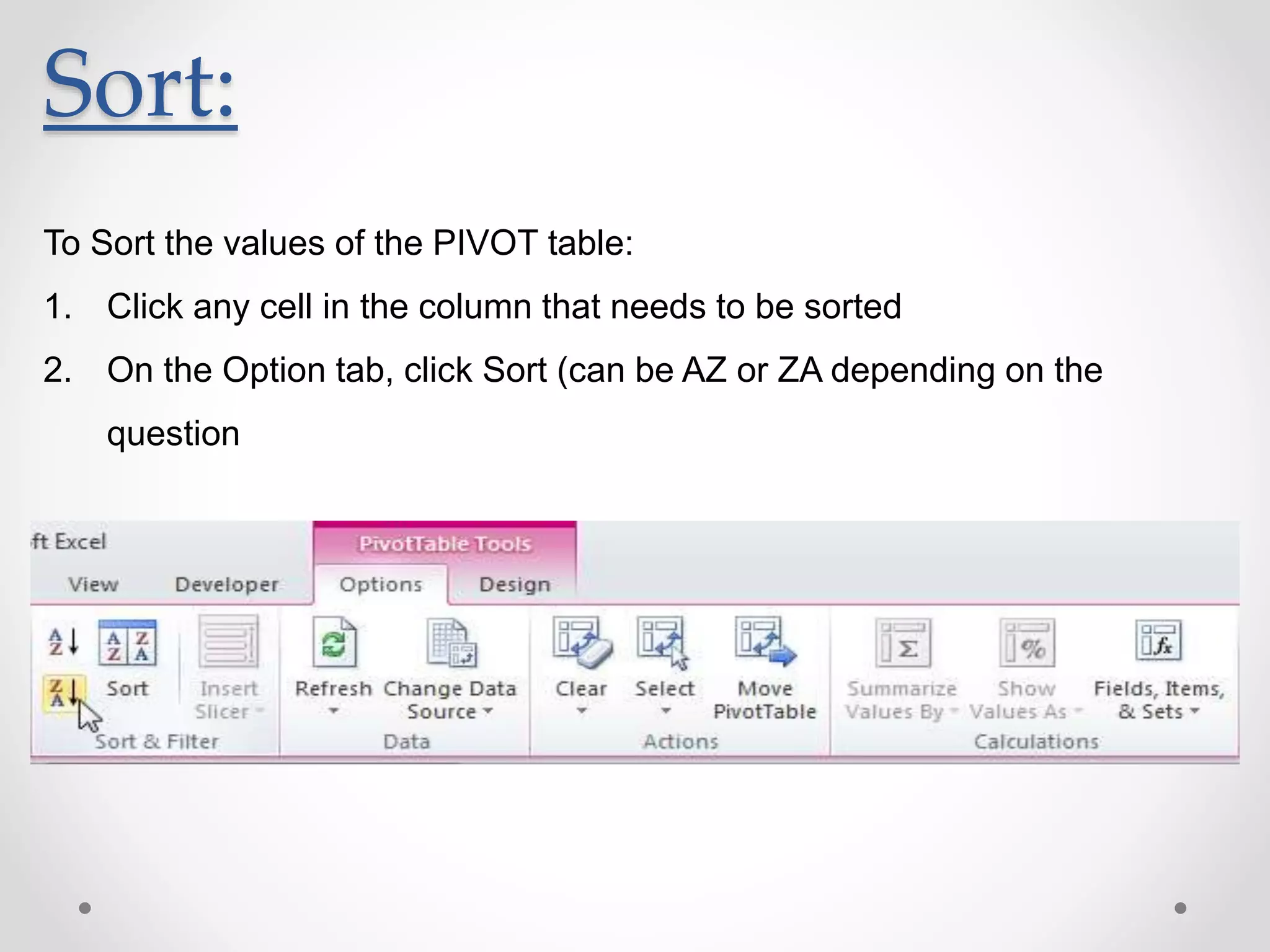
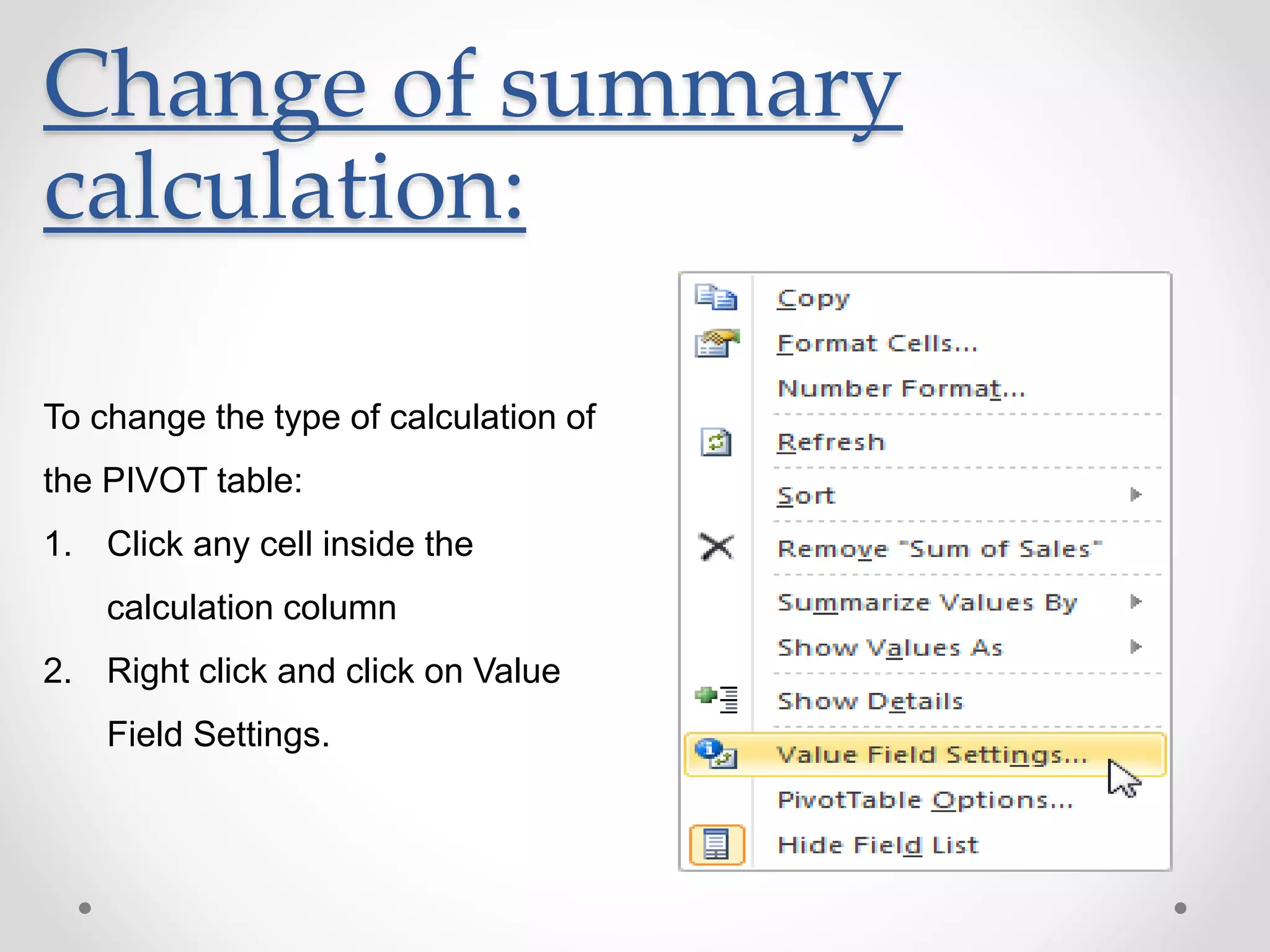
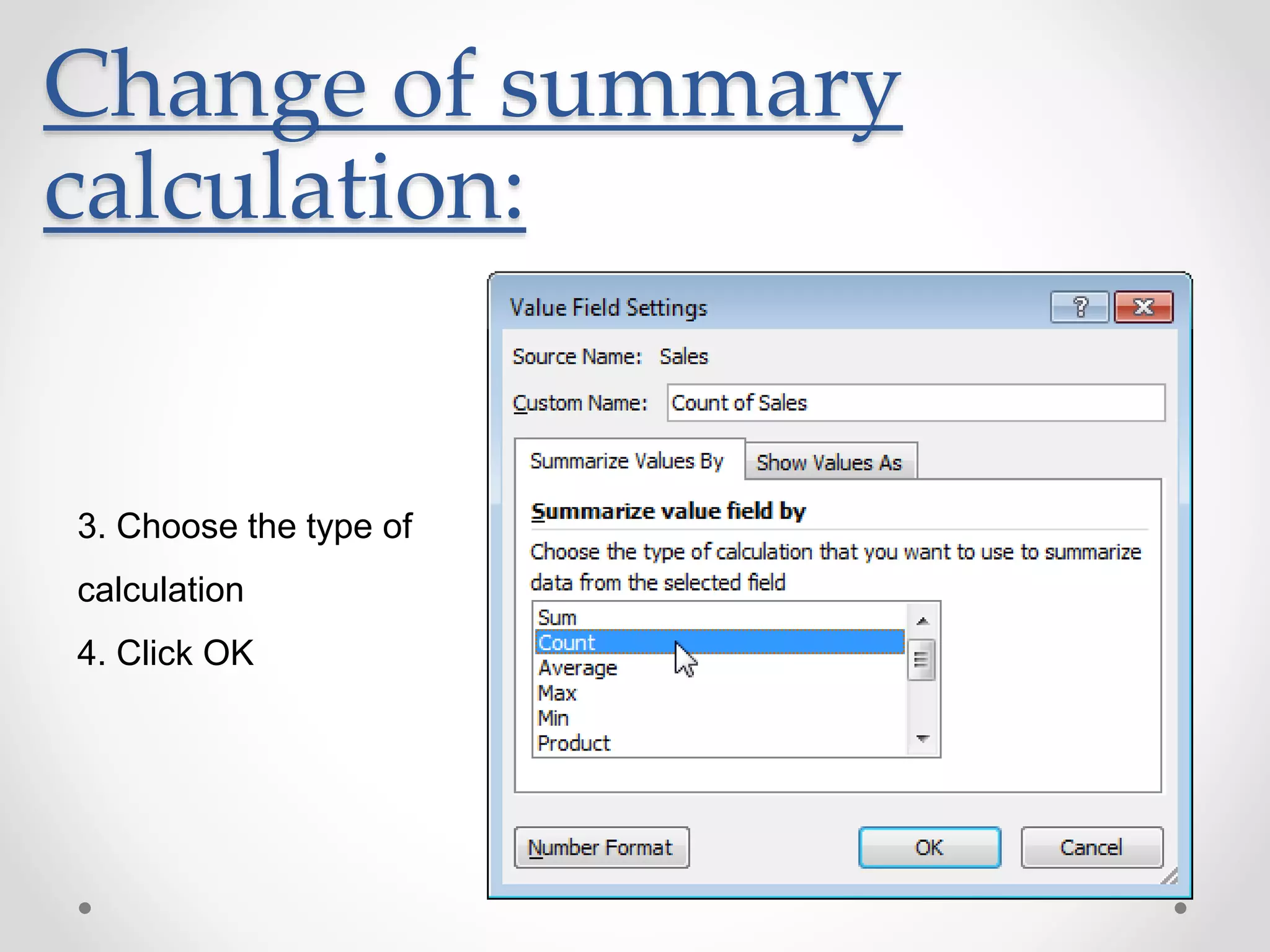
This document provides an overview of basic Microsoft Excel functions and features. It explains that Excel is commonly used in businesses for tasks like accounting, calculations, and reporting. The key components of an Excel spreadsheet include cells organized into rows and columns. The document then describes important basic functions for counting, summing, logic, lookups, statistics, and pivot tables. Examples are provided for how to use count, sum, if, lookup, average, and other functions. Pivot tables are highlighted as one of Excel's most powerful features for analyzing large datasets.