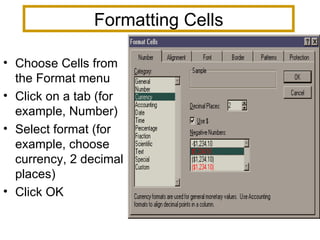
This document provides an introduction and overview of Microsoft Excel spreadsheets. It discusses the basic components and structure of a spreadsheet including workbooks, worksheets, rows, columns, and cells. It also describes how to enter different types of data into cells including text, numbers, formulas, and functions. The document provides instructions for common spreadsheet tasks like formatting cells, copying and filling cells, sorting data, creating charts and templates, and saving and printing worksheets.