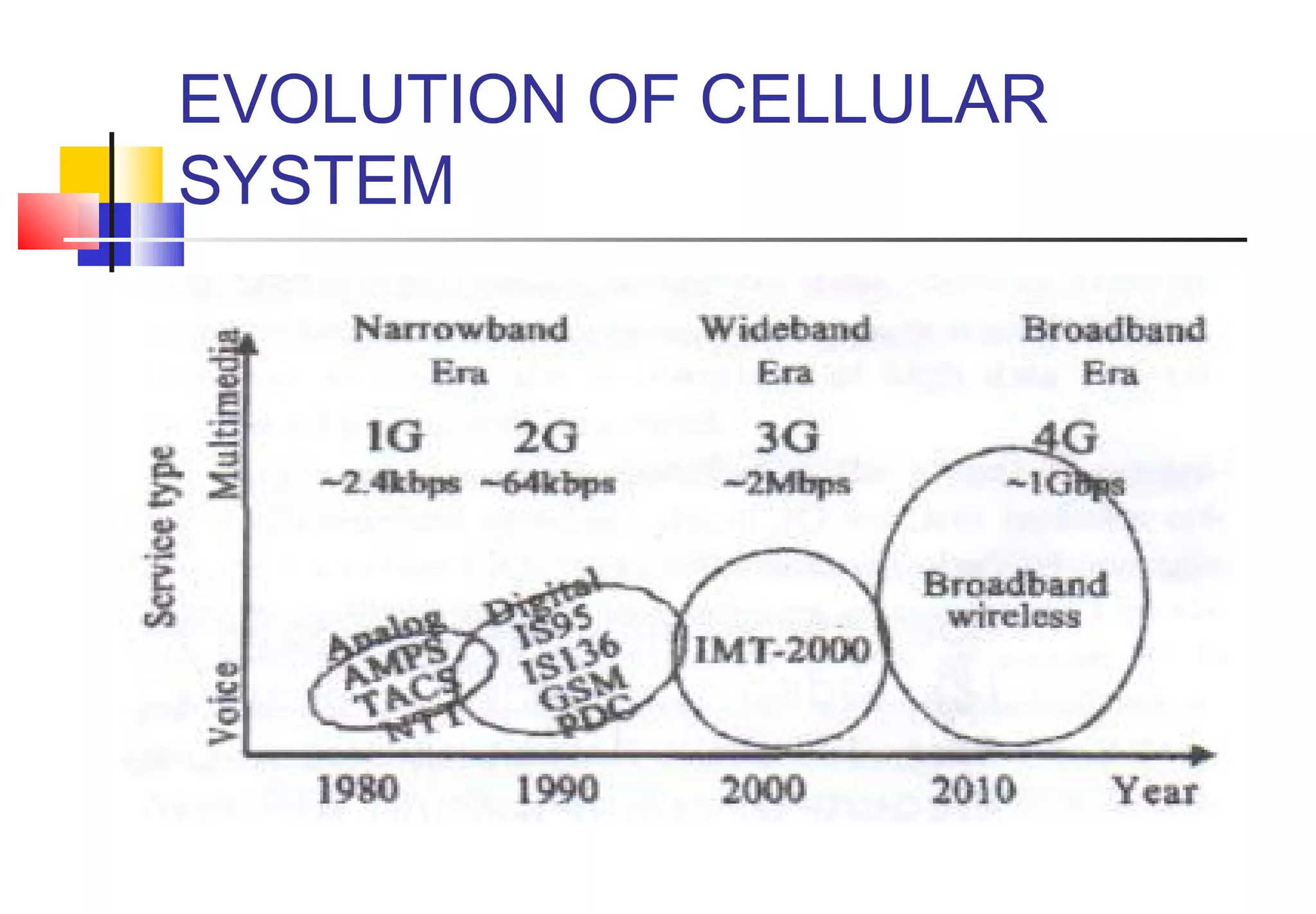
The document discusses the evolution of wireless communication networks from 1G to 5G. It introduces 1G as the first-generation analog cellular network allowing for voice calls. 2G brought digital networks for voice and low-speed data. 3G enabled higher data speeds for applications and internet access. 4G aims to provide broadband services globally at speeds up to 1Gbps. 5G is envisioned as the final wireless network with virtually unlimited bandwidth and true worldwide coverage.









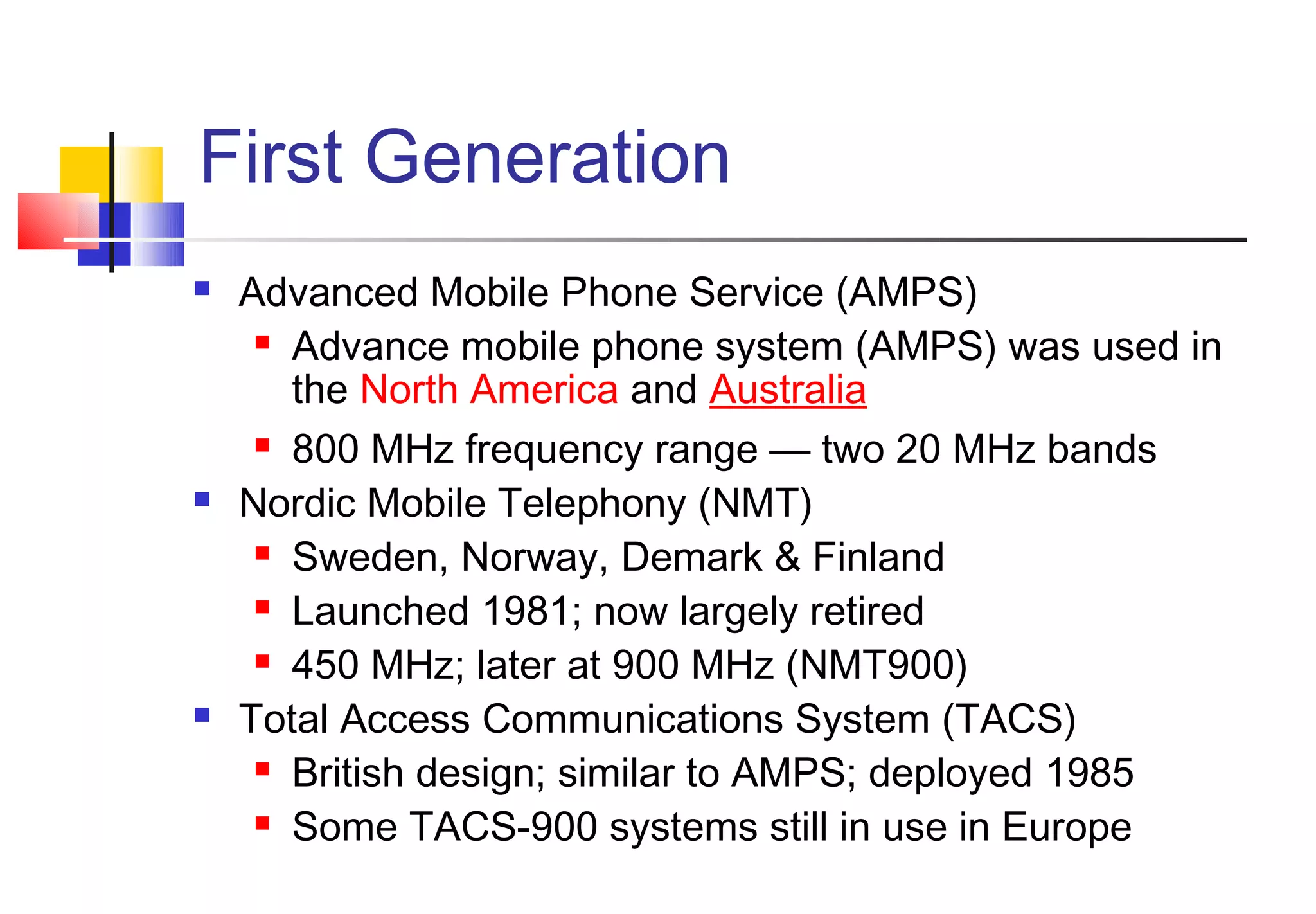





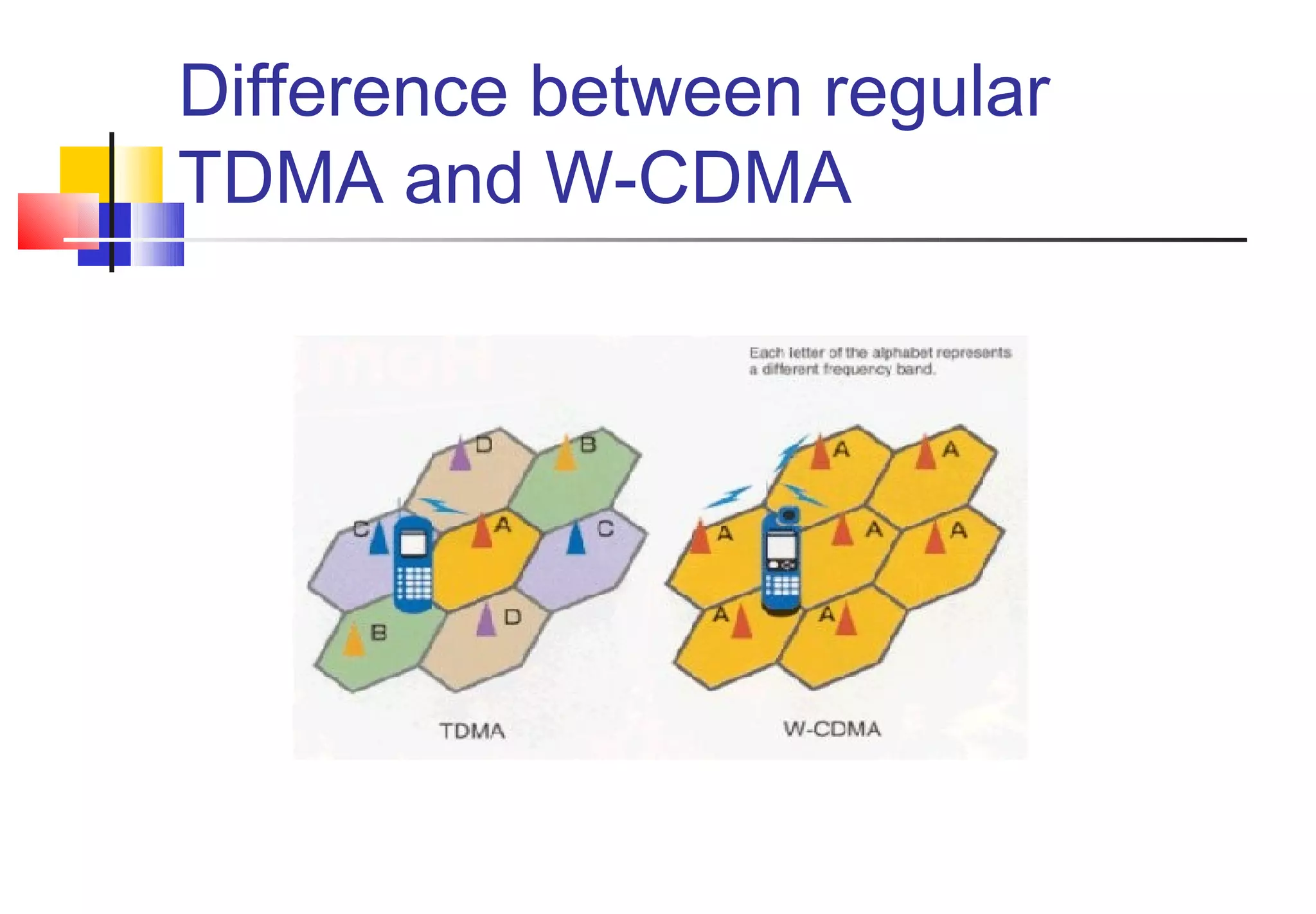
![4G WIRELESS SYSTEM
4G is a research item for next-generation wide-area
cellular radio, where you have 1G, 2G, 3G and then
4G [and 5G]
4G is a conceptual framework and a discussion point
to address future needs of a high speed wireless
network
It offer both cellular and broadband multimedia
services everywhere
Expected to emerged around 2012 - 2015](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/evolutionfrom1gto5g-120818113626-phpapp02/75/Evolution-from-1_g_to_5g-17-2048.jpg)