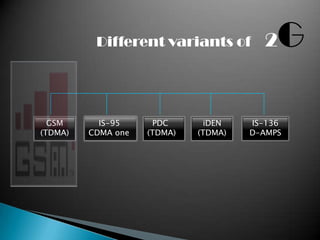
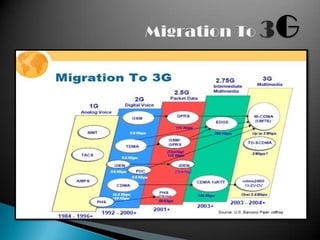
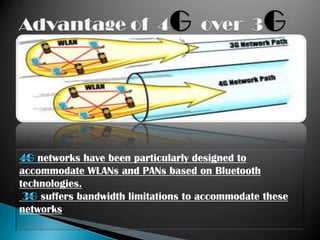
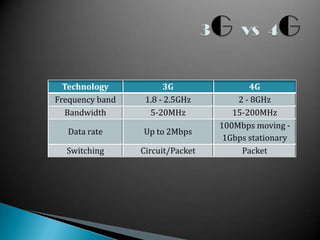
Mobile telephony has evolved through several generations from early 0G analog mobile radio systems to current 4G systems. The document traces this evolution from 1G analog cellular networks using FDMA in the 1980s with speeds around 10 kbps, to 2G digital cellular networks using TDMA and CDMA in the 1990s with speeds around 64-144kbps. 3G networks then provided higher speed multimedia access around 144kbps to 2Mbps in the early 2000s. 4G networks currently offer broadband speeds from 100Mbps to 1Gbps for more advanced applications.