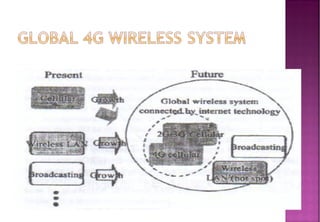
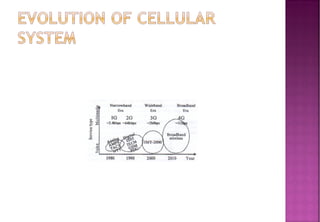
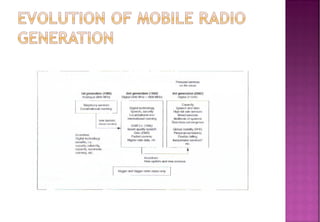
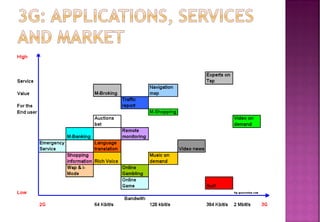
This document provides an overview of wireless communication networks and their evolution. It discusses 1G to 5G cellular networks, describing their key features and services. 1G allowed analog voice calls while 2G introduced digital networks. 3G enabled up to 2Mbps speeds for data, video calls and mobile internet. 4G aims to provide speeds up to 1Gbps for multimedia services anywhere. 5G is theoretical and would allow unrestricted global wireless connectivity. The document compares these generations and wireless is presented as an important infrastructure to efficiently connect dedicated systems from 2G to 4G networks.




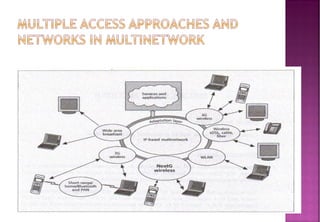













![ 4G is a research item for next-generation wide-area
cellular radio, where you have 1G, 2G, 3G and then
4G [and 5G]
4G is a conceptual framework and a discussion point
to address future needs of a high speed wireless
network
It offer both cellular and broadband multimedia
services everywhere
Expected to emerged around 2010 - 2015](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/evolutionfrom3gto4gandbeyond5g-140408031654-phpapp01/85/Evolution-from-3_g_to_4g_and_beyond_5g-22-320.jpg)