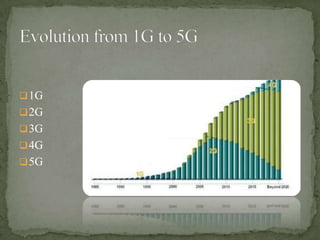
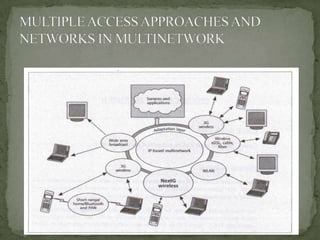
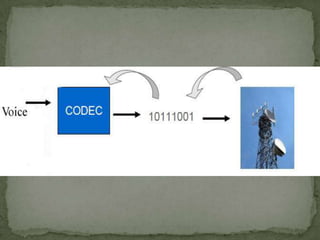
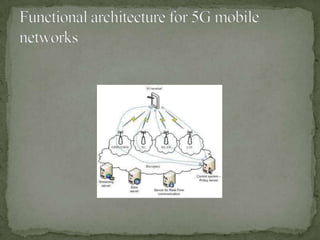
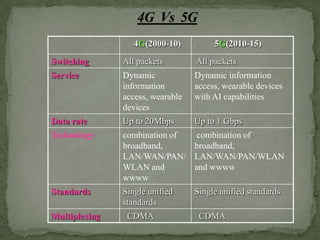
5G wireless technology will offer faster speeds up to 1 Gbps, lower latency, and better connectivity. It will allow for a unified global standard for wireless communication with almost no limitations. 5G will use technologies like UWB, smart antennas, and CDMA to provide higher bandwidth and more capacity than 4G. It aims to enable dynamic information access through wearable devices with artificial intelligence capabilities as part of a pervasive global network.