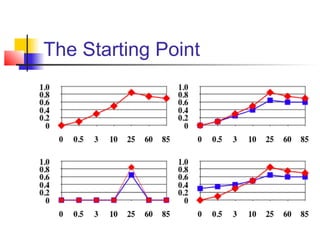
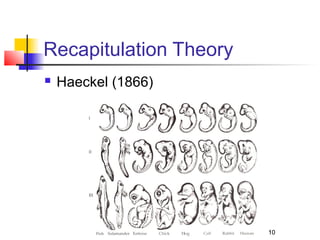
This document provides an overview of developmental psychology and some of its key concepts and theorists. It defines developmental psychology as the scientific study of behavioral changes as an organism grows and interacts with its environment. Some important themes discussed are the interaction between biological and environmental influences on development, and the active role children play in shaping their own development. Early influential theorists mentioned include Darwin, Freud, Piaget, Erikson, and Vygotsky. Their various stage theories and approaches, such as psychosexual development and sociocultural influences, contributed to understanding of child development.