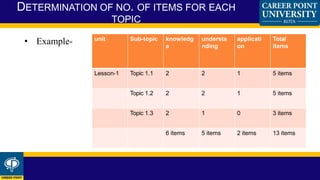
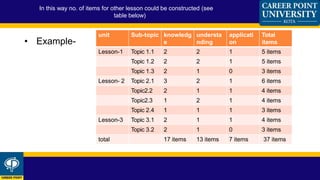
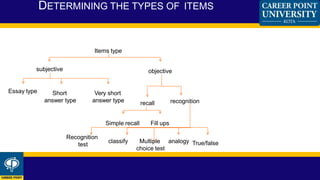
A blueprint provides a detailed plan or outline that can be used as a guide. In education, a blueprint outlines the test specification and examination strategy of an institution. It specifies the elements of performance being assessed and how items will be selected based on their importance. A blueprint is generally in a tabular format and divides the content into topics, assigning a number of test questions to each. This provides a framework for developing items that assess important concepts and skills while satisfying educational objectives. Blueprints benefit students and teachers by providing feedback on progress, determining if learning objectives were attained, and ensuring the reliability and validity of examinations.