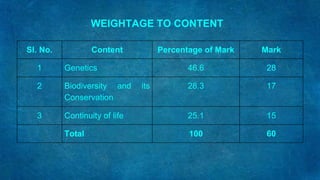
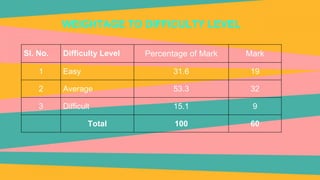
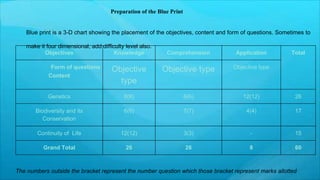
This document outlines the process for developing and validating an achievement test in biology. It discusses planning the test by selecting topics, writing questions at different cognitive levels, and constructing a blueprint. Items are developed and analyzed based on difficulty index and discriminating power. A scoring key is prepared and the draft test is administered to a sample. The final test is selected based on item analysis results and validated for content, criterion, and construct validity as well as reliability.