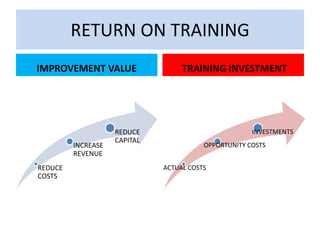
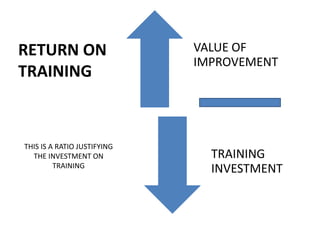
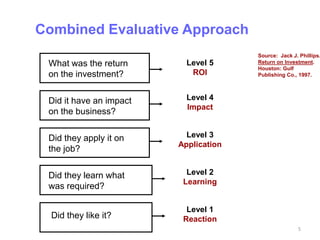
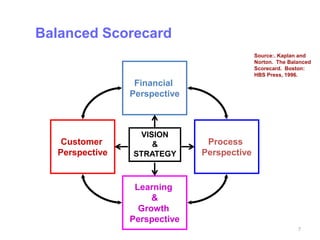
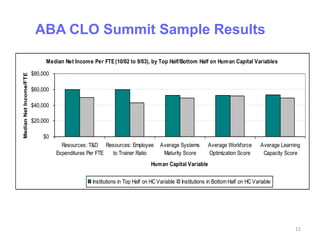
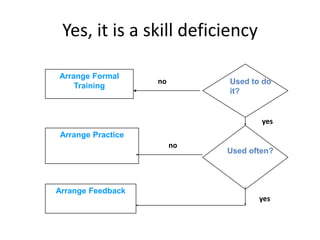
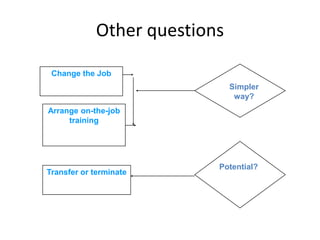
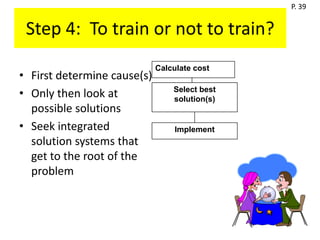
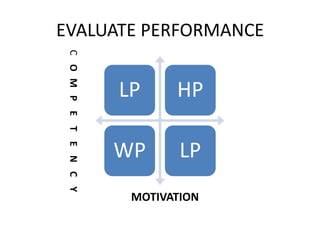
The document discusses conducting a training needs analysis to identify critical performance gaps, determine their causes, evaluate potential solutions like training, and calculate the projected return on investment to justify training investments before implementation. The goal is to improve work performance by addressing skill or knowledge deficiencies through appropriate and cost-effective training interventions.