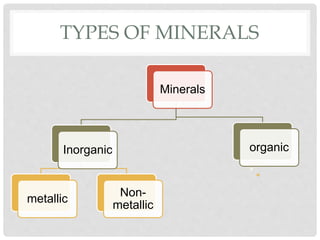
Minerals are naturally occurring inorganic substances that are formed through geological processes within the Earth. Some key points:
- Minerals can be metallic or non-metallic, and include substances like salt, copper, gold, and coal.
- They are extracted through mining and are important natural resources. India has potential for further exploration and mining of its mineral wealth.
- Conservation of minerals is important as they are non-renewable resources, and their use must be balanced to avoid depletion and ensure availability for future generations.