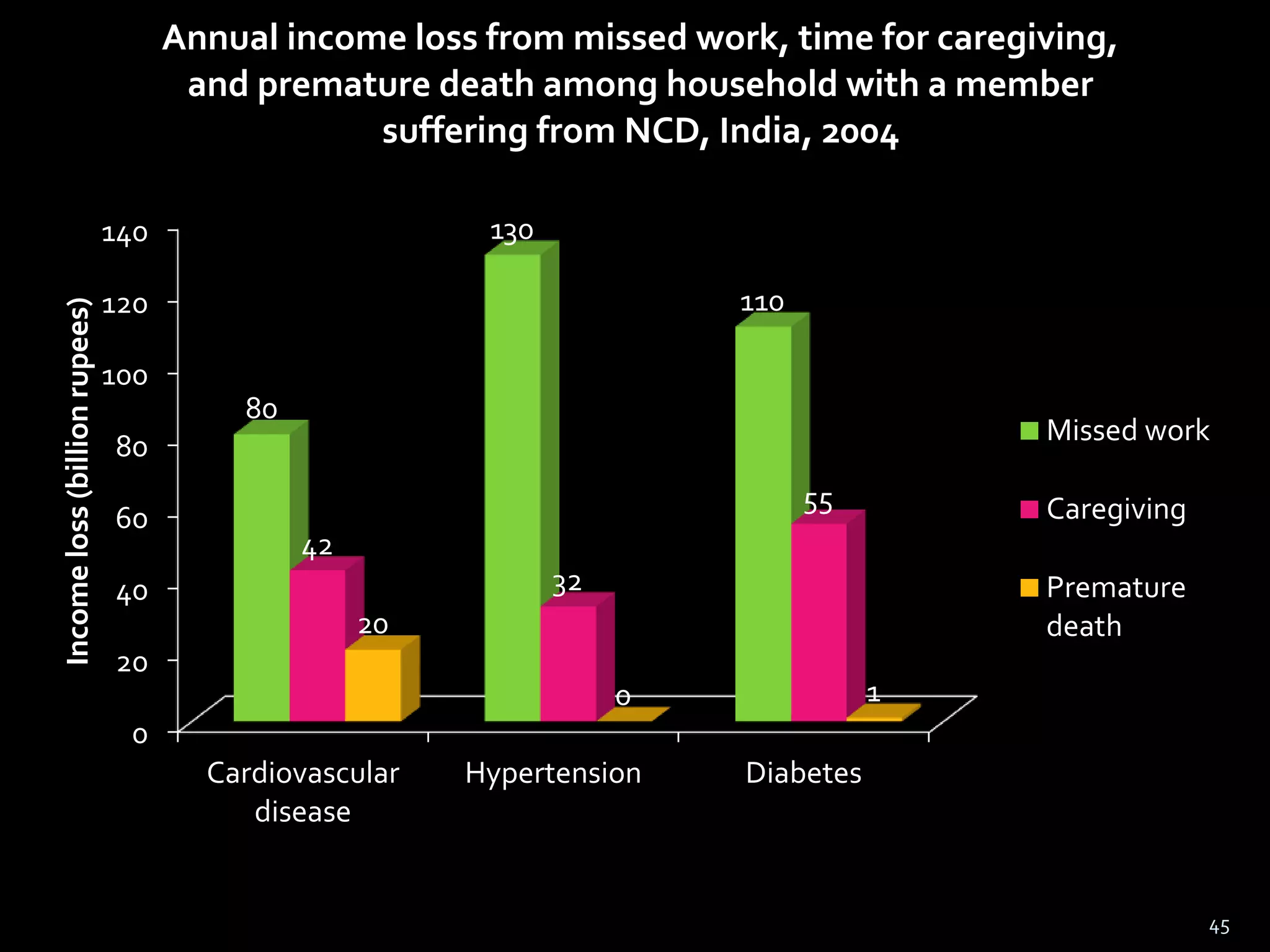
1) The document discusses the rising burden of cardiovascular disease (CVD) in India, highlighting that it is occurring a decade earlier and is a leading cause of death under 70 years of age.
2) It presents data on the traditional risk factors for CVD in India, such as high rates of hypertension, diabetes, tobacco use, physical inactivity, and air pollution. These risk factors are occurring at younger ages.
3) The National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, CVDs and Stroke (NPCDCS) aims to prevent and control non-communicable diseases through screening, early diagnosis, and management across primary healthcare centers and district hospitals in India.