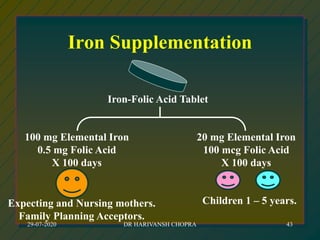
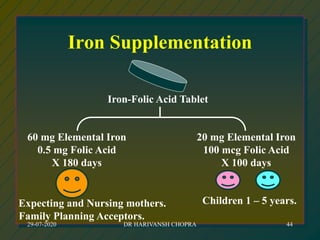
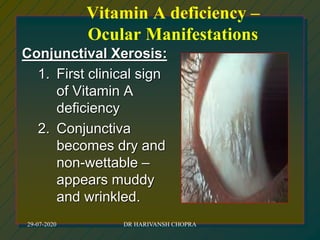
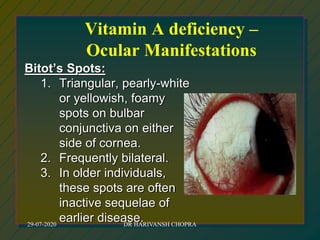
The document outlines various national nutrition programs in India aimed at addressing nutritional deficiencies, including the Integrated Child Development Scheme (ICDS), Balwadi Nutrition Program, and Mid-Day Meal Scheme. It discusses the objectives, beneficiaries, nutritional allowances, and implementation strategies for each program, focusing on improving the nutritional status of children and mothers. Specific programs target issues like anemia, blindness due to vitamin A deficiency, and iodine deficiency, detailing the nutritional interventions and health education measures provided.