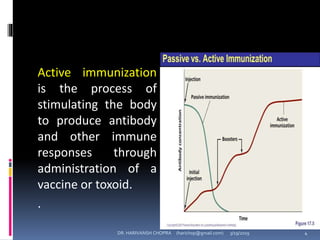
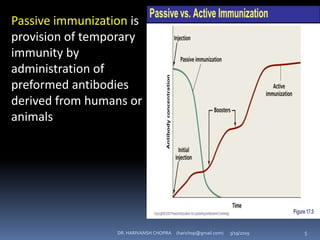
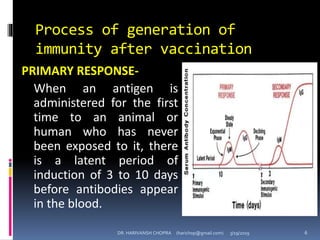
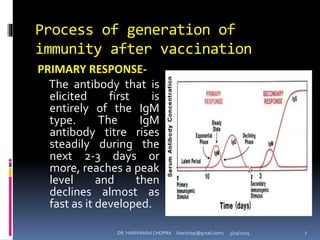
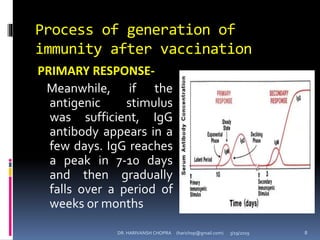
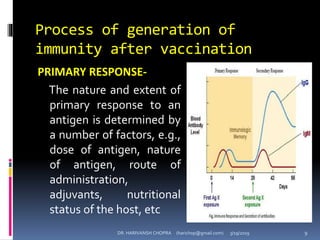
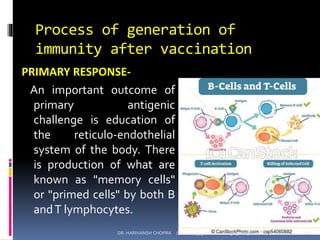
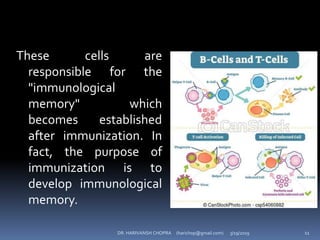
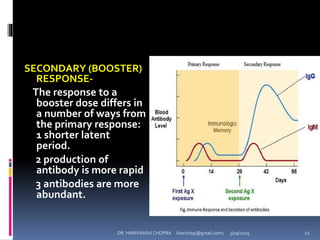
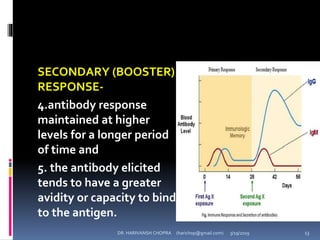
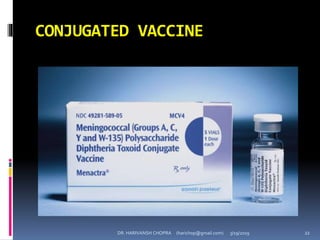
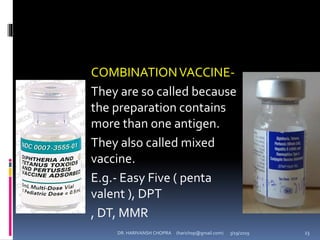
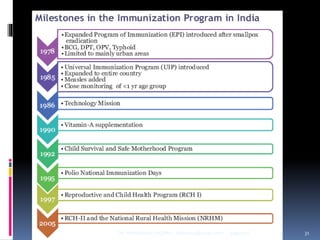
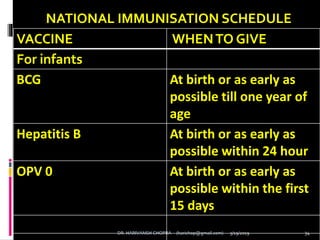
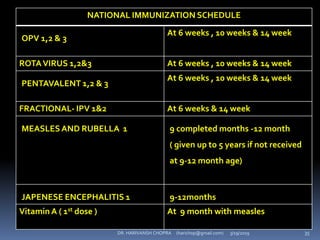
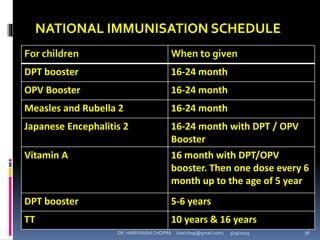
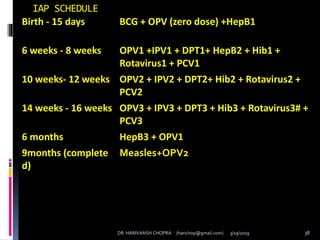
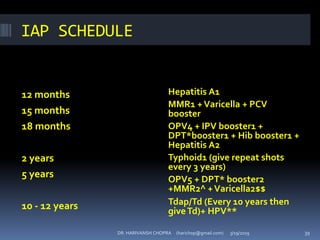
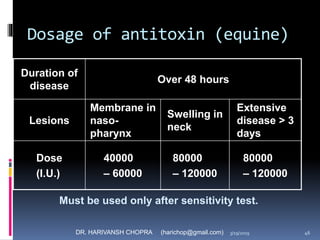
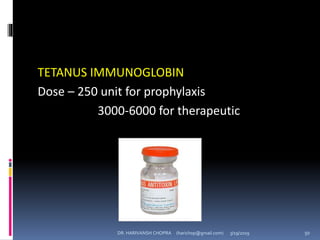
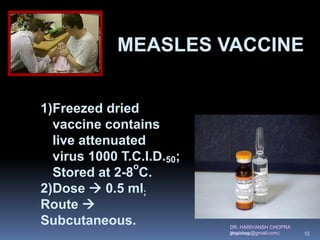
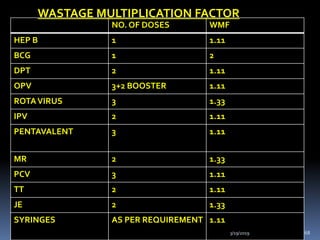
The document provides a comprehensive overview of immunization, including definitions, types of vaccines, historical milestones, and schedules for administering vaccines to infants and pregnant women. It discusses the concepts of active and passive immunization, the processes of generating immunity, and the importance of immunological memory. Additionally, it outlines key vaccination programs, specifically the Expanded Program on Immunization and the Universal Immunization Programme in India.