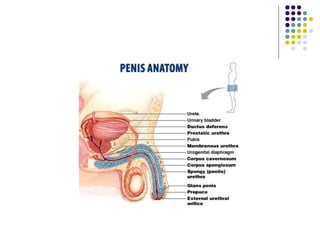
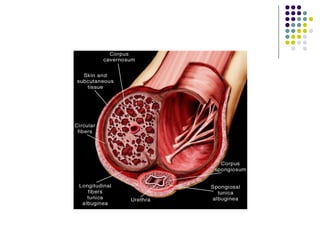
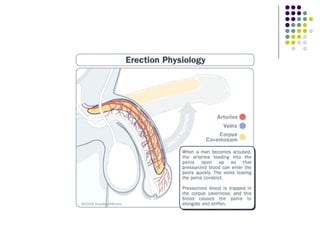
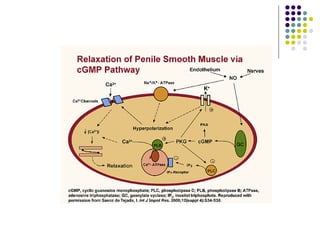
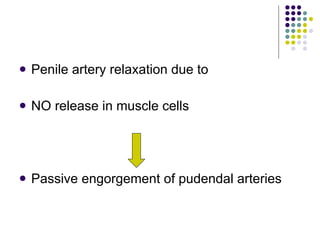
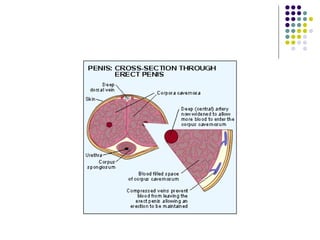
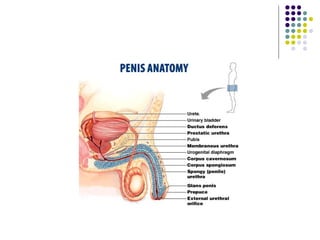
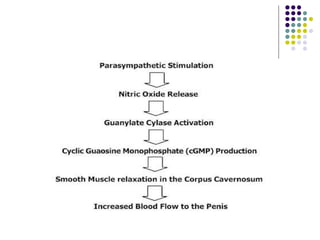
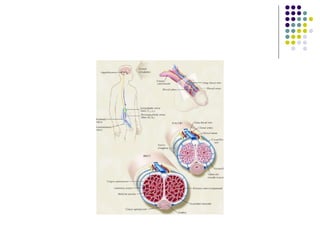
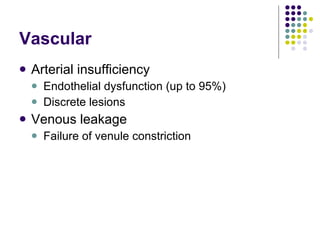
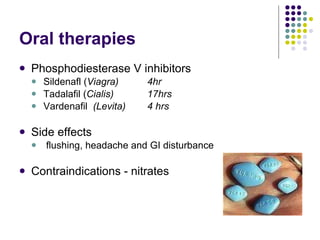
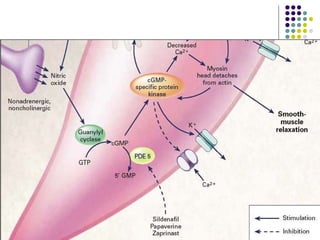
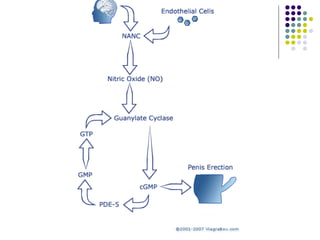
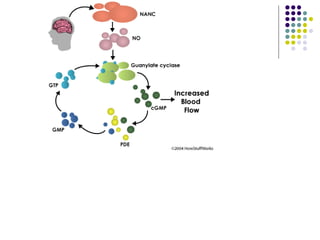
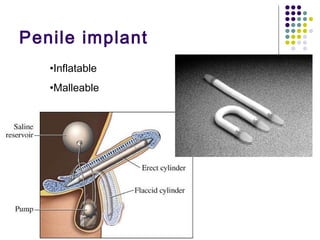
Erectile dysfunction is a growing problem that affects over 150 million men worldwide. It is caused by various vascular, neurological, endocrine, psychological, and pharmacological factors that can impair blood flow or nerve signaling in the penis. Common medical treatments include phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors like sildenafil (Viagra), which help maintain blood flow; penile injections; vacuum devices; testosterone replacement therapy; and penile implants. Counseling may also help address psychological aspects.