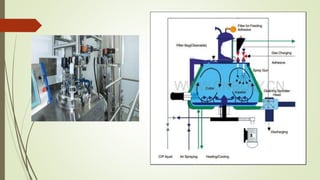
This document discusses different types of granulation methods used in pharmaceutical manufacturing. It describes wet granulation in detail, including the steps involved and various equipment used like high speed mixer granulators, high shear granulators, fluidized bed granulators, spray drier granulators, and spheronizers. For each type of equipment, it provides information on construction, working, and advantages and disadvantages. The overall document serves as an introduction to common granulation methods and equipment.