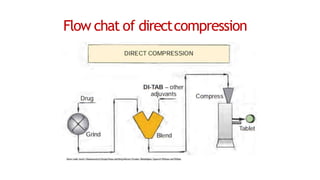
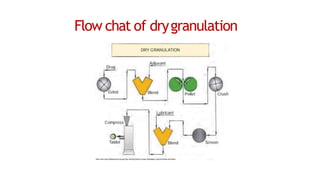
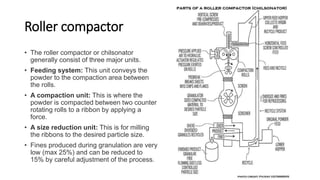
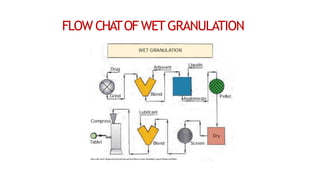
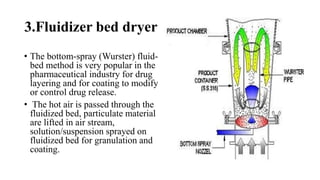
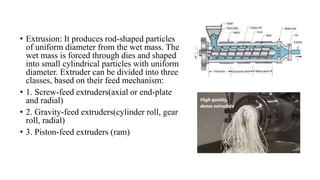
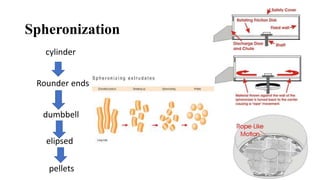
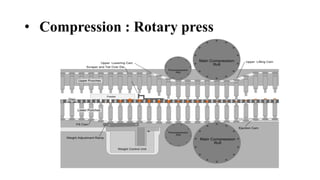
The document discusses the key equipment and processes used in tablet production, including size reduction equipment, mixers, granulators, dryers, tablet presses, and quality control equipment. It describes the main methods of tablet formulation as direct compression, dry granulation, and wet granulation. For wet granulation specifically, it outlines the steps of milling, weighing, mixing, wet massing using high-shear or fluid-bed granulators, drying granules, screening, lubricating, and compressing into tablets.