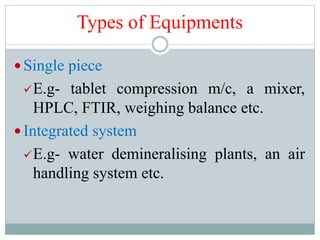
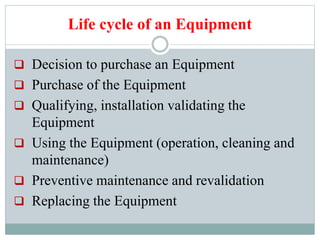
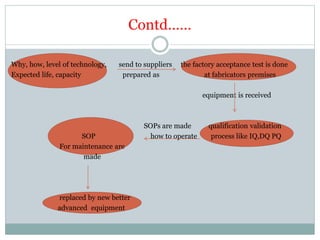
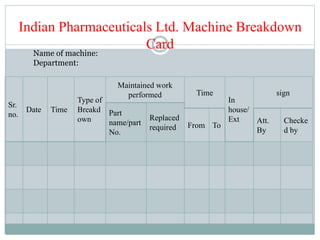
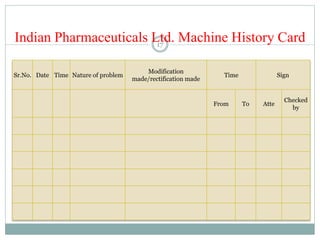
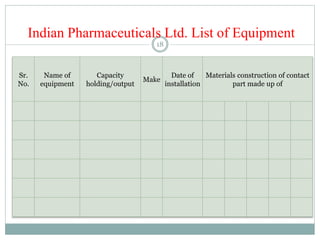
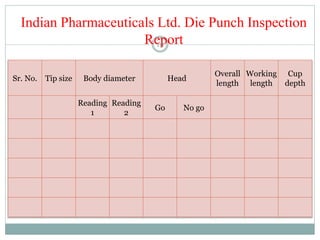
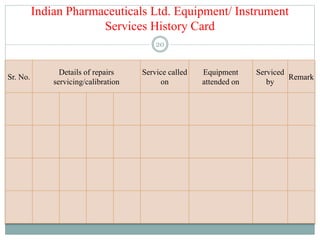
The document discusses the types, management, and maintenance of equipment in pharmaceutical plants according to international GMP standards. It covers aspects such as equipment life cycles, installation, cleaning, qualification, and the importance of proper labeling to minimize contamination risks. Additionally, it outlines guidelines for the operation and maintenance of equipment like weighing balances and filtration systems.