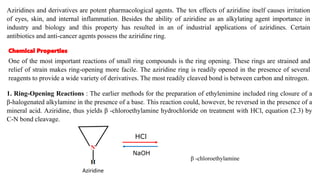
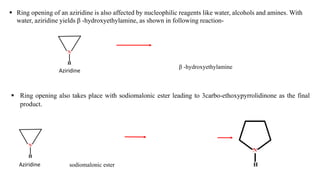
Aziridines are three-membered heterocyclic compounds containing two carbon and one nitrogen atom, noted for their pharmacological properties and industrial applications. The document discusses various nucleophilic ring-opening reactions of aziridines, which occur under various conditions and lead to diverse derivatives due to the strained nature of the ring. Key reactions and mechanisms are highlighted, including acid-induced and nucleophile-mediated ring openings, revealing the complex behavior of aziridines in chemical syntheses.