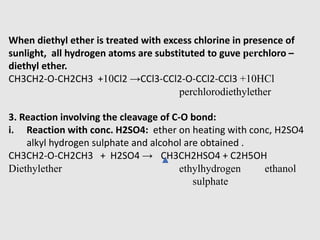
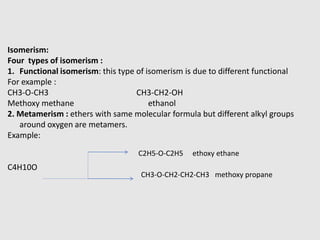
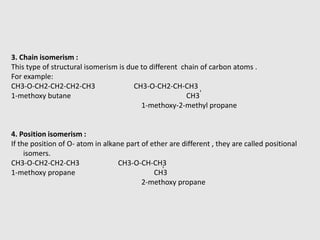
1. Ethers are organic compounds having an -O- functional group where the oxygen atom is bonded to two alkyl or aryl groups. Common examples include dimethyl ether, diethyl ether, and methyl phenyl ether.
2. Ethers have lower boiling points than analogous alcohols due to an inability to form hydrogen bonds between molecules. They are generally inert but can form oxonium salts with acids or decompose to alcohols and alkyl halides with halogen acids.
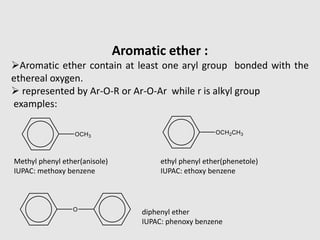
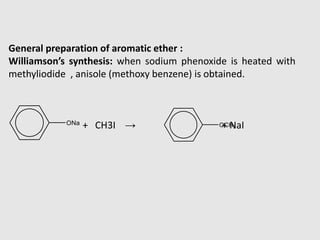
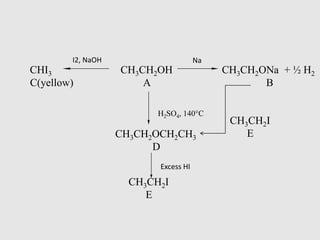
3. Aromatic ethers contain an aryl group bonded to the ethereal oxygen. An example of preparation is the Williamson synthesis of anisole from sodium phenoxide and methyl iodide.








![CH3CH2-OCH2CH3 + HCl →
]
[
+
Cl -
Oxonium salts are stable at low temperature in strongly acidic
solution . On dilution with water oxonium salts dissociated to give
ether and acid.
CH3CH2-OCH2CH3 + HCl
+
Cl -
]
[ →
H2O](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ether-6087-240123131522-eb04b31b/85/ETHER-6087-pptx-12-320.jpg)