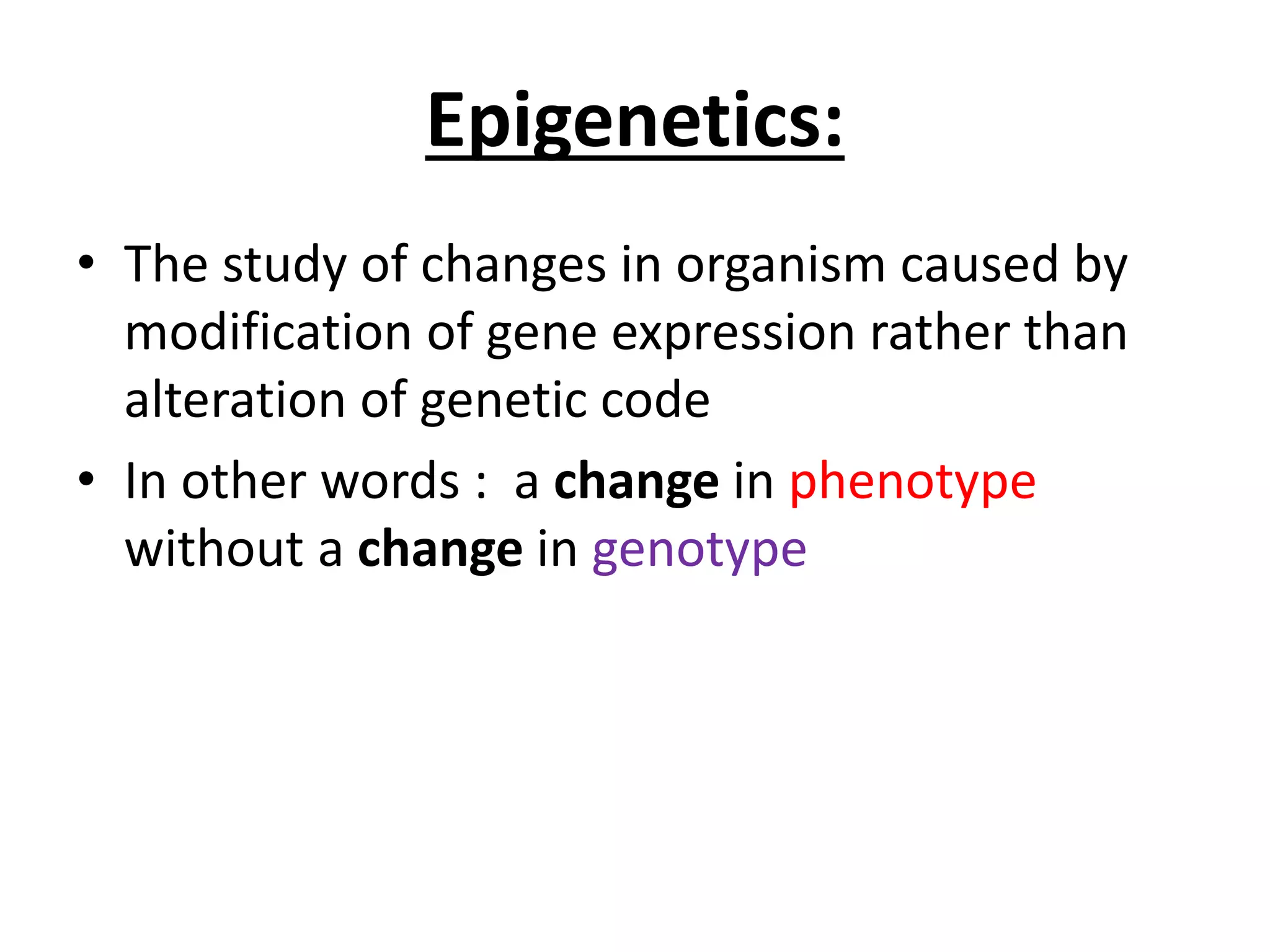
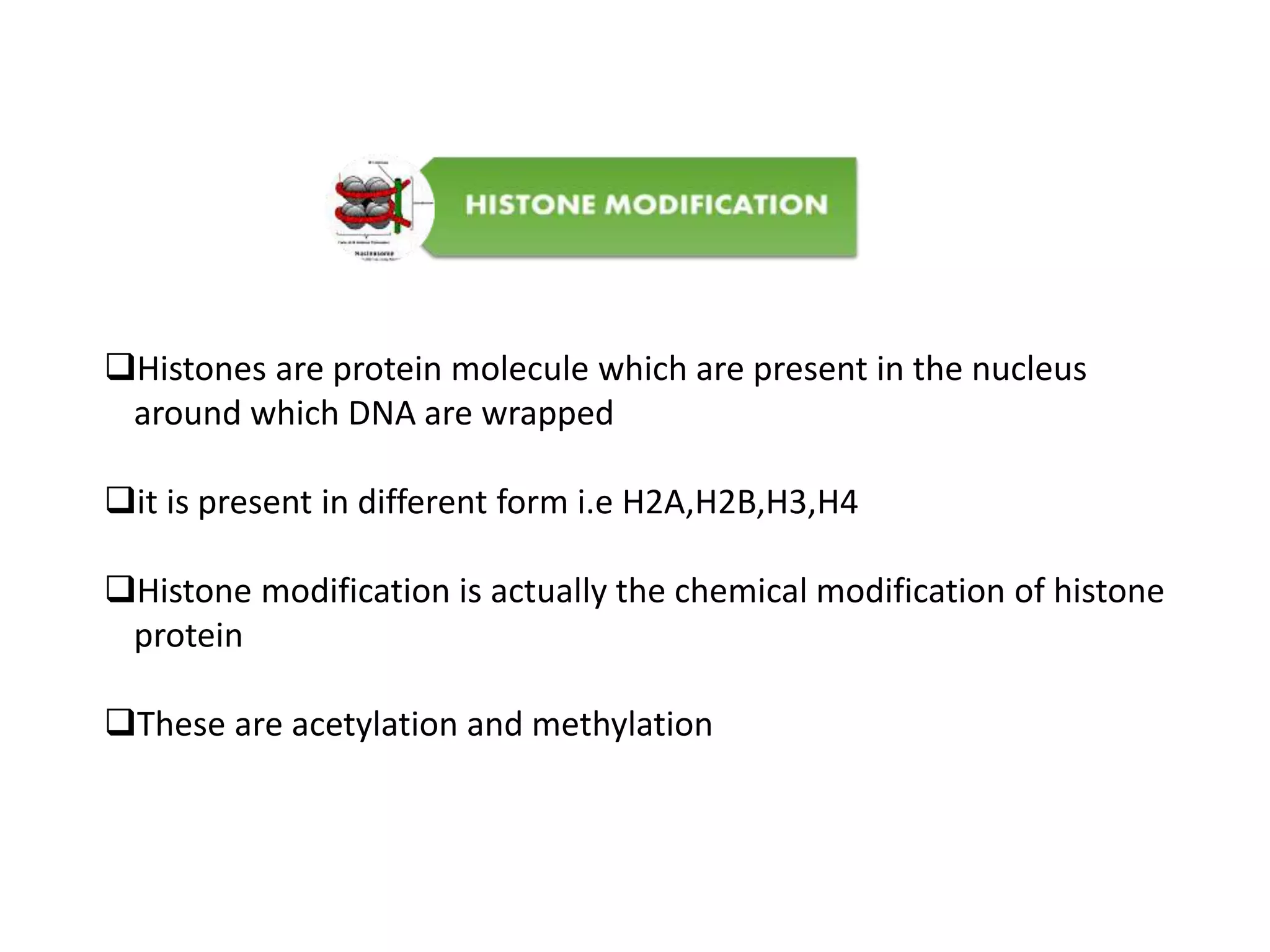
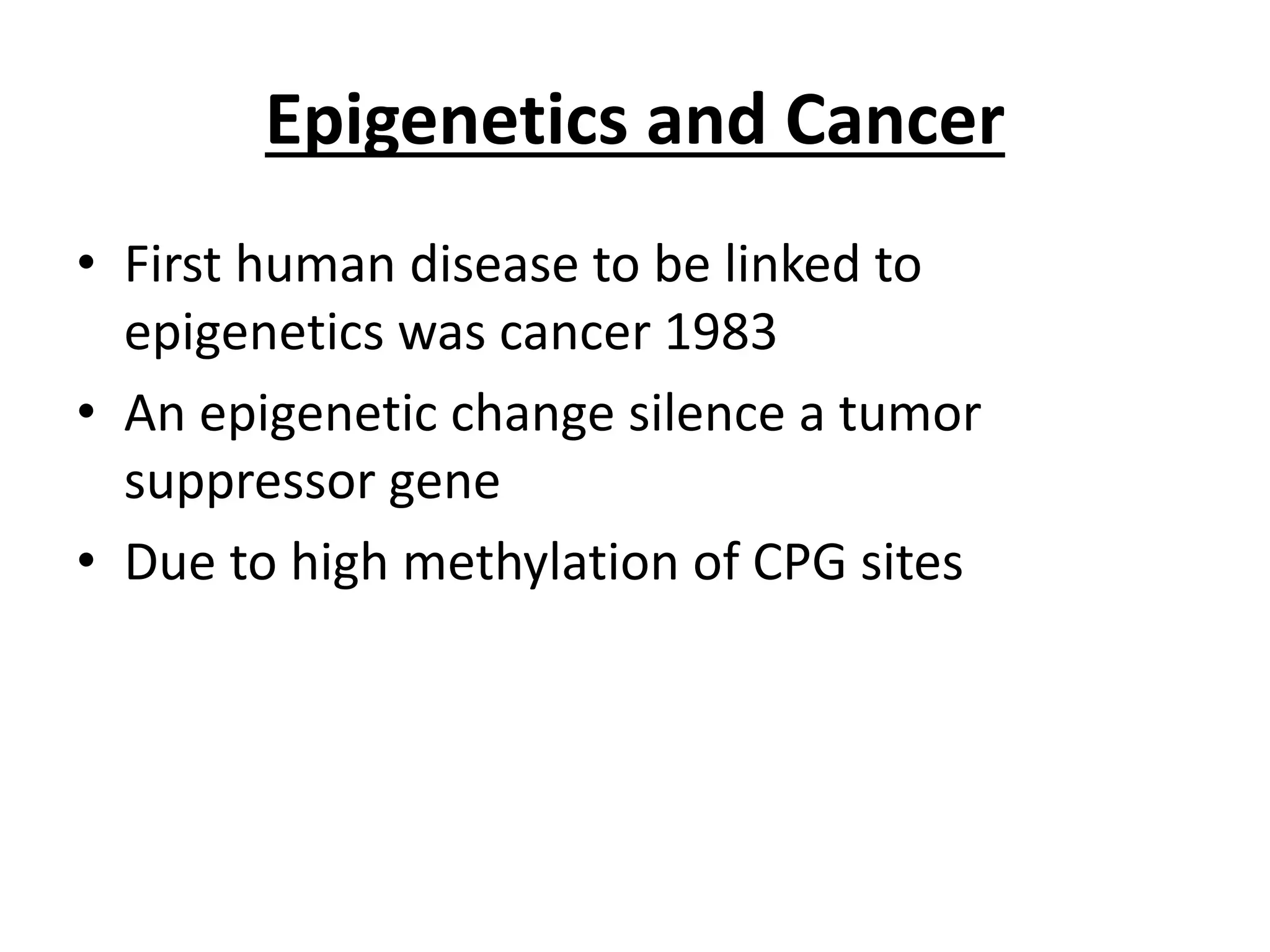
Epigenetics is the study of changes in organisms caused by gene expression rather than changes in genetic code. Epigenetics refers to mechanisms such as DNA methylation and histone modification that control gene expression without altering the underlying DNA sequence. These epigenetic changes can be caused by environmental interactions and can affect phenotypes. Examples of diseases linked to epigenetics include cancer, mental retardation, and cardiovascular disease.