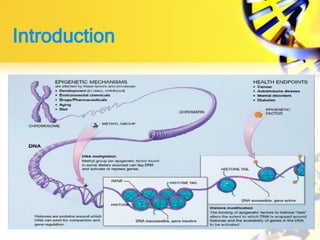
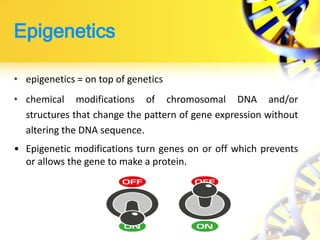
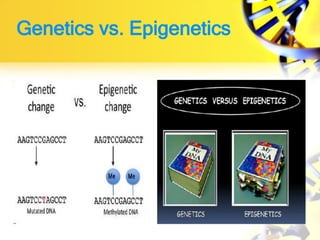
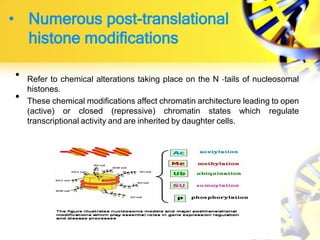
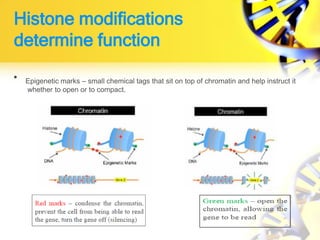
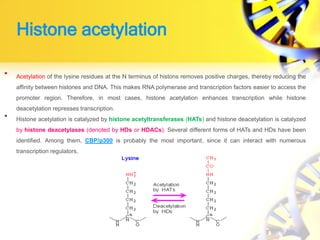
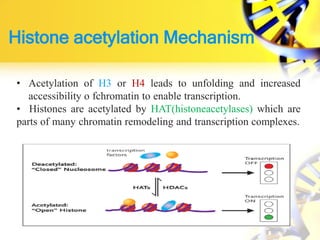
Epigenetics refers to chemical modifications of DNA and histones that regulate gene expression without altering the underlying DNA sequence. There are several key epigenetic mechanisms:
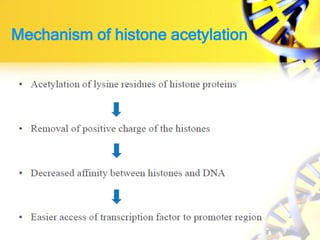
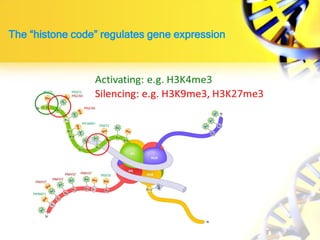
1. Histone modifications such as acetylation and methylation can open or close chromatin and thereby activate or repress genes.
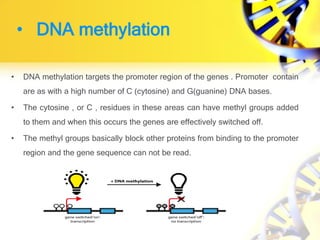
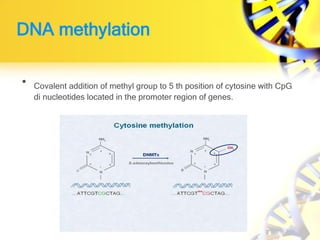
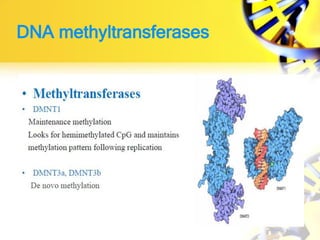
2. DNA methylation involves adding methyl groups to cytosine bases in CpG islands in gene promoters, repressing gene expression.
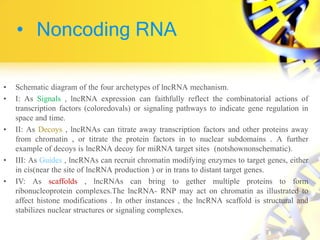
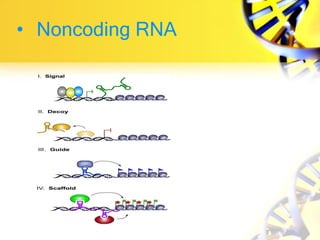
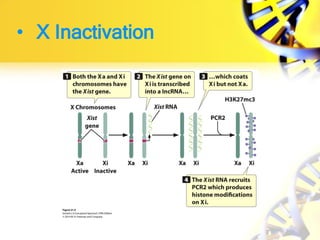
3. Non-coding RNAs can regulate genes as signals, decoys, guides, or scaffolds.
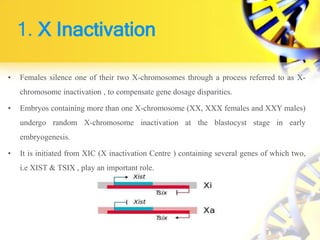
Epigenetic modifications are important for normal development and can be influenced by environmental factors. They regulate processes like X-chromosome inactivation and genomic imprinting, where genes are expressed based