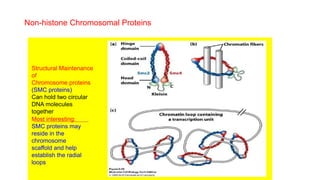
This document summarizes a presentation on non-histone proteins. It defines non-histone proteins as those that remain bound to DNA after histones are removed. Non-histone proteins play important structural and regulatory roles in chromatin organization and chromosome compaction. There are hundreds of types of non-histone proteins that function in DNA replication, transcription, and chromosome segregation. Examples provided include scaffold proteins, heterochromatin protein 1, DNA polymerase, and polycomb proteins. The main roles of non-histone proteins are compacting chromatin into chromosomes and organizing chromosome structure within the nucleus.









![Reference:
• Woodcock, C.L.; Ghosh, R.P. Chromatin Higher-order Structure and
Dynamics. Gold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, a000296. [Google
Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
• Bekhor, I., Kung, G.M. & Bonner, J. (1969). Sequence-specific interaction of DNA and
chromosomal protein. J. Mol. Biol. 39, 351– 364
• Bhorjee, J.S. & Pederson, T. (1972). Nonhistone chromosomal proteins in synchronized
HeLa cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 69, 3345– 3349
• Curtis Seubert. “The Difference Between Histone & Nonhistone.” Sciencing. Leaf
Group, 24 Apr. 2017. Web. 15 May 2017.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/non-hisatoneproseminar-230614144159-b30a641c/85/Non-Hisatone-Pro-seminar-pptx-11-320.jpg)