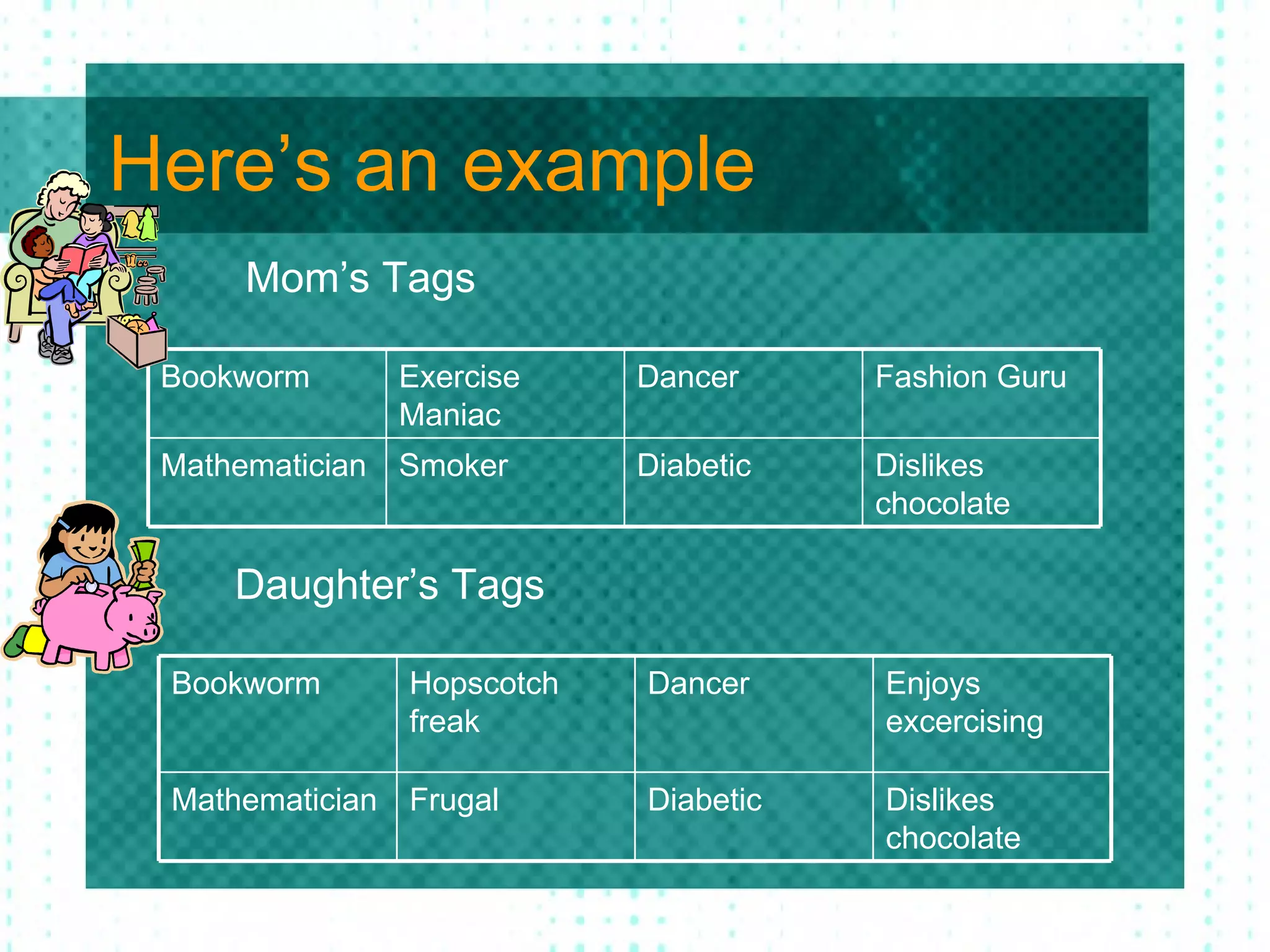
Epigenetics refers to factors above genetics that determine which genes are expressed. The epigenome controls which genes are expressed more than others through mechanisms like methyl groups binding to DNA and histone proteins winding DNA more or less tightly. Epigenetic changes can occur throughout life in response to environmental factors like diet, stress, and lifestyle, and some changes can be passed down from parents to children. While scientists originally thought epigenetic tags were removed before reproduction, it is now understood that some tags can be inherited intergenerationally.