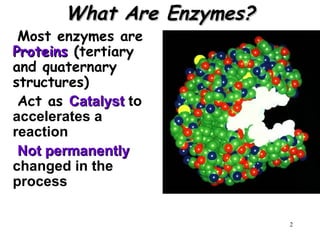
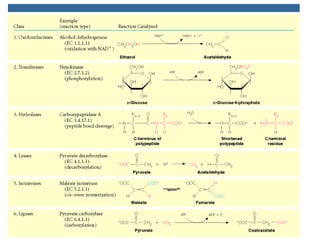
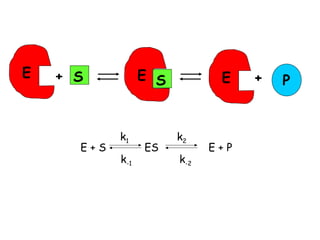
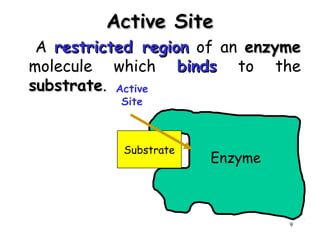
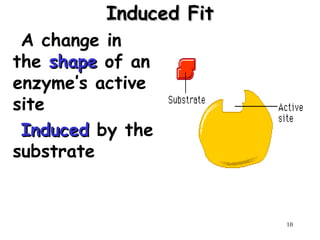
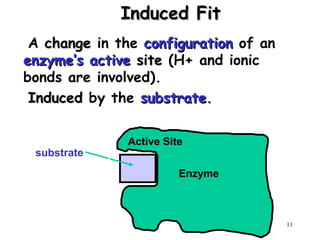
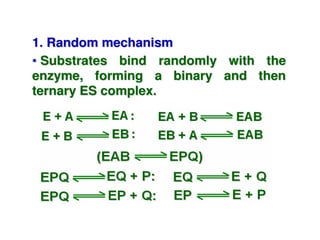
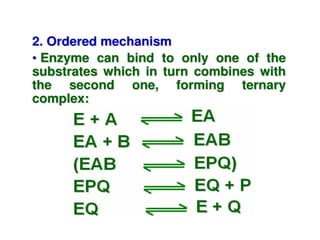
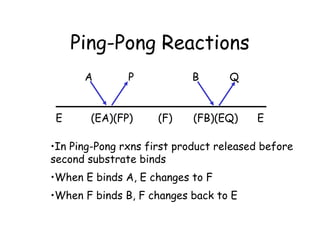
Enzymes are mostly proteins that act as catalysts to accelerate biochemical reactions without being permanently altered. They are classified based on the type of reaction they catalyze. Co-enzymes are non-protein molecules that help enzymes function by associating with their active sites. The Michaelis-Menten equation describes the relationship between substrate concentration and reaction rate. Kinetic parameters like Km, Vmax, and kcat can be determined experimentally to characterize enzyme kinetics. Enzymes are widely used in industries like food and beverage manufacturing for processes like fermentation, clarification, and mashing.



![Plot Vo vs. [S]
Vo 1 mM
Vo 5 mM
Vo 10 mM](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzyme-180423154030/85/Enzymes-class-lecture-7-320.jpg)
![Initial Velocities
[S] = 1 mM
[S] = 5 mM
[S] = 10 mM∆[P]/∆T = Vo10 mM
D[P]/DT = Vo5 mM
D[P]/DT = Vo1 mM
[P]
time](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzyme-180423154030/85/Enzymes-class-lecture-8-320.jpg)
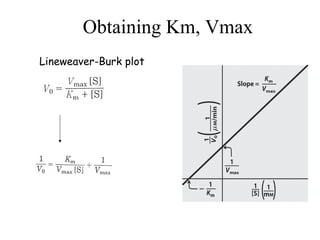
![• Michaelis-Menton Equation
• Describes rectangular hyperbolic plot
• Vo = Vmax [S]
Km + [S]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzyme-180423154030/85/Enzymes-class-lecture-12-320.jpg)


![Km = [S] @ ½ Vmax
(units moles/L=M)
(1/2 of enzyme bound to S)
Vmax = velocity where all of the
enzyme is bound to substrate
(enzyme is saturated with S)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzyme-180423154030/85/Enzymes-class-lecture-15-320.jpg)
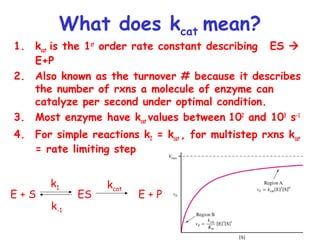
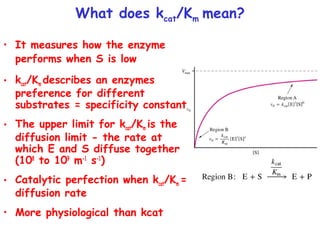
![How do you get values for Vmax, Km and kcat?
• Can determine Km and Vmax experimentally
• Km can be determined without an absolutely
pure enzyme
• Kcat values can be determined if Vmax is known and
the absolute concentration of enzyme is known
(Vmax = kcat[Etotal]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzyme-180423154030/85/Enzymes-class-lecture-19-320.jpg)


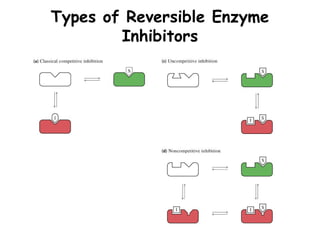
![1. Irreversible Inhibitors:
Covalently bind and inactive enzyme
Suicide Inhibitor
2. Reversible Inhibitors:
E + S <-> ES -> E + P
E + I <-> EI
Ki = [E][I]/[EI]
• Competitive
• Uncompetitive
• Non-competitive](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzyme-180423154030/85/Enzymes-class-lecture-26-320.jpg)

![Data from a single experiment
performed with at a single [S].
(single point on Vo vs. [S] plot)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzyme-180423154030/85/Enzymes-class-lecture-29-320.jpg)