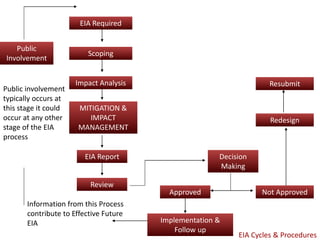
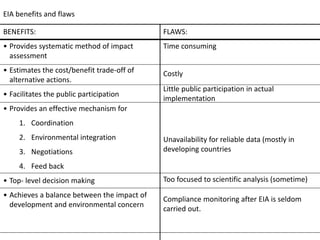
The document provides an overview of environmental impact assessment (EIA). It defines EIA as assessing the effects of proposed projects on the environment. EIA identifies alternatives and aims to balance economic and environmental costs and benefits. It integrates environmental concerns early in project planning. EIA started as a mandatory regulatory process in the US in 1969 and is now required in over 100 countries. The key stages of EIA are screening, scoping, baseline data collection, impact analysis, mitigation planning, public hearings, decision making, and monitoring. EIA aims to be fair, provide credible information for decisions, and ensure sustainability.