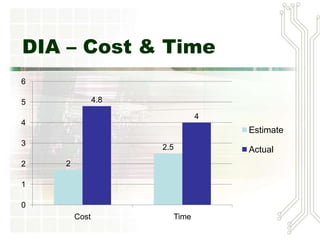
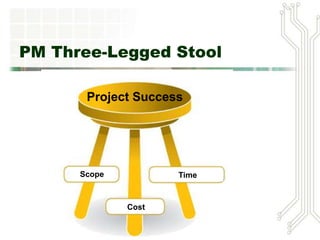
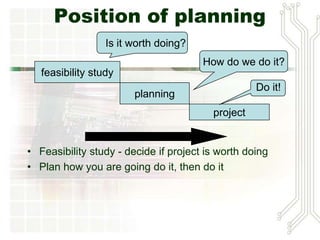
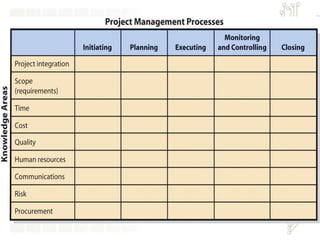
A project is a temporary endeavor undertaken to create a unique product, service or result. Projects can vary in size and duration. The Denver International Airport project faced challenges including changing requirements, cost overruns, delays and technical issues that led to it being over budget and behind schedule. Successful project management requires balancing scope, time and cost, and relies on skills such as leadership, communication and problem solving. The Project Management Institute provides standards and certifications to disseminate best practices. Project managers must coordinate teams and resources to deliver projects successfully.