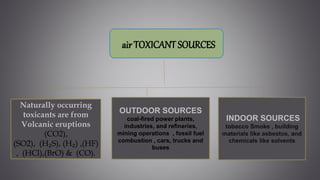
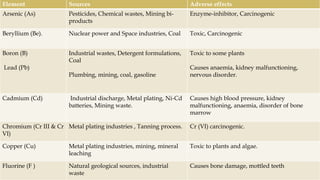
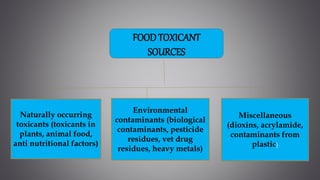
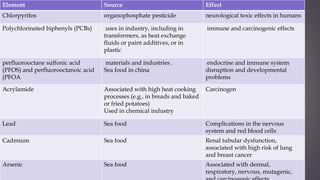
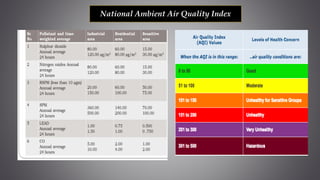
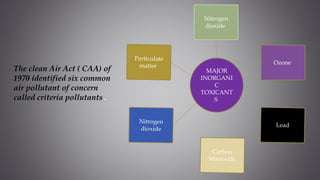
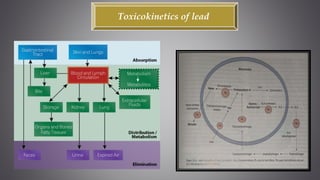
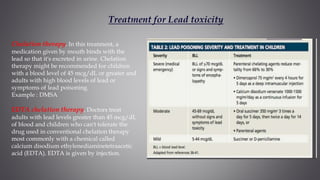
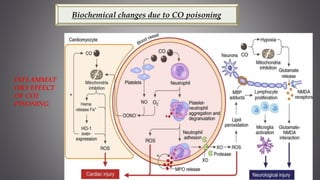
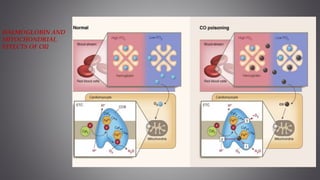
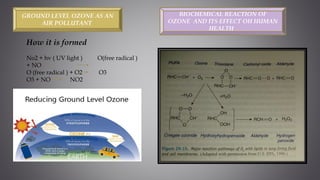
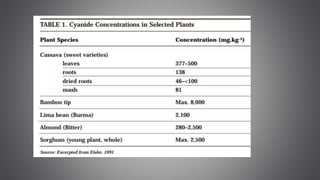
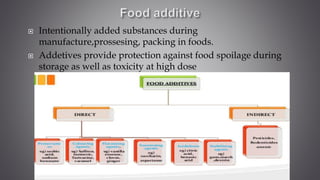
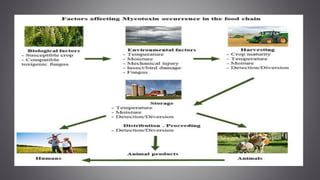
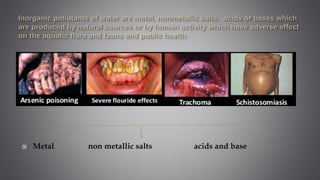
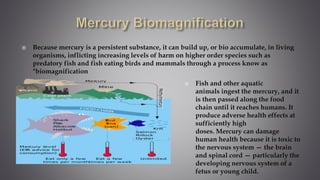
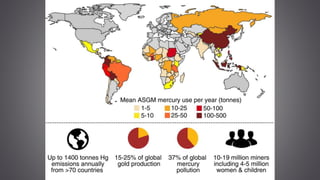
This document discusses several inorganic toxicants and their sources and effects. It describes how heavy metals like arsenic, chromium, and lead from industrial and agricultural activities can pollute the environment and harm human health. Specific toxic metals mentioned include arsenic, which causes cancer from long-term exposure, and lead, which can damage the nervous system and cause developmental issues in children. The document also examines air pollutants like sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and carbon monoxide emitted from fossil fuel combustion in vehicles, power plants, and industry.