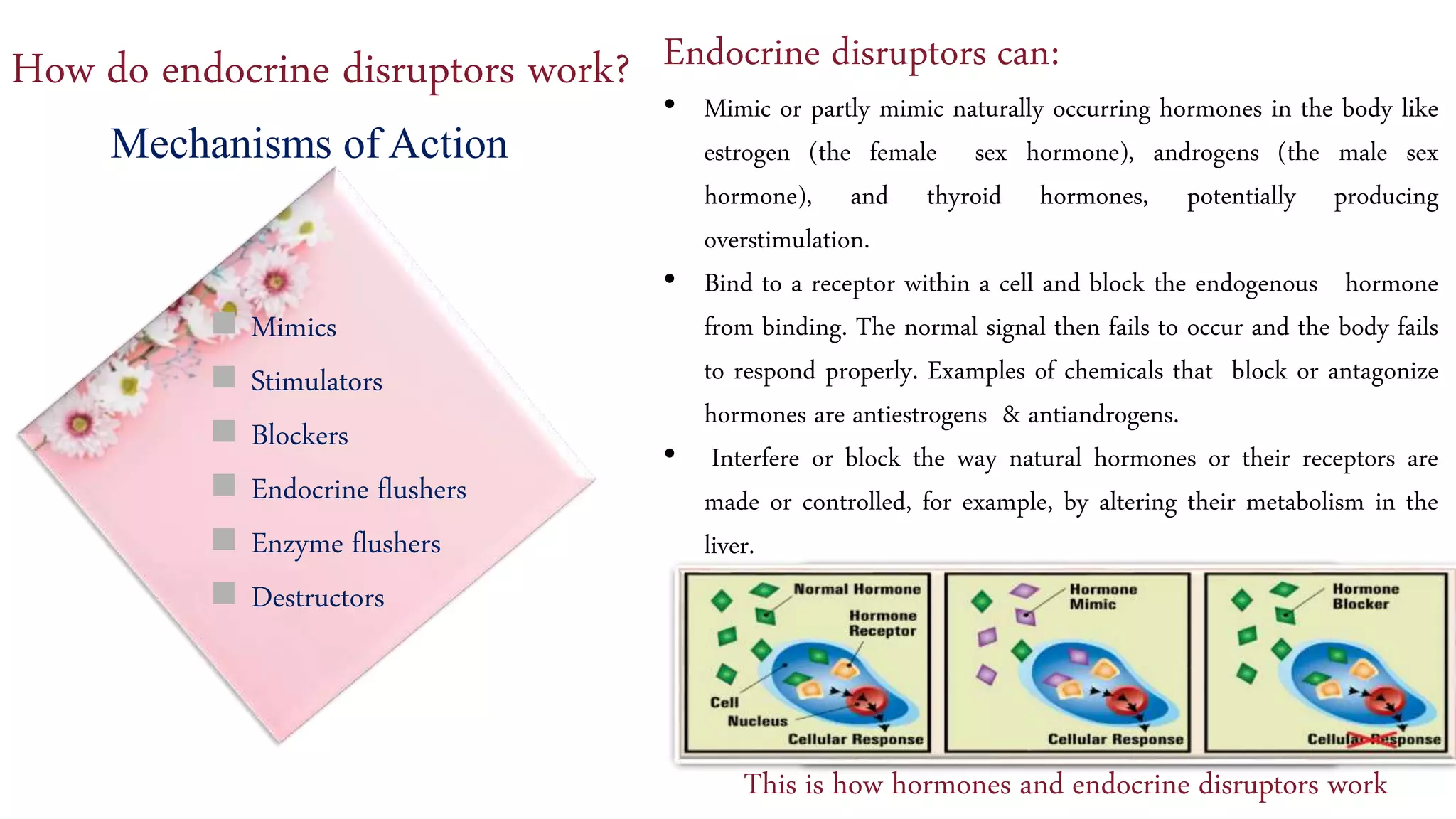
Endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) impact hormonal systems in humans and wildlife, leading to negative health effects such as reproductive issues, immune disorders, and increased disease risks. Common sources of EDCs include pesticides, plastics, and personal care products, with DDT being a notable example that has persistently harmful effects. Strategies to reduce exposure involve dietary choices and decreasing the use of certain materials and products.