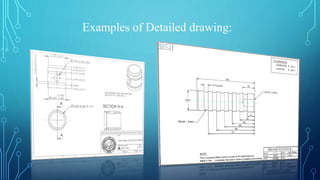
This document provides an introduction to basic engineering drawing. It defines engineering drawing as a graphical representation that conveys ideas and information needed for construction using geometric shapes, lines and dimensions. Engineering drawings are the language of engineers and represent objects precisely to fully communicate shape, size and details needed for manufacture and inspection. The document outlines the types of drawings including freehand sketches, detailed drawings, part drawings, assembly drawings, collective drawings, and combined drawings. It provides examples and describes the key information included in each type of drawing.