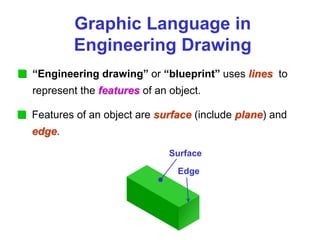
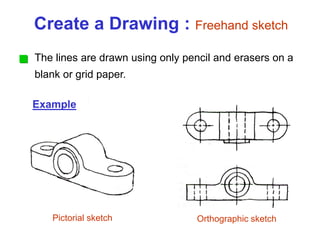
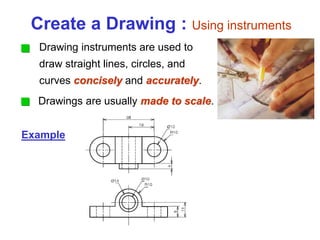
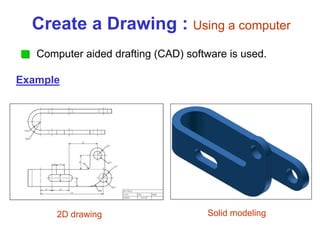
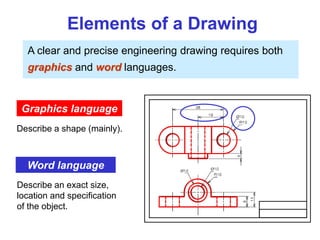
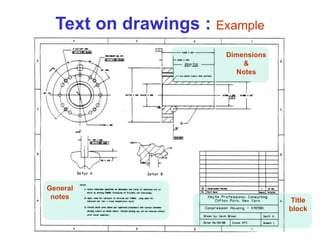
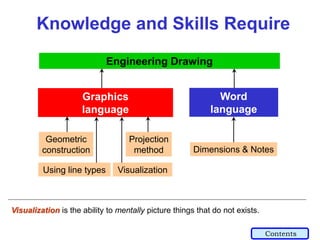
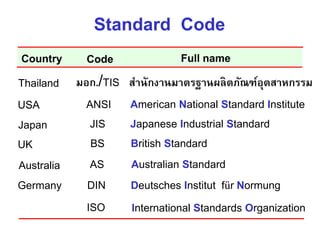
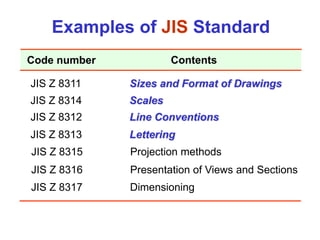
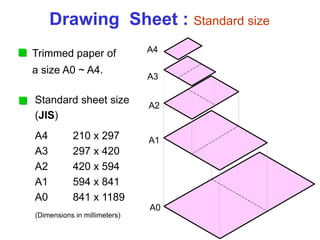
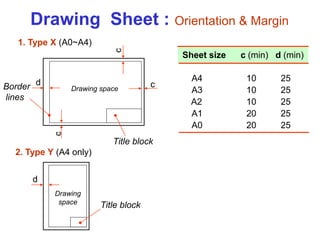
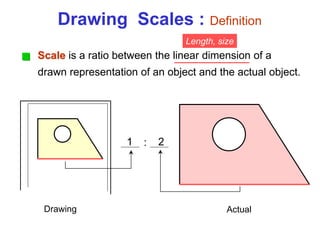
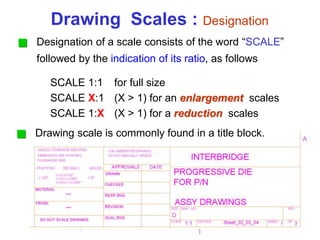
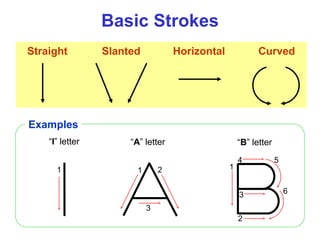
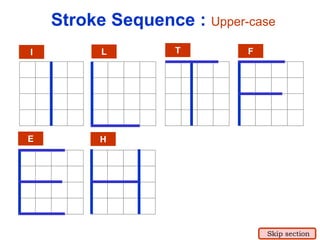
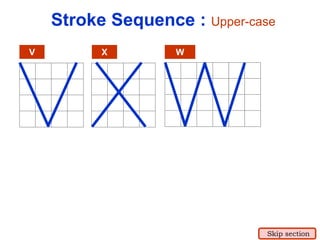
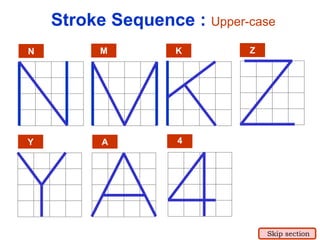
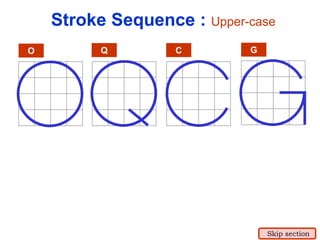
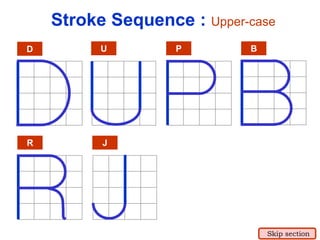
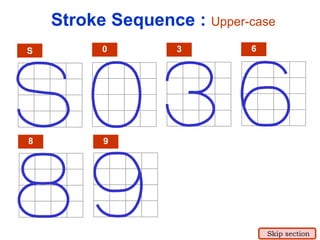
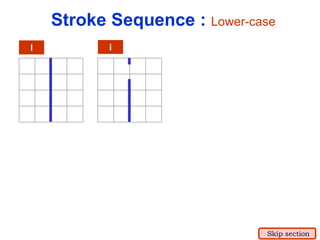
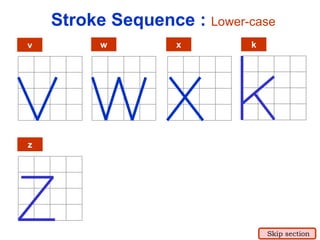
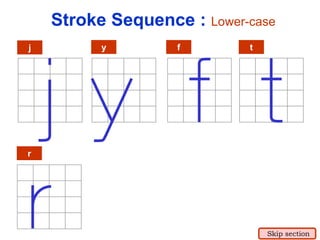
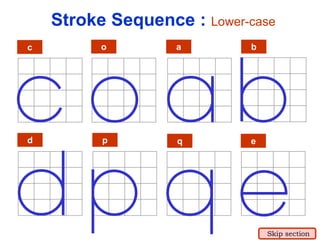
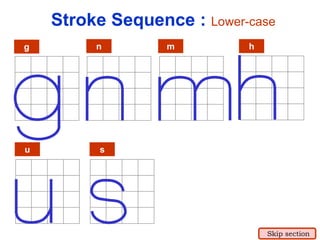
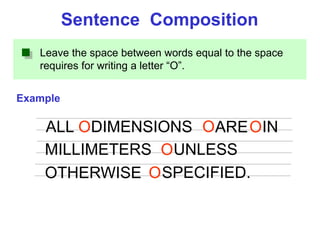
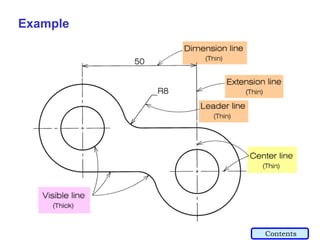
This document provides an overview of engineering drawing standards and concepts. It discusses drawing sheets, scales, lettering, and line types. Drawing standards are sets of rules that govern technical drawings to ensure consistency. Common international standards include ISO, ANSI, JIS, BS, and AS. Key elements covered include appropriate sheet sizes, title blocks, scale designation, text styles, stroke sequences, word spacing, and basic line types. Engineering drawings use defined graphics and text to precisely depict an object's shape, size, and specifications.