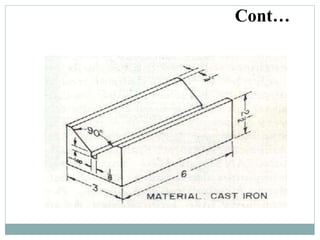
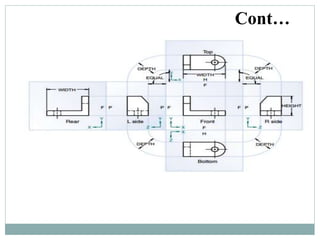
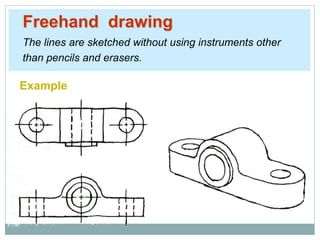
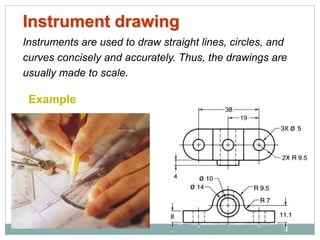
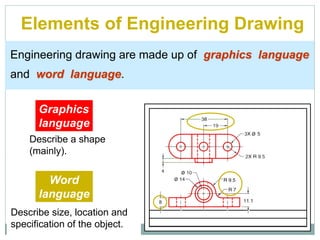
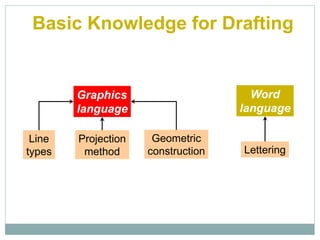
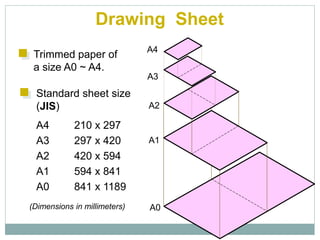
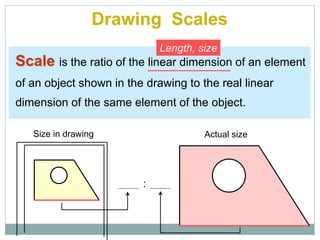
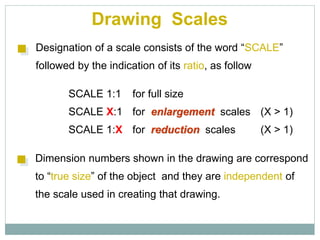
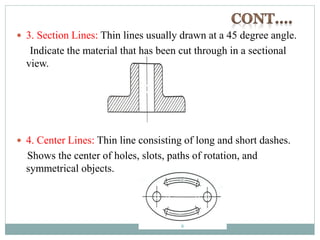
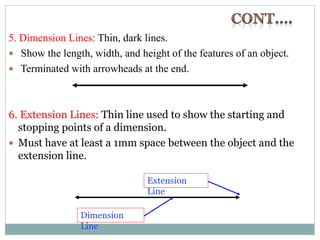
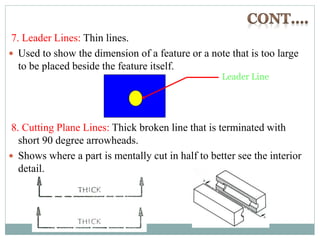
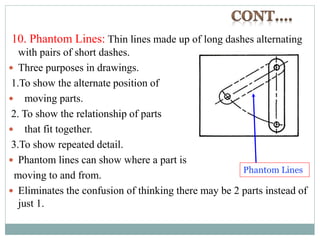
The document provides an overview of engineering drawings and graphic communication. It defines graphic communication and discusses different types of drawings including freehand sketches, instrument drawings, and computer-aided drawings. It explains the key differences between artistic and technical drawings. Technical drawings are used to clearly convey design information to allow objects to be manufactured. The document also outlines various drawing elements, standards, scales, lines types, and common drawing tools used to create precise technical drawings.