1. The document discusses the endocrine system and changes that occur during adolescence.
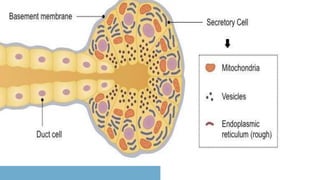
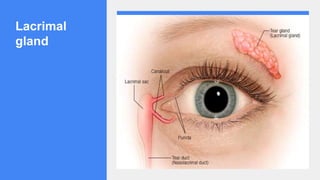
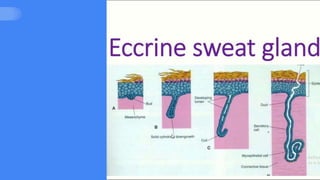
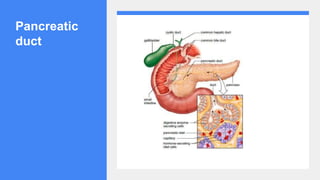
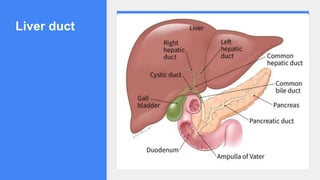
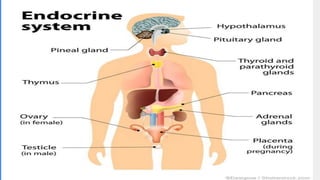
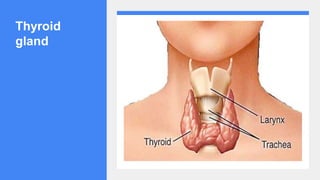
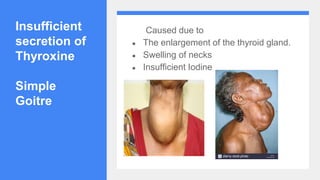
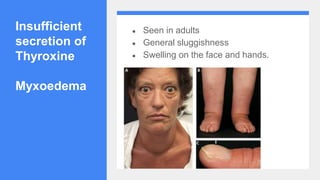
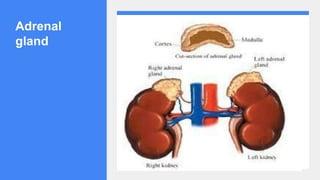
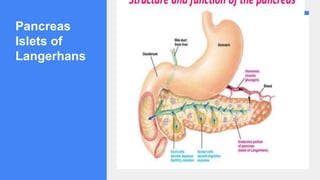
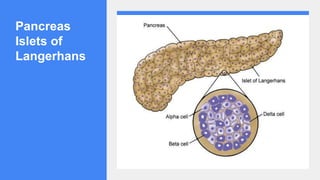
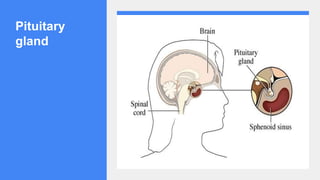
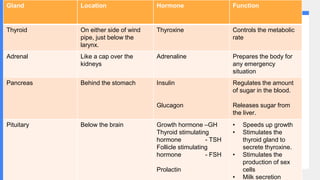
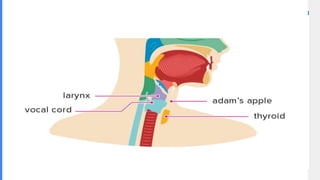
2. It describes the functions of various endocrine glands like the thyroid, adrenal, pancreas, pituitary glands and the hormones they secrete.
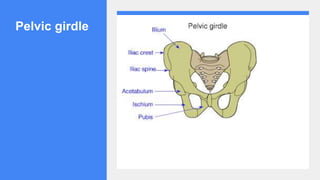
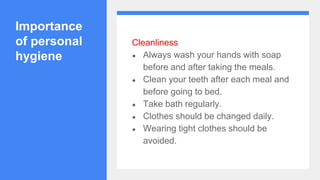
3. The stages of puberty and physical changes during adolescence like increased height and weight, development of secondary sexual characteristics, and reproductive maturity are explained.