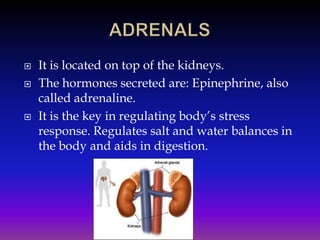
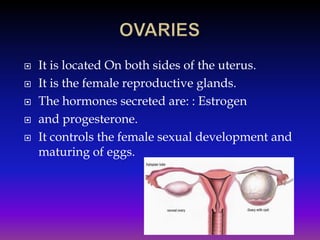
The document discusses the endocrine system and its glands. It describes the main endocrine glands, including the pituitary gland, pancreas, ovaries, testes, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, and pineal gland. It explains the hormones each gland secretes and their functions in regulating growth, metabolism, sexual development, and other bodily processes. Additionally, it discusses puberty and the physical and emotional changes caused by the endocrine system during adolescence for both males and females.